OCTANE RATING; WHAT DO YOU KNOW ABOUT IT?
Hello here, it has been quite a while and I am glad to be back. I am very glad to have my hands on the keyboard once again.
Today I would be discussing a quite unpopular but very relevant topic to the automobile world. This phenomenon actually connects to our daily lives more than we think because we use cars and board airplanes. I am talking about octane rating of fuels and all you need to know about it.
Throughout this post, I would be talking in automobile terms with specific reference to petrol engines.
Have you ever experienced knocking of a petrol engine? Well, if you haven’t, you sure would have heard of it. Trust me, a knocked engine is not something anyone would pray to have. All I can say about it is; BAD EXPERIENCE, BAD EXPERIENCE!
All through the second half of the year 2016, I was on industrial attachment at an automobile workshop. On one fateful day, a vehicle was brought in with the issue of knocking sound in the engine and the technicians diagnosed it to be due to bad fuel. Bad fuel you say? I never knew fuel could be bad! I later got to know the simple mystery behind it and here it is.
Although a lot of factors could be responsible for a knocked engine (I am talking in automobile terms now), the octane rating factor or simply the octane content of the fuel used is one of the possible culprits.
First off, let’s do a little basics
Internal combustion engines run on two types of fuel; Diesel or petrol. These engines are referred to as internal combustion engines because the fuels are made to combust (burn) inside the engine and the energy released by burning of these fuels is harnessed to drive the engine. The petrol engine does this by compressing the fuel mixed with air and igniting it with the aid of a spark plug. Diesel engines rather compress air and inject the fuel at high pressure to the compressed air.
Fuels are generally made of hydrocarbons (carbon and hydrogen compounds) of which octane is one.
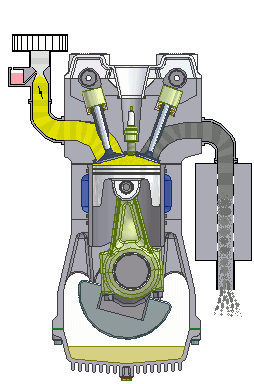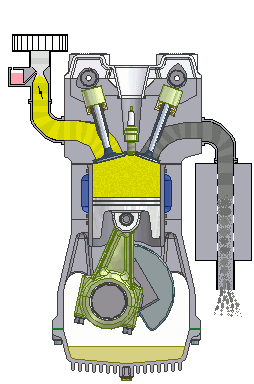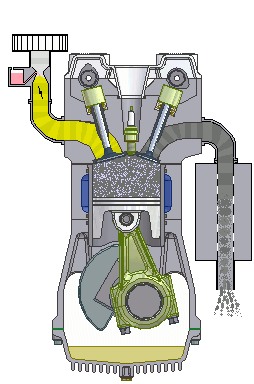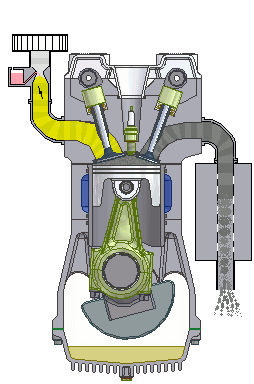 simple internal combustion engine wikipedia commons
simple internal combustion engine wikipedia commons
WHAT IS THE OCTANE NUMBER
According to online sources, octane number is a measure of the performance of a fuel. It is based on the ability of a fuel to withstand compression before self-igniting. Basically, the amount of compression a fuel can withstand depends on the octane number of the fuel (the higher the octane number, the more combustion it can withstand).
Simply put, octane rating is a measure of the ability of a fuel to avoid knock!
WHY IS OCTANE NUMBER SO IMPORTANT?
As much as internal combustion engines are concerned, the timing and precision of the processes involved in its operation are very important factors as a slight change in the timing or timeliness of a process can damage the engine for good.
In the case of octane number, it is related to the effect of compression on the ignition of fuel. If a fuel does not contain the right octane content i.e. the right octane number for the engine it is used on, the fuel could ignite too early and cause an imbalance In the operation of the engine. If this happens, there would be a “knocking” sound and if not quickly attended to, can ruin the engine for good.
This occurrence of igniting before the required time is known as pre ignition
PRE-IGNITION
In simple terms, pre-ignition is the detonation of a fuel in an engine before the required time.
When this occurs, shock waves are sent out which disrupt the conditions for which the engine component are made for and thus, a damage to the engine occurs. The common indication of pre-ignition is a knocking or pinging sound in the engine while operating.
Fortunately, technological advancements in automobile engines have seen the introduction of knock sensors which are tasked with sensing the possible knock and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) does the job of controlling the parameters of the engine operation to counter the situation.
OCTANE RATING AND FUEL ECONOMY
As far as fuel economy is concerned, octane rating has little or no effect on it. An automobile engine (in the right working condition) would use as much fuel as required for the load it is subjected to.
Octane rating only affects engine performance as related to the ignition of the fuel in the engine, as much as i know, it is not related to fuel economy.
.jpg)
fuel pump showing octane rating source
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT OCTANE NUMBER
- Most manufactures indicate the octane rating of fuel required for the vehicles.
- The octane rating tells how much air-fuel mixture can be compressed before self-ignition can occur
- A fuel with a particular octane rating performs best in an engine that is designed to operate at that particular level.
- Ethanol can be added to fuel (petrol) to increase the octane rating
- Some fuel pumps in some countries display the octane rating of the fuel they are dispensing (usually BLACK NUMBERS IN YELLOW BACKGROUND)
- Most petrol vehicles are made to work on 87 octane but some others are designed for higher.
- Use of a fuel with lower octane can cause the engine not to run smoothly and further damage the engine and/or emission control system.
- Using of a fuel with higher octane can improve the performance of the engine and even reduce the Carbon dioxide emissions but this only happens in the case of heavy duty usage as it does not have a significant effect for normal driving conditions.
- Usually, fuels that have higher octane cost more
CONCLUSION
In countries like mine (Nigeria) octane rating of fuels are not given attention as fuel dispensing pumps do not offer a variety of fuels with different octane rating and thus, one can only know that a fuel has lower than required octane rating if he has bought it and used it. The technicians would simply say
you have bought bad fuel
The only remedy is to drain the fuel and get another.
It is usually important to watch out for knocking sound in the engine to avoid the “tragedy” of a knocked engine.
REFERENCES
OCTANE RATING
FUEL ECONOMY
OCTANE NUMBER DEFINATION
OCTANE RATINGS AND FUEL

