Experimental Study of Boundary Layer Effect on the Aeroacoustic Characteristics of the Incompressible Open Cavity
1. Presentation
Swaying caused by stream over Cavity can build the drag enormously and even prompt basic vibration also, weariness harm. To recognize the wavering from commotion age instrument precisely is basic and earnest. For the investigation of the stream in hole, since the 1950s, numerous remote exploratory examinations have been done. Since the 1980s, numerical reproduction is more utilized as a part of concentrates identified with the system of cavity stream and clamor examination. In China, the examination for hole stream begins just lately, and works predominantly in the field of numerical reproduction for little scale depression. The streamlined focus carried on exploratory comparing investigation of stream qualities and acoustic attributes for subsonic and supersonic cavity. Certain exploration results[1-7] demonstrate that the cavity geometric parameters, for example, length to profundity proportion L/D, the angle proportion W/D, and stream parameters, for example, Mach number Ma or different impacts of the pit shear layer flimsiness, accordingly influencing the stream writes and clamor ghastly qualities. At the point when the low speed turbulent stream go through the rectangular depression, the stream inside the hole is extremely complex, and the weight range created by the hole contains both wide band commotion and unadulterated tones. The pit test stage was worked in a low-turbulence wind burrow; led analyses to measure the depression stream clamor and to give approve information to numerical reproduction. This article centers around the impact of changing limit layer profiles in the depression bay on the aeroacoustic qualities of cavity stream. With the estimation technique for divider weight sensors, mouthpieces and hotwire, in view of the open depression of length-to profundity proportion 2 and 4, the bay limit layer profile was changed through various square establishment techniques. The acoustic properties of depression in various bay limit layer stream state were acquired, giving a premise to pit stream commotion concealment investigate.
2. Trial display
Open pit display utilizes wooden structure. The model blockage degree in wind burrow test area is about 8%. The greatest profundity of the cavity Dmax=116mm, most extreme length Lmax=700mm, and the greatest width Wmax=120mm. Depression display was appeared in Figure 1. the contact surface of Model with wind burrow divider was cushioning with delicate froth to stay away from nearby stream cross all over, while lessening the impacts of wind burrow vibration on the models stream structure.
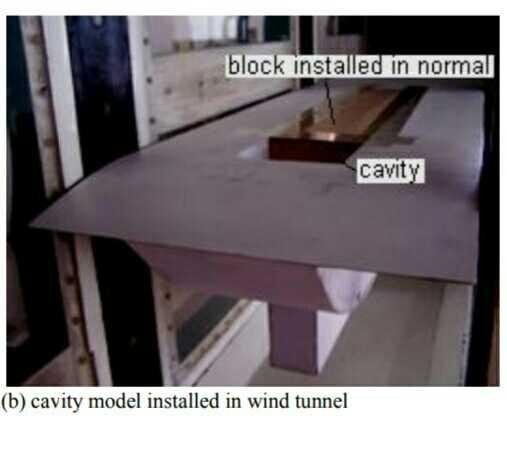


By hindering the cavity along the stream heading from the front edge or back edge, the impacts of various limit layer at cavity channel on stream aeroacoustic qualities was examined. Indicated programs are appeared in Table 1.
Table 1. Trial program

Fig.2. Number imprints relating to various estimating areas of acoustic tests along focus line on hole base
3. Test types of gear
The test is done in low turbulence wind burrow (LTWT) of Northwestern Polytechnical College. The hole is tried in two dimensional test segment which has the cross-sectional measurement of 1.0m × 0.4m. The breeze speed for this paper is 30m/s. Static weight information obtaining use DSY104 checking electron small scale weight estimation framework, which has 192 manometer channels, with channel examine rate of 50,000/sec, and the framework exactness is ± 0.1%F.S. Dynamic weight range was estimated by Belgian LMS dynamic estimation framework, which has the LMS SCM01 Mobile 8-channel information obtaining front, PCB acoustic sensors, demonstrate type 130P10/D10, and the recurrence extend 10-15 KHz. The miniaturized scale parameters in limit layer, and so forth were estimated utilizing one-dimensional hotwire test 55P11. The hotwire was bolstered by high-accuracy 3-arrange auto-move gear with the littlest moving accuracy of 0.01mm. The gathering of 3-pivot hardware on test segment of the breeze burrow was appeared in
Figure 3.

Fig.3. 2D test area of wind burrow outfitted with 3-arrange high accuracy moving gear
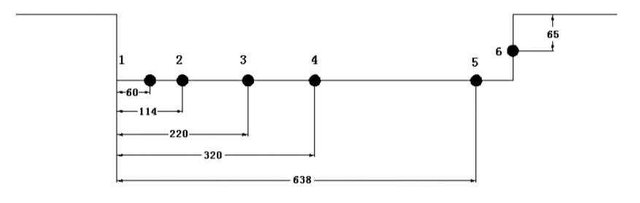
4. Acoustic properties of various areas inside a similar pit
Figure 4 indicates pit commotion qualities of various estimating focuses for the open cavity (L/D=2 and 4) with the square introduced in typical state. For both L/D=2 and 4, Location 6 is the estimating point on the back mass of the pit, and Location 1 is in the front of the pit base, the estimating focuses 2 and 3 are on base place for L/D = 2 and 4 individually, and the estimating point 3 and 4 are situated on the cavity base close to the back divider. As anyone might imagine seen from the outcomes, the radiation commotion recurrence is amassed in the locale of low-to-center recurrence; the back divider is the fundamental commotion radiation region. SPL on raise divider is higher than the clamor on base at any rate 10dB,which demonstrate the broadband qualities with the pinnacle diminishing. For cavity L/D=2, the entire base areas are mirroring the stream qualities of solid swaying recurrence crest. At the point when the length-to-profundity proportion expanded to 4, the pit commotion mirrors the essential recurrence increment, and when near the back divider, the SPL increments to a similar extent arrange with back divider.
6. Impact of limit layer profile on the cavity stream
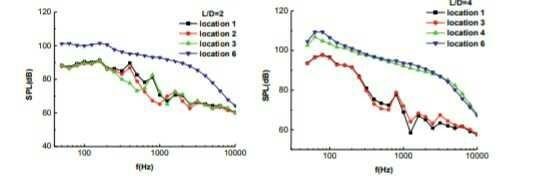
In view of the two holes of length-to-profundity proportion 2 and 4, tests were completed with squares introduced inside depressions typically and turned around. The impact of limit layer changes on stream design in depressions was gotten. The weight appropriation on bottoms are given out in Figure 7. Figure 7 demonstrates that the limit layer profile influences the depression stream design essentially. At the point when the piece introduced contrarily, limit layer thickness increments, while influencing the general strain to rise essentially, what's more, then again, unfavorable weight inclination diminishes. This demonstrates, with the expansion of turbulent dynamic vitality in limit layer stream, the depression shear layer steadiness improved and the turn around stream speed in pit debilitated.
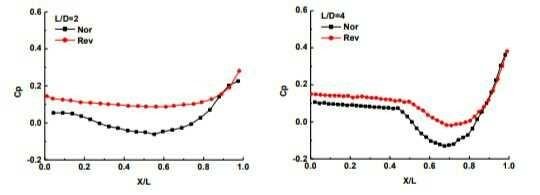
Fig.7. Weight circulation on cavity bottoms with delta limit layer change(V=30m/s)
Figure 8 demonstrates the impact of limit changes at pit entrance on clamor range with estimating area on the base focus and the back divider individually. the outcomes show that the SPL at raise divider increments marginally, and the change size is under 3dB. For the length-to-profundity proportion of 2, the SPL at base focus changes seriously, with the limit layer thickening, in a wide range (the low-recurrence locale under 600 and high-recurrence district higher than 1,500), commotion radiation is enormously stifled with the biggest reductions of around 10dB. For the length-to-profundity proportion of 4, in the center and low recurrence area, the sound weight is marginally lessened when piece introduced contrarily, however at the recurrence around 1000Hz, SPL increments with the thickening of the limit layer.
7. Conclusions
On the basis of the cavity, with the measurement of wall pressure, hotwire and sound pressure acquisition,
the clean cavity aeroacoustic characteristics under different inlet flow boundary conditions were studies, basic
conclusions are as followings:
(1) With the boundary layer thickness increases, the pressure on the cavity bottom increased greatly with
adverse pressure gradient decreases;
(2) When block installed reversely, for open cavity L/D=2, SPL greatly reduced, for L/D=4, the low
frequency sound pressure is reduced with small amplitude, while sound pressure significantly increase in middle and high frequency.
source:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212671614001255?via%3Dihub
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/