Competing with the Antimicrobial Advancements, Bacteria produces proteins to help them survive, grow and evade the immune system
Hello Steemians,
Today I’ll be talking about the advancements bacteria makes in their genome to survive the upcoming antimicrobial agents and survive. Bacteria produces different classes of antimicrobial peptide to survive within their own population and with these peptides they also produces some other proteins which can let them survive the conditions which we give to inhibit their growth or which generally our body made to eliminate them. These proteins help them survive the acidic conditions in the stomach and even evade the immune system.
“Microbes are much smarter than what we think of them, and every time we come up with new strategy to inhibit their growth, they come up with new ways to evade those.”
It’s the nature of life, which always evolve. Life always find a way out, every time we try to stop bacterial population they come up with something else to survive and every time become stronger and stronger. This the way we all have evolve. In the process of doing this they synthesize several protein, enzyme and other compounds to bypass the inhibition. In today’s I’ll article I’ll be talking on some of those proteins which help them survive and further divide in that environments, some of the proteins even give them the ability to evade the immune system.
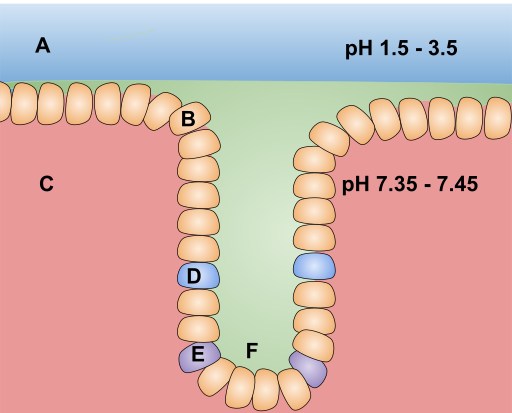
Microbial Flora surviving the stomach acid
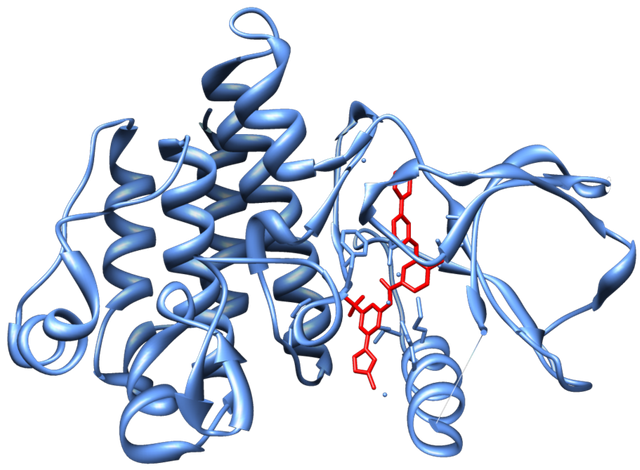
Microbial species present in the small intestine stayed there for a long period and produces endotoxins which were injected into the tissue through a sieve like injecting molecule present on the walls of the bacterial cell and causes infections and make us sick. All these microbial species are generally enters into the body through the mouth, our body contain the physical barrier and chemical barrier to stop these bacterial species but they pass all the barrier. To enter in the small intestine they have to pass through the stomach and the acid present in the stomach should kill all the bacterial sp. passing by. Some of the species survive such acidic condition and reach the small intestine. Cells present at the site for nutrient absorption on small intestine are the target for the pathogenic bacteria to attach and release the toxin. Intimin are the adhesion protein (name was based on “intimate adhesion” property) which sticks to the intestinal cells and forms a channel between the bacteria and cells, through which the bacteria transfers the diarrhea causing toxins (1). Intimin get inserted into the bacterial membrane and attaches to the peptidoglycan. The whole process can only occur in the acidic environment and hence provide them with the stability in the harsh environment of stomach acid. Hence, the protein Intimin supports the infection process and helps the virulence of pathogenic species (2).Plastic Protein Protects the bacteria from unfolding in the Acidic environment
Acid present in the stomach helps in the food digestion and also keeps away the pathogenic microbes, the basic way of inhibiting the microbial growth is by disrupting the protein structure in acidic environment. The protein at higher temperature or low pH unfolds and get aggregated and sticky just similar like what happens to egg white when exposed to heat. It’s not possible to fold the unfolded protein again and this causes the death of the organism when exposed to the low pH (acidic). However, as I already described microbes do find a way to evade such issues and survive in such condition. E.coli a disease causing bacteria able to surpass such acidic condition by producing a protein called HdeA (3). In a recent study by Bradwell and group shows the importance of this protein in the survival of bacterial species in acidic environment. This protein like the other proteins get opens up or unfold when exposed to the acidic environment by unlike others losing their activity, this protein gets activated. Upon unfolding this protein cover the unfolded protein which are unfolded because of acidic pH and just like a plastic wrapper it covers the unfolded proteins and don’t let then get stick together or form aggregates (4).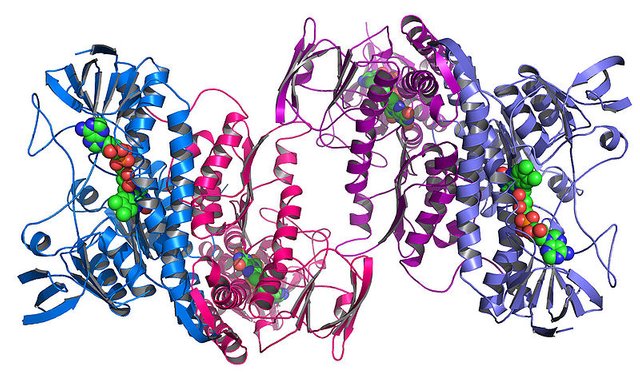
The researchers further concluded that the protein HdeA can sense the acidic nature of environment and can change its form from inactive to active within fraction of seconds. As in the presence of acid, it does not get totally unfolded but remains in a partially unfolded state which gives it a flexibility to act like plastic and take shape like the distorted protein and cover it up just like a plastic and stops the sticking of two different protein. Amazing function of this protein let the E.coli evade the deadly acidic environment (5).
Sticky Adhesive Protein produced by Bacteria
In a bacterial secretory system there are several different types of proteins being synthesized and exported to the extracellular region for several functions. To survive in an environment and to feed on to the host cell they need to stick to the host cells and pilli just cannot help them to achieve it as there are several defense mechanism which hinders their attachment and growth. So, in order to achieve that bacteria produce an extracellular protein called adhesins which help them to attach to a surface and infect the cells. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are among the bacterial species which produces these serine rich adhesins and which can further cause some serious infections (6). Tom Rapoport from Harvard Medical School suggested that apart from the normal secretory machinery, bacteria do have one more machinery which only does produces one protein nothing else. On further study it was found that to transport the formed adhesion proteins to the extracellular layer it needs some modification. The protein need to be modified with some specific sugars and three enzymes which act in a step wise manner (7). The sugars which modifies the protein are involved in the enhanced function of its adhesion and two more proteins whose function was earlier unknown was revealed to be involved in the adhesion process. After binding to these sugar moieties the protein is transported to the membrane where channels to release these are present. This adhesive protein helps bacteria to stick to the host surface and enhance their population and infect the cells (8).Bacterial Proteins which misdirects the Immune System
Apart from all these advancements made by bacterial system to evade the certain physical barrier this is the most important one where bacterial protein binds to any antibody and hinders it’s binding to the antigen and hence evades the immune system. There are several bacterial species like E.coli, Helicobacter pylori and Hepatitis C Virus are known to form the chronic diseases like lymphomas and myelomas. In an effort to understand the process of infection and formation of multiple myelomas from these deadly pathogens, a group has studied the whole process in mycoplasma (9). It was found that mycoplasma associated with the infection for a long time and upon testing the antibodies from the different samples it was found that one protein from the Mycoplasma genitalium was associated with it.
On examining the reactivity of antibodies against the bacterial protein it was found that every single one shows reactivity, but on further study it became clear that these reactions were not in response to the bacterial infection. Instead, it was found that the antibodies were simply binds to the any antibody. Which became a serious issue as the antibodies are meant to combat the infections from pathogens. But the M.genitalium has evolved as a decoy as it binds to every antibody it comes in contact with and are capable of taking cover of the whole immune system (10).
The protein was named as ‘Protein M’ and to get further insight of the structural and functional parts of the protein X-ray crystallography and TEM was performed in a state where the protein was attached to the antibody. The 3D atomic structure of the protein came to be a unique one when compared to the data bank. The data shows the site of attachment which was conserved and binds to the tip of the antibody arm. Now the study is going on, the main focus is to understand the function in the infection of M.genitalium, being the smallest parasitic bacteria on earth represents so much evolutionary changes to evade the several barriers. These are some of the examples of the proteins produced by the bacterial species to evade the physical and chemical barriers and even the human immune system (11).Conclusion
As for the defense purpose we develop certain barriers to stop the microbial growth and stay healthy and in response bacterial species also develop different strategies to overcome such barriers. Focusing on the strategies they develop, here are some of the proteins they synthesize in response to these hurdles and to survive and infect the host to multiply. Here, I have mentioned some of the proteins which let them survive the harsh acidic environment and proteins which let them stick to the surface of the cell to carry on their infectious role and also proteins which behave like plastic and covers the essential proteins so as to save them from the acidic environment and restores their functionality. There are proteins which can also helps the bacteria to bypass the immune system and which in many cases have a huge impact as due to blocking the immune several other pathogens can also have a chance to attack.
These are some of the advancements adopted or you can say invented by the microbes in response to the advanced medications to inhibit them and posing a tough competition to the current medical science.
References
Kern et. al., 2007 Escherichia coli HdeB Is an Acid Stress Chaperone. 189(2):603-610
Kyle et. al., 2008 Multiple myeloma. 111:2962-2972.
Hope you enjoyed reading it, Please upvote and follow my page for further reads on such topics. Feel free to comment.