Magnetic Resonance Imaging : How Magnets Spin Protons In Your Body To Produce Images
My favorite sport just ended its season recently. With the golden state warriors winning their third NBA championship in four years. Sports technology and injury treatment has improved over the past years. Injuries that were career ending in the 80’s are now six months injuries. These days when a player goes down with injury, in a week or two reports will come out in the following lines “player X has suffered a grade two meniscus tear was which confirmed after taking an MRI scan” or “player Y was stretched off the court for an MRI which confirmed he has torn his ACL”
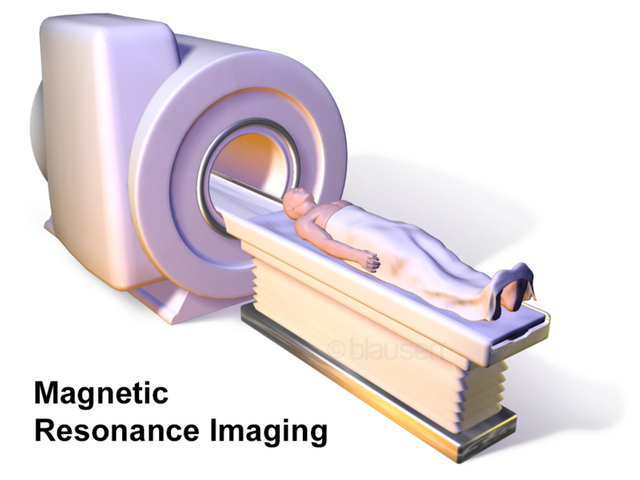
What is the difference between now and the 80’s? The answer is pretty obvious, we have new information. Then, they knew you had tore your ACL but to what extent? They didn't know. With new sophisticated equipments, injury diagnoses has been much easier for doctors. Chief in these new equipments is the MRI scanner.
MRI simply stands for magnetic resonance imaging which is another medical imaging technology used in examining the body of a patient and showing results in 3-D without using ionising radiations. It is a non-invasive technique has the patient is not required to be cut open or will have anything inserted in him or her.
Like we were all told in elementary school, matter is anything that has weight and occupies space. We humans can be classified as matter. In matters exist atoms, in atoms exist the proton, neutron and electron. The MRI works based on some atomic nuclei that acts like magnets when in an external magnetic field.
MRI was formerly regarded as NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging) but because of the fear it had put in patient's minds about how nuclear represents bombs it was dropped and hence renamed MRI. The major feature that separates MRI from other imaging technologies is the images it produces, how well detailed and clear they are.

The principles of nuclear magnetic resonance
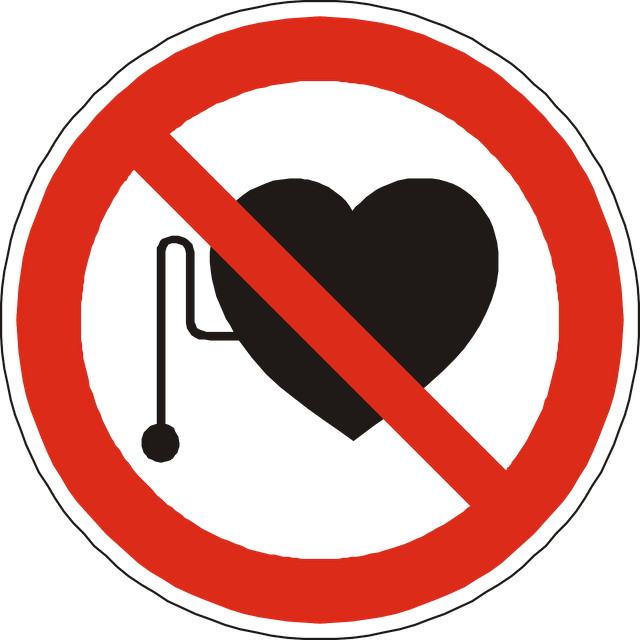
Writing electronic configuration of atoms goes like 1s 2p 3d 4f. Unless you are a chemistry enthusiast like myself, you may not know what exactly those letters (s, d, p, and f) stand for. S is spin, P is principal, D is diffuse and F stands for fundamental. The only one of the four I will be talking about is spin. Spin makes the nucleus of atoms act like magnets in a magnetic field.
The tissue of humans contains a particular element in it in form of hydrogen. Tissues contains water and what does water contain? Hydrogen and oxygen. The principles of nuclear magnetic resonance is based on the nucleus of the hydrogen atom. Hydrogen as we all know is the first element in the periodic table and has an atomic number of one. Atomic number is the sum of protons and neutrons in an atom. But in the case of hydrogen, it only has a proton and no neutrons.
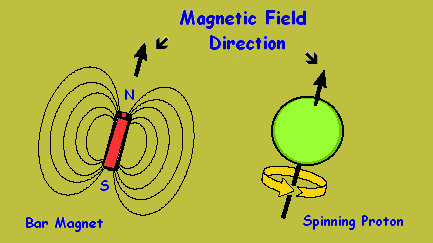
Proton carries a positive electrical charge and because of its spin property it acts like a magnet with north and south poles. When you apply an external magnetic field with strong intensity to proton particles. You will notice the protons will line up side by side like football teams do when going into a pitch. With players from a particular opposite players from the other team but never together. The protons line up in field with their poles facing the opposite pole of the external magnetic field.
Ideally, a proton does not actually line up side by side with the external magnetic field. The proton rotates along the axis of the field created by the external magnetic field. This rotation is a phenomenon known as precession.
Precession is the wobbling motion of an axis of a spinning body when there's is an external force acting on such axis. Precession has an angular frequency called Larmor frequency and it depends on the gyromagnetic ratio of the nucleus of the body (in this case the hydrogen nucleus) and the magnetic flux density. The strength of the external field determines the speed with which the proton precession about it.
As these protons precess about the external field, it is exposed to radio frequency waves that has frequency that matches the frequency of precession of the proton. Each proton is excited into an higher energy state has they absorb a photon of radio frequency energy. When this happens, you can say nuclear magnetic resonance is achieved.
When the source of the radio frequency waves is turned off, the protons are no longer excited and recedes back into their natural low energy state. In the process of doing so, they give off the excess energy and I'm sure you guessed the form in which this energy will come off. Since they gained the energy in radio frequency form, the energy they give off is in the same form.
The energy each proton gives is noted and the rate of relaxation i.e the rate at which the proton releases excess energy to go back to its natural state will help understand the surrounding areas of each proton. What do I mean? Let me try to explain using this analogy. You are at the airport waiting for three of your friends. You don't know where each of them are coming from. The first comes in around two hours, the other six and the the last friend comes in around sixteen hours. If the airport you've been waiting for is in London. You will know the first friend might be coming from France, the second from Nigeria and the third from Australia.
Relaxation time is totally dependent on the where the nucleus is. Like I mentioned earlier, tissues contain water and that is the basis of the nuclear magnetic resonance principle. There are various tissues in the body and these tissues have different water composition which leads to different rate of relaxation.

How does the MRI scanner work
The MRI scanner world's based on the principles of the nuclear magnetic resonance. The major components of an MRI scanner are, superconducting magnets, radio frequency coils, a computer and gradient coils.
The superconducting magnets is responsible for the production of the external magnetic field which is used in aligning the protons in the human body. To avoid the heat this type of magnets will produce, the magnets are supercooled using liquid helium.
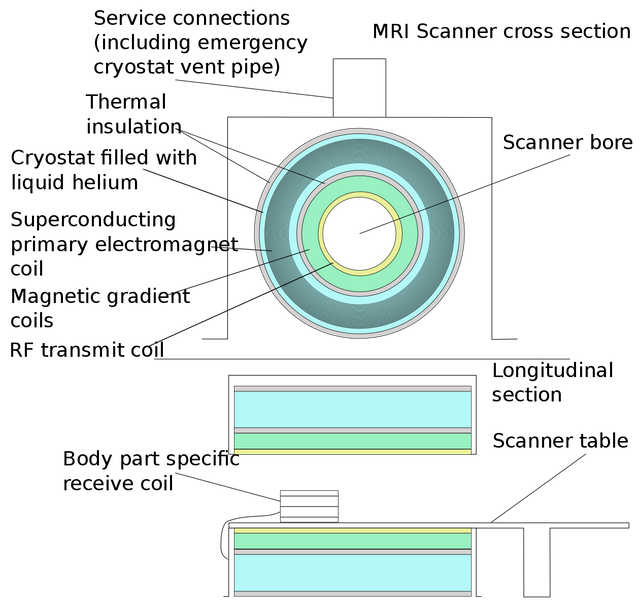.png)
The radio frequency coils are of two types. One is responsible for the transmission of radio frequency waves into the body while the other one detects the rate of relaxation of the protons.
The gradient coils add to the already existing magnetic field and ensure even distribution of the magnetic flux density across the body to be scanned.
The computer is the heart of the scanner has it is responsible for the all of the actions the MRI scanner takes. It also receives the data from the radio frequency coils and stores it. After which it analyses the data and turns it into images.

What really happens during MRI scanning
Once the patient is placed in the scanner, the patient must hold still in order to avoid blurry images which are produced when patients moves during the scanning process. After which the following occurs.
A strong magnetic field is produced which makes the proton in the body align with it and start processing around the axis of the magnetic field. Radio frequency waves is then passed through the body of the patient. The protons are excited and moves to a state of higher energy. After a while, the source of the radio frequency waves is turned off and the receiving coils detects the amount of excess energy released and the time it takes as the proton realigns with the magnetic field.
All these data are sent to the computer which then turns it into images which a physician will be able to tell the differences between the tissues based magnetic property of the protons. There are times where a contrast media is used in order to speed up the time it takes for the protons to align. The quality of the image produced depends on two things, one is how still the patient is during the scan and the other is how fast the protons realign with the magnetic field.
What are MRI scans used for?
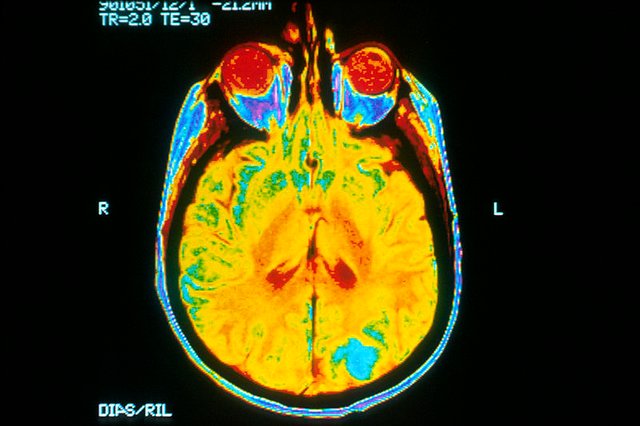
The area where MRI scans finds it application is in taking a scan of areas of the body without soft tissues or bones. They produce clearer images than those gotten using other forms of imaging when used to take scans of the same part of the body. Majorly, the parts MRI scan is used for are the brain, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. Like I mentioned earlier, they are very effective in the injury diagnoses.
To distinguish between white and grey matter in the brain. MRI is used. Should a tumor want to be viewed and examined in the brain, an MRI scan is prescribed.

Why use MRI
Since there are lots of other medical imaging technologies, you may be curious as to what edge does MRI have over other techniques.
MRI scans does not involve the use of any radiation unlike X-rays and CAT scans whose ionising radiation are sometimes responsible for cancer formation in the body. MRI uses a non-ionising radio frequency electromagnetic radiation. Contrast agents used in MRI have little or no chance of causing a allergic reaction like the iodine based agents used in X-rays.
Images gotten from MRI scans are in 3D therefore you can see the difference in overlapping tissues from over hundred angles and unlike ultrasounds where you have a probe moving all over your body, MRI scans involves nothing of such.

Why you may not want to use MRI
The number one thing that can discourage you from taking an MRI scan is the cost of the scan. Over here in my country, the average MRI scan costs well over 350,000 Naira. That is equivalent to about $1000.
We know the MRI scan involves the creation of a strong magnetic field. This magnetic field however extends beyond the space of the scanner and will attract any metal object left in the room. People who have metal implants in their body like heart pacemakers or ankle screws can't take MRI scans because the magnetic field will try to force out the metal implants.
Also, it may be hard for someone like me who is claustrophobic to take the scan as I will not be able to stay still during the scan process thereby creating blurry images. Should a case arise where I will need to take the scan, I will have to be sedated to have a successful scan. But, with sedation medicine comes the risks associated with it.
Clicking and beeping of the machine can become so loud that one might need to make use of an earmuff or earplug.

Conclusion
In cases where repeated scanning is required to track the growth of say a tumor in the brain. MRI is the worldwide accepted method recommended due to its use of non-ionising radiation.
A new form of MRI called the functional magnetic resonance imaging is the novel way of checking activities in the brain. It can show areas of the brain that consumes more oxygen when performing cognitive activities which is used in understanding the organization of the brain.
With all I have said, the major reason why is MRI scans are so common and widely used is because of the area of the body it can cover in just a scan. Ultrasound imaging use non-ionising radiation too, but the area it covers during scans is very small compared to MRI scans which is why it is preferred.
References
Barentsz J, Takahashi S, Oyen W, Mus R, De Mulder P, Reznek R, Oudkerk M, and Mali W. "Commonly used imaging techniques for diagnosis and staging." Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2006 Jul 10;24(20):3234-44.
Hollingworth W; Todd CJ; Bell MI; Arafat Q; Girling S; Karia KR; Dixon AK (2000). "The diagnostic and therapeutic impact of MRI: an observational multi-centre study". Clin Radiol. 55 (11): 825–31.
Basics of MRI
MRI on FDA
All you need to know about MRI
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details.


Wow, I'm just knowing the full meaning of MRI. Got to know why MRI is widely used compared to Ultrasound. I believe MRI covers more area than Ultrasound when it comes to scanning.
You are right sir? or maybe ma'am?
Go here https://steemit.com/@a-a-a to get your post resteemed to over 72,000 followers.
Congratulations! this post got an upvote by @steemrepo and was manually picked by the curator @horpey to be added on STEEM REPOSITORY, simply comment "YES" and we upload it on STEEM REPO Website.
Want to know more about the Steem Repo project? Contact us on Discord
It's amazing how the technology change over the past years.
One of the most interesting post I've read today. worth reading.
Thank you for the nice words.
CONGRATULATIONS....
YOUR AWESOME POST WAS SELCECTED IN THE @wafrica DAILY CURATION
COURTESY: @julietisrael
Nice Job. 👍
Interesting read. Yeah. Every technology has its own down side. MRI is simply amazing. magnetic resonance has been applied in various fields with significant results.
Yes, you are right. MRI is amazing.
The world is advancing with each moon. @addempsea is there any medicine disadvantage that accompanies the use of MRI scanning machines?
Yes @akiripromise. Under the
why you may not want to use MRI
Amazing post I must say. I haven't myself seen a MRI machine tho but with your post, now I know it and the physics and chemistry behind how it works.
Great one @addempsea
Glad you can learn from my blog.
Hy @addempsea, thanks for the breakdown of what MRI really is and I've also come to know the pros and cons, keep it up sir!
Thanks for dropping by
You're welcome sir
20.000+Followers can see you.(@tenorbalonzo,@hakanlama,@cemalbaba,@asagikulak) Send 0.200 Sbd or Steem. Post link as memo for