PHARMACOKINETICS: Taking a closer look...
Arguably, the most important medical invention of the last couple of centuries are ‘drugs’. Many would argue this, most others would agree to this without doubt. This is actually due to the fact that drugs are the most used chemicals in the health sector and others may argue that many other substances are drugs in essence; this claim has widened the scope of drugs and hence the term ‘pills’ have been used while referring specifically to the pellets we take and ‘syrups’ to mean the liquefied medicines we take orally.
Image credit Pixabay. CC0 creative commons license. Author ColiN00B
These terms ‘pills’ and ‘syrups’ however limits the scope of drugs amidst the fact that they are also diverse in normal sense; but common to these three terms is the fact that they enhance the actions of the human system; this may be stimulatory or inhibitory in effect.
Before the idea of drugs, disease and sickness were perceived as totally different from our contemporary perception, many arbitrary theories were proposed and applied in an attempt to explain the causes and treatment of diseases. While some school of thought defined diseases as an imbalance between the body fluids, the religious institutions holds the belief that diseases comes as a punishment from the spirits for sins committed.
Owing to this erroneous perceptions, many theories were also experimented in another attempt to proffer solutions to these abnormalities. I could remember my grandmother applying oil to the knife which I accidentally cut my hand with while playing as a kid, according to her, it would hasten the healing; this worked however, as the wounds heals faster whenever she does this than when she fails to do so. But in essence, these beliefs are untrue and the wounds healed faster only because the body was more functional at this time and due to her habit of paying close attention to my nutrition when injured.
Medical psychology also explains better how these beliefs tends to aid recovery because sometimes one just needs to believe that he/she is healed to be healed; even in present day medicine, placeboes are used in disease therapy, here a patient is treated with either an unrelated substance or procedures just to make him belief that the doctor actually did his job, this belief gives him the assurance that he will be healed; hence this calmness he feels will hasten the body’s healing process. Placeboes are not drugs, in fact, they are ‘non-drug’ therapies and procedures.
The scientific study of human physiology demystified the concept of injuries, diseases, systemic dysfunction and other discomforting human condition and this better understanding paved way for the invention of drugs and right procedures for disease therapy and more accurate treatment for these conditions. The study of plants by the early physicians led to the discovery of the earliest form of drugs and phytochemicals and juices from plant leaves, seeds, fruits and stem were used to treat various infections.
CONCEPT OF DRUGS
Drugs are substances which interact with the body system by binding to the body’s regulatory molecules and through biochemical processes, they either enhance the action of the body system or inhibits the effect of other molecules. In correct and medical use, these substances are used to treat, prevent and diagnose diseases, unfortunately, this is actually just one of the various use of drugs as drugs have also been used indiscriminately as hallucinating agents and also to stimulate the body system towards the performance of many abnormal and deleterious activities.
Hence drugs exceeds the scope of pills and syrups, these are actually medical xenobiotics as they are foreign substances taken either orally or by medical injection either intramuscularly or intravenously to effect changes in the body. You’d wonder how you get healed sometimes even without taking drugs? Yes, this is because the body also takes care of itself by synthesizing substances which regulates the activities of other systems or the system that produces it so as to restore a normal internal environment amidst the turbulence created by the injury and disease.
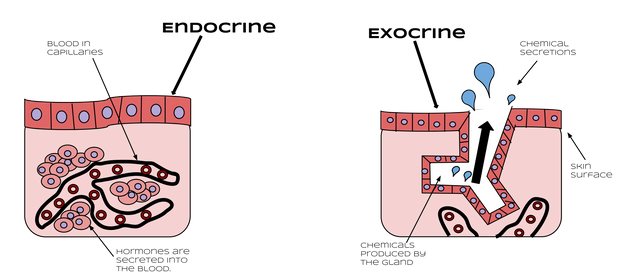
Image source Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.Author Mntrue
These are endocrine and exocrine substances respectively, endocrine substances are hormones such as glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones produced by the adrenal glands and thyroid glands respectively, glucocorticoids helps to inhibit inflammation reactions while thyroid hormones increases the body’s rate of metabolism.
*These are just few examples of how the body system heals itself via hormones, kindly refer to the references to read more about hormones.
Exocrine glands such as most part of the pancreas also produces substances which functions in a similar manner as hormones to restore the internal environment, only difference being that the area of action of Exocrine secretions is within a very short range. Hence hormones are also drugs and homeostasis can be regarded as therapeutic as the action of these hormones and exocrine secretions are actually geared towards the maintenance of a constant internal environment amidst ever varying external environment.
))
Image source Wikimedia. Creative commons license. AuthorNational Institute on Drug Abuse
According to Paracelsus, ‘drugs are poisons’, the reverse is also true, poisons are also drugs, dosage is in practice what differentiates a drug from a poison, that is poisons are drugs taken in the wrong dosage usually exceeding the normal prescription to a reasonable extent. Drugs are also poisons taken in the right dose, this will be a bit misunderstood, but in reality, some poisons are therapeutic when processed and taken in the right dose; for instance the poisonous venous from reptiles and insects when purified and administered correctly serves as a cure to various infections.
Pharmacology is the branch of science which studies these drugs and their interaction with the human system, pharmacologists also takes into consideration how these drugs were produced, the processes which a chemical goes through before it is approved by the National Association for Food and Drugs Agency and Control (NAFDAC) in Nigeria or the Food and Drug Association (FDA) in the United States of America.
Drugs in production passes through four stages of assessment before it is fully registered as a drug, these are time tasking and painstaking in the quest to ensure that these substances do not have adverse effect on the consumers when taken according to the doctor’s prescription.
*In the phase I of drug production, the drug is experimented in laboratory animals such as rats to determine the effect of these drugs on the animals and it’s ability to cause harm to a given population of the animals. The LD50 of the drug is determined, this is a measure of the toxicity of the drug and it’s the dose of the drug that would kill half of the total population of the laboratory animals, a Guinea pig is also used for this test.
*In the second phase of drug test, the drug is supplied to a local health institution, usually a hospital, where these drugs are administered to a patient with their consent or with the consent of their parents or guardian if the patient is not up-to the age of eighteen (18). Here the administrator may or may not know the name of the drug, this is to exclude psychological factors in the experiment.
*If the drug passes the second phase, it is supplied to a much higher hospital to be tested out in a larger number of patients also with the consent of the patient or the patient’s parents in case of underage patients, the drug must be able to pass the above tests before it proceeds to the fourth and probably the last phase, failure to pass these stages of the test convincingly, the drug is disapproved.
*In the fourth phase, the drug is introduced into the market in a regulated quantity and is watched closely by the NAFDAC or FDA depending on the country, if this drug is noticed to cause harm to the consumers, it is withdrawn from the market and the production is either stopped totally or it is reprocessed; if it doesn’t, the production and sale continues. Drugs which passes this stage is still kept in close surveillance and can be withdrawn even after years of sale, maybe due to a reduction in quality or cases of abuse by the consumers; for instance codeine and tramadol which are normally used in cough syrups and stress relief drugs respectively are currently abused highly and are subject of withdrawal from the market.
Pharmacologists are not pharmacists, in fact, there is a reasonable difference between these two, while pharmacists produce drugs, pharmacologists studies the interaction of these drugs and the body systems.
Pharmacologists studies pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics in an attempt to unravel completely unravel the way these drugs produced by pharmacists are utilized by the body, while pharmacists also have a very good knowledge of pharmacology, they only apply it in drug production and not necessarily drug administration.
Pharmacokinetics is the study of how the body handle drugs, this includes the processes through which the body perceives these substances as drugs and moves to break them down into useful smaller molecules and also how the body gets rid of them after their action is completed to prevent the accumulation of toxins from these drugs, it also includes how the body handle toxins, poison and drugs in wrong administration, Toxicology, a branch of pharmacology studies this aspect better, toxicology is the pharmacology of toxins.
RECEPTORS IN PHARMACOKINETICS
Receptors in pharmacology is similar to our everyday scientific definition of what a receptor is; they are macromolecules which can be a polysaccharide, a protein or a glycoprotein to which drugs binds in order to initiate it’s action. The role of receptors in pharmacokinetics is a very essential one as receptors have the ability of amplifying, integrating or reducing the effect of the drug which binds to it.
In amplification, the receptors increases the effect of the drugs, this is in contrast to reduction where the receptor decreases the effect of the drug, receptors also integrates the action of drugs by incorporating the drug to another biochemical pathway, hence the effect felt by the consumer is sometimes not the actual effect he’d feel if the receptors are just neutral cross-links between the drug and the target system or organ. The effect of drugs is also dependent on the sort of receptor it binds to. The physical features of the drug such as its size, shape and the type of bond it makes with its receptor are very important in pharmacokinetics.
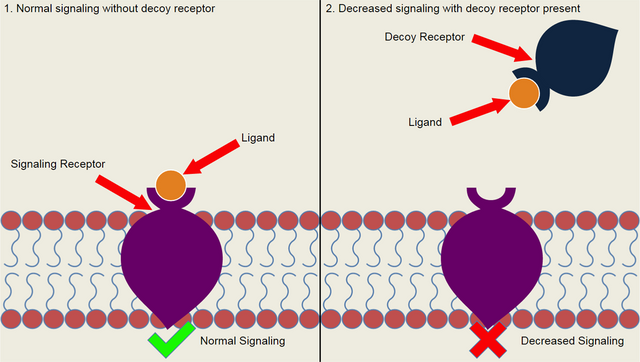
Decoy receptors/ bind to ligands and inhibit signaling through actual receptors. Image source Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Generic license. Authour Offnfopt
Most drugs have molecular weights between 100 and 1000, thus for a ligand to be recognised as a drug by the receptors, it’s molecular weight must exceed the lower limit of this range, drugs which binds weakly to its receptor in hydrophobic bonds are more selective than drugs which binds in stronger bonds such as covalent and electrostatic bonds.
According to the Michealis Mentens, receptors binds drug in the same fashion as an enzyme and it’s substrates, the drug binds to its receptor in a lock and key fit to form a Drug-Receptor complex, this sort Of complex is very common in human physiology and relays to the body system the effect conveyed by the drug.
The information relayed by the drug-receptor complex may not be the actual information conveyed by the drug as there are cases of amplification and reduction, for a drug to bind to a receptor, it must have a complementary shape with the receptor, this is where the shape of the drug molecules comes into play. The sort of receptor to which the drug binds determines it’s effect.
Each drug binds to a specific sort of receptor, binding of one drug to more than one receptor may dampen it’s effects,some drugs also function by blocking receptors , the blocking of this receptor prevents the binding of any other ligand and transmission of signals through them, hence the receptor do not relay any information and as a result the effect which accompanies the integration of signals from this kind of receptor is not felt by the body, anaesthetic drugs function this way, they block the pain receptors and hence the patient feels no pain.
Drugs which blocks more than one receptor at the same time such as propanol which block both B1 and B2 Adrenergic receptors is no a good drug and administration and consumption of this type of drug is not advised, drugs such as Metapro-ol which selectively block two receptors at a time is also not advised in normal practices. Receptors in pharmacokinetics may be cholinergic, Adrenergic, serotonin or brain receptors, these receptors binds the drugs.
Cholinergic receptors binds acetylcholine and drugs which contains acetylcholine and acetylcholine related ligand. Adrenergic receptors binds adrenaline and adrenaline containing drugs. Serotonin receptors binds hydroxytryptamine and drugs which contains hydroxytryptamine related ligand. Brain receptors binds to Benzodiazepans and barbiturates.
However, many receptors have been discovered but there is a little idea of the ligand which binds to these receptors, these receptors are known as Orphan receptors. The development of a true new drug (drugs which are not related to any kind of already existing drug) might be possible when the ligand which binds to these orphan receptor is discovered.
OTHER RECEPTORS IN PHARMACOKINETICS
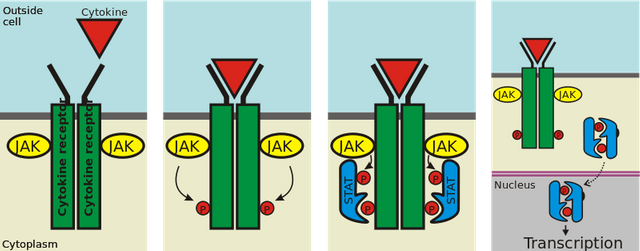
Cytokine receptors
The Jakstat pathway. Image source Wikimedia. Creative commons license. Author Peter Znamenkiy
Cytokine receptors binds to peptide ligand such as hormones and interferon; the cytokine receptors dimerize following the binding of these ligand, this activates the Janus kinases(JAKs) which phosphorylates the tyrosine residues on the cytoplasmic membrane of the receptors, signaling of the impulse conveyed by these peptides is commenced on activation of another set of proteins known as Signal Transducers and Activators of Transduction (STATs)
Gated channels
These are not actually receptors, but these ‘gates’ open or close in response to the presence of certain ligand and ions. Many drugs mimics the actions of these ligand which causes the gates to open.
These gates do not bind to drugs but they are controlled by either membrane potential created by these ions or by phosphorylation by these ligand or the inflow of these ligands, as seen in the nervous system, these mechanisms enables learning and memory.
*This article is not exhaustive on the role of drug receptors in pharmacokinetics, kindly refer to the references for more information on drugs and receptors.
FACTORS AFFECTING DRUG UTILIZATION BY THE BODY SYSTEM
Drug administration and utilization is a very important part of patient’s treatment and recovery, thus care should be taken when giving drugs to patients so as to ensure that these drugs do no have adverse effect on the patient, many factors are taken into consideration before administering drug to a patient. This includes:
- Type of drug: The type and amount of chemicals used in the production of drugs differs from one drug to another, hence the toxicity and subsequently the quantity of such drug to be taken by a patient differs. The receptor which a drug binds to also determines the dosage. Hence these two factors–the sort of chemicals used in production of the drug and the receptor it binds to should be considered by medical professionals or anyone administering the drugs.
- Route of administration: Drugs may be administered orally, intravenously or intramuscularly, the route through which this drug is given to the patient also contributes to the potency of the drug and determines the dosage and type of drug taken by the patient. Orally taken drugs pass through the digestive tract hence the effect is reduced by the processes which it goes through in the digestive tract, hence the dose of orally taken drugs tends to be higher than that injected into the veins or muscles. Intravenously administered drugs also have a higher effect than orally taken drugs as the body received a large and more concentrated quantity.
- Patient’s physical features: physical features of the patient such as size and age plays a vital role in dosage determination, the weight in kilogram (Kg) of the patient should be known as specified range of dose should be prescribed for a given body weight. The age of the patient should also be determined as the body’s ability to handle drugs also increases with age.
- Intensity of sickness: The intensity of the injury or sickness also depicts the amount and rate of damage the injurious agent has caused or is causing to the patient, it also gives an insight on the immunogenicity/harmfulness of this agent, hence, a more intense dosage is prescribed for the patient so as to get rid of the them before irreparable damage is done to the patient.
Conclusion
Drugs are not mild chemicals, strict adherence to professional advice on the consumption of these drugs is advised as pathogens may stay latent after a mild administration of drugs such as seen in incomplete dosage, hence it is better to desist from taking a drug than not completing the prescribed dose. Drug abuse also has a longer lasting effect than the brief hallucinations and intoxication felt when these drugs are consumes in an unregulated dose, as such individuals should avoid drug abuse.
Adherence to prescription by a professional ensures that these drugs works as normal and the patient recovers completely, prescription of drugs should be done by qualified professionals, self-medication and purchase of drugs from unregistered stores is strongly advised against.
Stay healthy.
REFERENCES
- Pharmacokinetics -Wikipedia
- Drug -wikipedia
- Transmission control protocol -wikipedia
- Pharmacology -wikipedia
- msdmanuals
- Structural and Functional Basis of Cytokine Receptor Activation
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.

))
drugs must bind to a receptor to elicit pharmacological action (agonist) and also to prevent another drug from eliciting pharmacological action (antagonist). The idea of always binding is not the case for every drug however as some drugs like hydrogen peroxide attack cells directly without even binding to receptors.
I know you meant Janus Kinases but this is funny lol
Looking at your topic, i expected you to talk about LADME, single and multi-compartmental models as well as bioavailability to say the least. I am surprised you take a bizarre approach in talking about pharmacokinetics (which hugely elucidates the movements and fates of drugs in an organism). I think your topic should be edited to

Pharmacology: Drugs and Receptors‘instead of binding to them’ here was used to reiterate that binding of drugs that block receptors is different in action from the other drugs which binds to elicit a response instead of inhibit it.
Yeah I actually meant JAKs thanks a lot.
Before proceeding to LADME which I'm certain you're talking about Adsorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion of drugs, the readers first has to understand how this drugs gets into the body systems, I guess you should ask if this post has another part coming up, cos pharmacokinetics is too vast to be contained in just one article, a reader might not be able to settle down and get the whole information, hence the breakdown. Hence I retain that the title fits the article
Thanks for stopping by, I really appreciate that you painstakingly read through.
it is good to signify that it will come up in the following series but this post actually says nothing significant about pharmacokinetics :) and instead of binding implies that there is no binding.
I don't think so, pharmacokinetics is centred on drugs' interaction with the body, which most part of this articles have been centred on too, the title says ‘taking a closer look’ which implies a more in depth look at how the drugs react with the body.
I'll change the ‘instead of binding’ if that keeps you uncomfortable, but that will affect the information I wish to pass.
lol let me make this easier for you. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug as opposed to pharmacodynamics which is the study of how a drug affects an organism.
You actually just talked on pharmacodynamics and not pharmacokinetics
“Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical
after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as
well as the metabolic changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic
enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and
the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. [1]
Pharmacokinetic properties of chemicals are affected by the route of
administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the
absorption rate.”
Wikipedia
“FACTORS AFFECTING DRUG UTILIZATION BY THE BODY SYSTEM
Drug administration and utilization is a very important part of patient’s treatment and recovery, thus care should be taken when giving drugs to patients so as to ensure that these drugs do no have adverse effect on the patient, many factors are taken into consideration before administering drug to a patient. This includes:
Type of drug: The type and amount of chemicals used in the production of drugs differs from one drug to another, hence the toxicity and subsequently the quantity of such drug to be taken by a patient differs. The receptor which a drug binds to also determines the dosage. Hence these two factors–the sort of chemicals used in production of the drug and the receptor it binds to should be considered by medical professionals or anyone administering the drugs.
Route of administration: Drugs may be administered orally, intravenously or intramuscularly, the route through which this drug is given to the patient also contributes to the potency of the drug and determines the dosage and type of drug taken by the patient. Orally taken drugs pass through the digestive tract hence the effect is reduced by the processes which it goes through in the digestive tract, hence the dose of orally taken drugs tends to be higher than that injected into the veins or muscles. Intravenously administered drugs also have a higher effect than orally taken drugs as the body received a large and more concentrated quantity.
Patient’s physical features: physical features of the patient such as size and age plays a vital role in dosage determination, the weight in kilogram (Kg) of the patient should be known as specified range of dose should be prescribed for a given body weight. The age of the patient should also be determined as the body’s ability to handle drugs also increases with age.
Intensity of sickness: The intensity of the injury or sickness also depicts the amount and rate of damage the injurious agent has caused or is causing to the patient, it also gives an insight on the immunogenicity/harmfulness of this agent, hence, a more intense dosage is prescribed for the patient so as to get rid of the them before irreparable damage is done to the patient.”
my post
I feel you should ‘take a closer look’ lol
so with that you have really talked about pharmacokinetics ? i see a definition of pharmacokinetics and a general subheading which does not say much about pharmacokinetics. i suggest you take cues from here, here, here, here and for the umpteenth time, here.
That's just a bit of what I wrote, if you can read again, this time with a better understanding, you'll find more information about how the body affects the drug action and how dosage and route of administration distinguishes a drug from a poison, this was clearly stated, if only you could calmly read the post
Your Post Has Been Upvoted by @a-0-0! 👍
Hello @joelagbo,
Thisbis certainly an exciting revelations on drugs and their workings..
I very much agree with the above because I am a living testimony to the efficiency of positive beliefs in accelerated healing outcome. Nearly died in 2001 suffering from what could not be diagnosed medically. At a point, I rejected every drugs and declared mystery healed and surprisingly, it stayed.
Drugs use the same mechanism of action used by enzymes to exert their influence to the site of target/substrate.
This post is rich and detailed.
Regards,
@eurogee of @euronation and @steemstem communities
Drugs are mysterious, just as the body molecules it works with/on, unravelling these mysteries means a complete end to life-taking illnesses, unfortunately that's a bit far from science, medicine without psychology will definitely be a more tedious practice.
Thanks for reading through, I appreciate.