Voluntary Sleep Deprivation #1: A Self Induced Cognitive impairment
Introduction
It might interest you to know that humans spend one third of their lives sleeping. But in today's world, it's quite easier for a cattle to pass through a needle than for an average human to prioritize a good night sleep. Unfortunately, voluntary sleep deprivation is an offense committed by both the learned and the unlearned. 'Voluntary' in this context means that the individual involved intentionally stays awake despite feeling drowsy.
However, though career driven personalities, students, and administrators have tangible reasons (such as important business deals, all-night study sessions, etc) for depriving themselves of quality sleep. The fact is that, these reasons are not capable of excepting one from the impending consequences of sleep deprivation.
Is that project worth your sleep?
Personally, I believe that humans are rational beings and must always weigh options. Based on several scientific researches, though sleep deprivation does not cause direct death (in humans), nevertheless, the effects could help fasten the process.
According to the National Sleep Foundation (NSF), sleep, along with diet and exercise constitute the very foundation of good health. Inasmuch as this may sound like a lazy man's article, however, it is pertinent to say that sleep is as important as food to man.
Just like several parts of the body are affected during starvation, sleep deprivation also hampers most of the biochemical and physiological processes that takes place in the body.
Physiological implications of a sleepless night on the human body
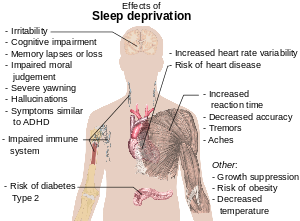 Physiological effects of sleep deprivation (License: CC-BY 3.0, Author: Mikael Häggström]: Wikipedia Commons
Physiological effects of sleep deprivation (License: CC-BY 3.0, Author: Mikael Häggström]: Wikipedia CommonsMost people believe that the only effect of sleep deprivation is basically daytime fatigue. However, this physical outcome is just a tip of the iceberg. Numerous cellular reactions and processes are affected by a single sleepless night resulting in catastrophic outcome. In this series Voluntary sleep deprivation, we will consider the negative effects on most of the body organs and reaction processes.
Effect on the brain
When considering the proper functioning of the human body, the brain is always the central unit. Once anything tampers with the brain, integration and coordination of information functions are similarly affected.
The region of the brain called the prefrontal cortex that is responsible for memory and reasoning is seriously affected after a sleepless night. This is the reason why sleep deprived persons take extra time to complete a simple task. Hence, suggesting a decrease in brain activity.
Aside from decreased in brain activity, sleep deprivation disconnects the prefrontal cortex from the amygdala. It is worthy of note that the amygdala is the emotional control centre, and by staying connected with the prefrontal cortex, emotional responses can be regulated. However, once sleep deprivation triggers disconnection of these two brain areas, what happen is irrational emotional responses. Individuals are seen overreacting to very minor issues or situations.
The next area of the brain affected by sleep deprivation is the hippocampus. It is the brain region responsible for storage of new memories. Just a single sleepless night drastically decreases the ability of hippocampus in memorizing new information. Hence, one must sleep so that old memories can be transferred to other parts of the brain.
According to Centre for Disease Control (CDC) the scary way sleep deprivation affects the brain is that brain neurons are dampened. This means that instead for the brain cells to carry out rapid reactions, they are weak and slow. In this case, certain portions of the brain are asleep while others are awake. Most of the accidents occur as a result of this inability of the brain neurons to function properly.
Summary
The idea of sleeping extra hours on weekends as replacement for the lost sleep during the busy working days is completely illogical because, daily sleep deprivation also have its resultant daily negative effects on the human brain. Unfortunately, these effects can be very fatal in most case.
In the next instalment of this series, we'll be considering the effect of sleep deprivation on the human eye. I hope You've learned something today?. Thanks for doing this with me.
References
Sleep deprivation. Wikipedia articles Retrieved on May 16th, 2018
Sleep deprivation on brain function Retrieved on May 16th, 2018)
Parts of the brain affected by sleep Retrieved on May 16th, 2018
Image Source
Images are from wikicommons licensed under creative commons and eligible for commercial use.
I am severely impaired sometimes from the lack of sleep.
Your statements are true and I have actually researched it and felt it.
Sleeping under 5 hours per night for 4 years effectively made me dumber :D
Only after changing my sleeping habits I was able to see everything more clearly. Cognitive impairment is not something that is easily observed.
You made me laugh. I'm pretty sure you ain't dumb jor. Thanks for reading.
Not anymore, since I now sleep for longer :)