CELL SUSTENANCE #5: Membrane receptor immunoglobulins in hypersensitivity and immunological disorders
Hi everyone and welcome to yet another part of this series, in previous parts of this series we've introduced several fractions of plasma proteins. Subsequent parts are centered on unravelling how these proteins actually functions to ensure that our body cells continues in normal functioning.
The need for a receptor marks a similarity between the nervous system and many other autonomous systems in the body. For the nervous system, a receptor is a protein molecule that receives chemical signal from outside a cell; this includes the cell’s environment, intracellular receptors also receives signals from inside the cell. These signals travels through nerves to the brain which contains the integratory centres for these impulses.
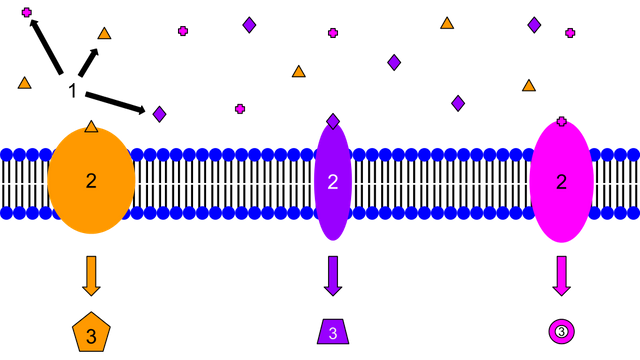
Different types of membrane receptors. Ligands(1), Receptors(2) and Secondary messengers(3). Image source: Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. Contributed by Isaac Webb.
The definition of a receptor for the immune system is not so different from this, even the process of transduction are basically related, the only difference being the molecules and parts involved in this action. Activation of the nervous system causes the mobilization of effector organs and tissues such as muscles, liver, and pancreas; in contrast the activation of the immune system involves the release of cells and molecules of immunity which helps to eliminate the invader, protect the body and initiate the restoration of the affected part of the body.
The B-cells displays many immunoglobulins on their surface which binds to the antigens and activate the B-cells, these immunoglobulins thus controls the activation, the extent and the intensity of the B-cells' reaction to an immunogen. Surface immunoglobulins includes:
These are monomeric immunoglobulins, however, the secreted form of these immunoglobulins may be polymeric. The antigens binds to the antigen binding site of the surface immunoglobulins and through the fragment crystallizable region, the surface immunoglobulins relay information about the immunogenicity of the bound antigen to the B-cells, this leads to the production of more plasma cells which synthesizes the antibodies.
The plasma cells produced are dedicated to the production of antibodies which are identical to the antibody which triggered it’s production, hence increasing the pool of exact antibodies, this makes for specificity as it ensures that only such antigens are attacked.
This is in congruence with the clonal selection theory of immune system reaction and ensures the specificity of the immune reaction, thus, only the antigen that triggered the reaction is attacked and the intensity of the attack is also relative to the immunogenicity of the antigen. The membrane receptor immunoglobulins are highly specific, they are designed to be specific only for a given antigen, this is due to the hypervariable region of the amino terminal.
))
Regions of the imunoglobulin. Image source: Wikimedia Creative commons license. Author AJVincelli
The hypervariable region is a region of extreme variability of the amino acid sequences, that is, the amino acid sequence in this region varies from one antibody to another, hence different antigens binds to different antibodies and activates the immune system in a relatively different manner. The antigen binding site consists of six hypervariable loops or complementarity determining region. The complementarity determining regions are separated by invariant stretches of amino acid sequences known as the Frameshift region.
The frameshift region are 15-30 amino acid sequences long and separates each complementarity region from its adjacent neighbor. Three complementarity determining regions each from the variable region of the heavy chain and light chain makes up the hypervariable loop. The high variation in the amino acid sequence differentiate one antigen binding site from another and thus different antigens binds to each antigen binding site. The complementarity determining region are so called because they are complementary to the epitopes on the antigen.
The membrane receptor immunoglobulins do not recognize the entire antigen, rather it recognizes the specific site on the antigen, these discreet sites on the Immunoglobulin are known as Epitopes. Epitopes are thus an amino acid sequence which are recognised by the Immunoglobulin, a single antigen may posses different epitopes. These are the immunological active sites of the antigen.
Amidst the presence of many epitopes on one antigen, the cells of immunity recognizes one a few epitopes the action of these epitopes are felt more than others, these are known as the immunodominant epitopes. B-cells recognise soluble antigens hence these epitopes are highly accessible sites on the on the exposed surface of the antigen. Antibodies binds to the epitopes by weak covalent bonds, this weak bond is strengthened by the complementarity of the epitopes, hence the size of the epitopes must not be larger than the size of the antigen binding site of the surface immunoglobulins.
B-cells' epitopes are either Sequential or Conformational.
Sequential epitopes are linear amino acid sequence on the antigen which are recognised by the antibody, this sequence cannot be destroyed by heating as it is within the proteins' primary structure, hence, even after heating the antigen, the antibody could still detect these sequences on the antigen and bind to them.
))
The Conformational epitopes. Image source: Wikimedia. Creative commons license. Author KC Panchal
Conformational epitopes on the other hand are amino acids residues which are far apart in the primary structure of the antigens' protein configuration but are closer in its tertiary structure; hence when heated, the antibodies are unable to recognise and bind to these antigen as these proteins are disconfigured by heating and the proteins are denatured B-cell epitopes are located on the flexible regions of the antigen’s amino acid configuration and exhibits binding site mobility.
Defects in these receptors and their sequences of action will predispose the body to autoimmunity, impaired immune reaction and hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity
In allergic reactions, antigens are presented to certain Immunoglobulins which produces some discomforting reactions in response to these antigen, hypersensitivity is generally an overreaction of the immune system, these reactions ranges from mere discomforting reactions to highly damaging and at the extreme, may be fatal.
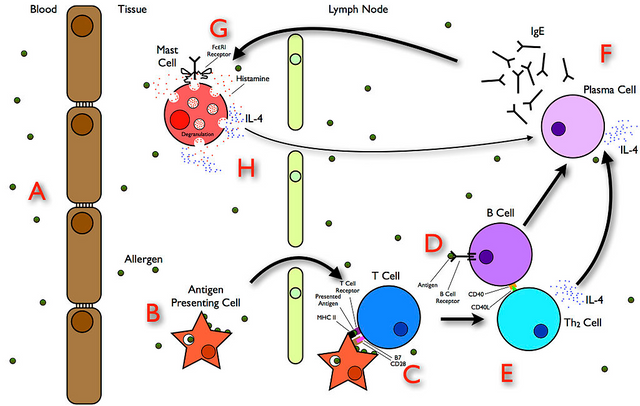
The allergy pathway (how allergy is initiated in the body). Image source: Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. Author SariSabban
Innate cells of immunity such as basophils and mast cells have affinity for the FC receptors of these immunoglobulins such as immunoglobulins E, when an antigen binds to the Immunoglobulin E and the FC receptors of this Immunoglobulin is cross-linked with the basophils or mast cells, these cells releases pharmacologically active substances from their granules, these substances includes heparin, histamine and platelet activating factor, these substances mediates hypersensitivity and inflammation, but in essence, these reactions are actually geared towards the elimination of the injurious agents.
Hypersensitivity is classified into five(5) types:
- Type 1: Allergy or immediate hypersensitivity; this is the most popular type of hypersensitivity, it is due to the binding of the basophils to the FC receptors of the Immunoglobulin E. This triggers the release of molecules which mediates anaphylaxis, this type of hypersensitivity is acute and it lasts just for few minutes. As seen in Asthma.
- Type 2: Antibody dependent cytotoxicity/ autoimmunity; the antibodies perceives the normal body cells as antigenic and binds to them, hence stimulating the immune response against them. As seen in thrombocytopenia.
- Type3: immune complex disease; Immune complex formed by the binding of the antigen to the antibody circulates in the body and gets deposited on the walls of the vessels, joints and kidney, this initiates an inflammatory reaction as seen in Arthus reaction and Systemic Lupus Erythomatous.
- Type 4: Delayed hypersensitivity; reactivation of the immune system by the memory T-cells causes inflammatory reactions, leading to tissue damage as seen in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Type 5: This is related to immediate hypersensitivity, type 5 hypersensitivity is an autoimmune disease due to a defect in the membrane receptor immunoglobulins as seen in Graves' disease.
Immunological disorders
- Autoimmunity :
This occurs when the antibodies losses it’s ability to differentiate self from non-self antigen. In this condition, the body’s immune system fights the normal body cells; this can be seen in Graves' disease and rheumatoid arthritis. The body sees it’s own proteins as antigen/immunoglobulis and thus reacts against them.
- Multiple myeloma :
Multiple myeloma. Image source: Wikimedia. Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. Author Blausen Medical Communications, Inc.In multiple myeloma, there is an abnormal increase in the serum concentration of immunoglobulins, this is due to a neoplastic proliferation of the plasma cells in the bone marrow; hence there is an increase I don’t the production of immunoglobulins, usually immunoglobulins A and G, risk of multiple myeloma occurrence increases with age and is rare in individuals below 45 years of age, however, the rate of occurrence increases in individuals of about 60 years of age.
In addition to normal symptoms of multiple myeloma such as weight loss, anaemia and recurrent infections and haemorrhage, there is an increase in immunoglobulin light chain and these can be detected in urine of multiple myeloma patients. These proteins have a characteristic properties of precipitating at temperatures bbelow 60 Oc, this is in contrast with the Normal temperature at which proteins precipitates, which is above 60 Oc, these precipitates redissolves at temperatures near the boiling point, this forms the diagnostic basis for assessing these proteins from the patient’s urine.
- Aggamaglobulinemia:
This disorder is linked to the X-chromosomes hence it affects only males, in this disorder, the gamma globulins are absent in the plasma. Gamma globulins includes the immunoglobulins and the C-reactive proteins, the patient is hence prone to infections as these globulins are vital part of the immune system. In a less intense but similar type of this disease, hypoaggamaglobulinamia, there is a decrease in the production or gamma globulins.
- Antibody -Wikipedia
- Introduction to Immunoglogulins -thermofisher
- Allergy -Wikipedia
- Autoimmune diseases -Webmd
- Multiple myeloma -mayoclinic
REFERENCES
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.

))
Hello @joelagbo,
Air-Clinic sends her greeting! We are happy that you are creating amazing medical contents on Steemit using the #Air-Clinic tag.
This article was found as a result of #Air-Curie Initiative!We encourage you to keep it up!
Expect an upvote from @Air-Clinic soon!
If you haven't joined us on Discord please do so by clicking here
Cheers!
Dr. Qamran Bashir- Air-Clinic Curator!
an you contact us (steemstem) on discord about your recent post series please? Contact me, mathowl, alexs1320 or any of the mentors.
Cheers
I'll do that right away