Understanding Interstitial lung disease (Interstitial pneumonitis)
Introduction
Hello steemians, it's really nice to be here again! Over my last three post, we've talked about some very dangerous diseases. Firstly, we talked about Cellulitis- a bacterial disease of the skin. Secondly, we talked about Vaginal yeast infection- a fungal disease of the vagina. And thirdly, we talked about the worldwide known disease called Ebola hemorrhagic disease (Ebola viral disease), commonly called Ebola.
This time around, we would be talking about a disease of the lungs. This disease is so bad that it causes a form of hypertension, which then leads to guess what?, right-sided heart attack(What ?). I'm sure most of you would be wondering, how can a disease of the lungs, lead to a heart attack!; that disease must definitely be a severe one. O yes!, it is indeed very severe. The name of this disease is called Interstitial lung disease, also known as Interstitial pneumonitis.
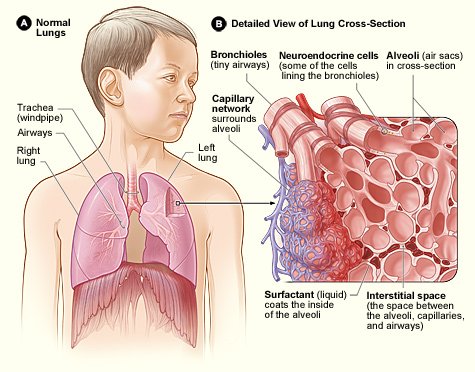
This disease causes thickening of the supporting tissues found between the air sacs of the lungs. Interstitial lung disease may result from a wide variety of causes. Take note, the air sacs themselves are not thickened, it is the supporting tissues around the air sacs that are thickened. There's a part of the lungs called the interstitium, it is a thin layer of tissues, it appears on imaging studies as fine lace. But in the case of interstitial disease, the interstitium appears as a thick lace on imaging studies (too bad, from a fine lace to a thick lace)
The interstitial lung disease has been described in different terms, it is sometimes called interstitial pneumonia. But as a result of the fact that pneumonia is a condition usually associated with an infection, hence medical professionals decided to choose the term interstitial pneumonitis.
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.Source
Interstitial pneumonitis refers to inflammation in the interstitial space. It may be acute (coming suddenly) or may be chronic (occurring over time).
Pneumonitis (noo-moe-NIE-tis) is a general term that refers to inflammation of lung tissue. Technically, pneumonia is a type of pneumonitis because the infection causes inflammation. Pneumonitis, however, is usually used by doctors to refer to noninfectious causes of lung inflammation.Source
Let's talk about the signs that indicate interstitial lung disease.
You see, the signs of interstitial lung disease occur as a result of damage of the interstitium of the lungs, leading to difficulty in breathing. There are two common symptoms of this disease and these are dry cough (not producing sputum) and shortness of breath. The symptoms are usually mild at the beginning and progress with time.
The presence of interstitial lung disease for a long time may lead to lowering of the oxygen levels in the blood which may cause clubbing of the fingertips (a condition in which the fingertips appear broader and rounder- that is, swelling of the finger tips) and enlargement of the heart.
Other symptoms may include fatigue, fevers, weight loss etc. It is really very difficult to diagnose this disease, because many other lung diseases can show signs and symptoms of dry cough and shortness of breath.
A cough is a reflex action that clears your airway of irritants and mucus. There are two types of cough: productive and nonproductive. A productive cough produces phlegm or mucus, clearing it from the lungs. A nonproductive cough, also known as a dry cough, doesn’t produce phlegm or mucus.Source.
Interstitial pneumonitis has a broad range of causes. The precise cause of interstitial lung disease is almost always not known (Idiopathic). Idiopathic is the term used to describe a condition that the cause is unknown. Some of the known causes may include environmental factors, toxins, cancer, chronic diseases etc.
It depends on the cause, interstitial pneumonitis can be resolved or may lead to irreversible scarring as well as damage of the lungs. The known causes include the following-
Radiation therapy- When high- energy rays of particle are used to kill cells and stop them from growing
Chemotherapy (Cancer treatment ) and amiodarone (cordarone)- a medication used for treating heart problems.
Environmental factors- which may include certain metals, dust, asbestos, grain dust, mold, bird droppings. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is the term used to refer to the disease caused by these irritants above mentioned.
Chronic diseases- Such as lupus, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Cancer- This disease can sometimes spread into the lymph system in the lungs and may appear as interstitial disease.
The above are examples of known causes. Here are some examples of unknown causes (idiopathic) of interstitial pneumonitis- Lymphphotic interstitial pneumonitis (LIP), bronchitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP), Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis (DIP), Lymphangiomyomatosis, sarcoidosis, Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
The difference between one of these diseases from another is based on the pattern of the lung damage, location and the severity of the disease.
How is this disease diagnosed? Let's discuss that right away!
As I mentioned above, there are so many causes of interstitial lung disease, and this makes it really very difficult to diagnose. Diagnosis may include imaging studies, blood test, pulmonary function test, and most times biopsy, other testing should involve good medical history and physical examination.
It is important to know the history of exposures to environmental toxins. It is also very necessary to investigate the occupation, vocation, exposure history and travel history of the patient. Let's take for example, a patient shows signs and symptoms of shortness of breath and dry cough and this patient enjoys playing with and caring for pigeons, one can conclude that the diagnosis would be hypersensitivity pneumonitis (caused as a result of irritation to pigeons). As I mentioned above, it is difficult to diagnose interstitial lung disease, but there are some studies that may be useful, and they include-
Blood tests- Blood test can very well help in the treatment of this disease. Usually, a test for arterial blood gases, collagen vascular disease and liver tests may be useful.
Bronchoscopy- This involves using a viewing tube to visualize and examine the airways of the lungs. Tissues samples (biopsies) or washing of the airways are obtained during the examination. Even at that, this does not still get definitive diagnosis. Although, it can be useful to evaluate the possibility of cancer, sarcoidosis etc.
Imaging studies- This is usually performed on the chest and lungs early in the process, when signs and symptoms are still apparent. High resolution CT scans and chest x-rays may be ordered. Echocardiogram may be helpful as well, it is a test that can evaluate the pressure in the lungs. Open lung biopsy may also be useful.
The treatment of this disease depends on the cause. The treatment may involve the following- Avoidance behaviour, antimicrobial agents, chemotherapy, immunosuppressing agents. If this disease involves hypersensitivity which I have explained above, then the suitable therapy would be avoidance of the irritant. If the symptoms are very severe, respiratory support may be needed, including supplemental oxygen and ventilator support, may also be needed. Smoking cessation is an important part of the treatment of any patient suffering from interstitial lung disease.
The use of corticosteroids may also be useful in controlling interstitial inflammation. Some drugs may also modulate immune function, such as cytoxan, azathioprine, cellcept may be useful along side with steroid treatment.
Corticosteroids (cortisone-like medicines) are used to provide relief for inflamed areas of the body. They lessen swelling, redness, itching, and allergic reactions.Source
Please note, these medications may only slow the spread of the disease, but are incapable of reversing the scarring in the case of interstitial lung disease that has been long-standing. Lung transplant may be done in cases with irrversible damage.
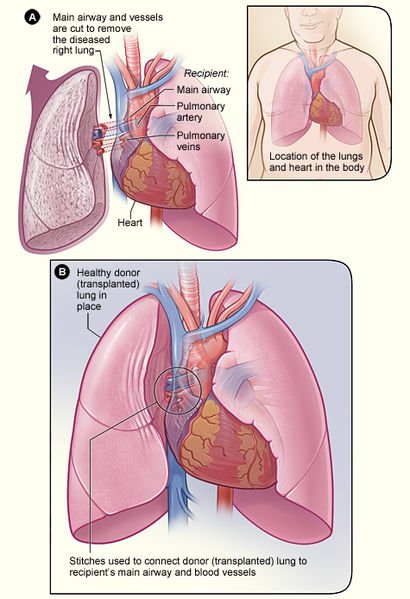
Prognosis of intersitial lung disease. Here we go!
As I mentioned above, interstitial lung disease of some forms may be resolved completely, while others may lead to irreversible scarring of the lungs and in some cases lung damage, which may be accompanied by respiratory failure. There's a form of high blood pressure called pulmonary hypertension; which affects the arteries within the lungs.
In long-standing interstitial lung disease, pulmonary hypertension may lead to enlargement of the heart and may cause right-sided heart failure (known as Cor pulmonale).
In one form of pulmonary hypertension, tiny arteries in your lungs, called pulmonary arterioles, and capillaries become narrowed, blocked or destroyed. This makes it harder for blood to flow through your lungs, and raises pressure within your lungs' arteries. As the pressure builds, your heart's lower right chamber (right ventricle) must work harder to pump blood through your lungs, eventually causing your heart muscle to weaken and fail.Source
The survival rate depends on the type and severity of interstitial lung disease and the health condition of the patient.
.jpg)
Conclusion
Interstitial lung disease can be prevented only when the individual can identify the cause of this disease. Take for example, if an individual has identified a particular environmental toxin as the cause, he/she can simply avoid that environmental toxin. But in severe cases, when the disease has led to irreversible lung damage, the individual has to consider lung transplant or face the risk of respiratory failure.
Thanks for reading!
References
Image Sources
All images used here are from free sources and liable for commercial use
all licensed under the Creative Commons.

Congrats @starrichie
Your great article has been selected to feature in this week Air-Curation Round 15.
Expect an upvote from a supporter of this initiative.
Continue using the #Air-Cliniic tag.
It is worth noting that, there are a lot of diseases which can be presented with the signs and symptoms described in this article. So, it is important to get a medical consultation in order to determine what kind of diseases that you (or anyone else) were having.
Wow. This is wonderful you did justice to it