Measurement and science - The metric system
We continue studying and investigating the world of science, a really interesting world. I'm not a scientist, but I've always liked to know the reason for things.
In my last publication, I told them that in the branches of science the scientists studied the topics based on the questions that are asked about the world. Today I want us to talk about how these scientists, coming from different parts of the earth, can work together and understand what they are doing; in a certain sense, they must speak the same language.
Metric - The international language of measures
Most experiments require data, and much of that data is measured. It is important that the measures are concise and that they can be easily communicated. That's why you should use a universal measurement system with standard units to avoid confusion.
To ensure that things go well, experts use the same standard measurement system. That system is the metric system or System of international units by its acronyms (SI).
This metric system is the one used by scientists around the world to compare and analyze their data, it is very simple to use. It is like the monetary system, a decimal system; that is, based on the number 10 and multiples of ten. Each unit of this metric system is ten times larger and 10 times smaller than the one that precedes or follows it.
Scientists use metric units to measure length, volume, mass, weight, density and temperature. .
Length
The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter (m). One meter equals 39.4 inches, or a little more than a yard. To measure the length of an object of less than one meter, the centimeter (cm) is used. As you can see, there are 100 centimeters in a meter.
| Length |
|---|
| 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm) |
| 1 meter = 1000 millimeters (mm) |
| 1 meter = 1,000,000 micrometers (μm) |
| 1 meter = 1,000,000,000 nanometers(nm) |
| 1 meter = 10,000,000,000 angstroms (Å) |
| 1000 meter = 1 kilometer (km) |
To measure even smaller objects we use the millimeter (mm) of the prefix milli, which means one thousandth, so there are 1000 millimeters in a meter. In sunlight, the diameter of the pupil of the eye measures approximately 1 millimeter.
But even millimeters are excellent when it comes to measuring microscopic organisms like bacteria. Bacteria are measured in micrometers, or millionths of a meter, and manometers, or millionths of a meter. Although you can not believe, these small measures are not enough. To measure atoms, scientists use a metric unit called angstrom. An angstrom is a tenth trillionth of a meter, everything to simplify things, I know that some of you for the first time hear these measures, but it is always good to know them.
On the other hand, when you need to measure long distances, for example, the length of the Orinoco River one of the most important rivers in South America that It is mainly executed in Venezuela. Such length can be measured in meters, centimeters and even millimeters. But it is very difficult to work with small units when the numbers result from long-distance measurements. For example, it is not very easy to talk about 2,140,000,000 (which would be the length of the Orinoco River expressed in millimeters). To avoid such large numbers, the metric unit called kilometer (km) is used. The length of the Orinoco River is approximately 2,140 km.
On Earth, meters and km are very useful units of measurement. But in space, distances are too large to measure in kilometers. (Once again, the numbers would be too large).
To measure large distances in space, astronomers use a unit of distance called light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in a year. You probably know that light travels very fast, around 300,000 kilometers per second and one light year is approximately 9.5 billion kilometers. Can you imagine how many centimeters there is in a light year?
Although it seems that a light year is an immense distance, it is not so immense in space. The star system closest to Earth is more than 4 light-years away. The light of that system takes more than four years to reach Earth. And it's nothing compared to the distance of the star system Trappist-1 that is 40 light years from Earth, in the constellation Aquarius , some 350 billion kilometers.
The volume
Volume is the amount of space that an object occupies. In the metric system, the basic unit of volume is liter (L). A liter is a little more than a quarter. To measure smaller volumes milliliter (mL) is used, which is equal to 1000 milliliters in a liter.
| The volume |
|---|
| 1 liter (L) = 1000 milliliters (mL) or 1000 cubic centimeters (cm3) |
Liters and milliliters are used to measure the volume of liquids, but the volumes of solids must also be measured. For this the cubic centimeter (cm3 or cc) is used. A cubic centimeter has the volume of a cube that measures 1 cm * 1 cm * 1 cm. A cubic centimeter is equivalent to one milliliter, so you can use cubic centimeters to measure both the volumes of liquids and the volume of solids.
Mass
The mass is the measure of the amount of matter an object has. A cargo truck, for example, has more mass than a medium-sized car. Remember that volume is not the same as mass, volume is the amount of space an object occupies and mass is the amount of matter it has. The basic unit of mass in the metric system is the kilogram (kg). The kilogram is used to measure the mass of large objects. To measure smaller objects, such as a coin, for example, the gram (g) is used.
Sometimes scientists need to measure the mass of objects even much smaller and for that they use the metric unit called milligram (mg). There are 1000 milligrams in a gram.
| Mass |
|---|
| 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g) |
| 1 gram = 1000 milligrams (mg) |
| 1000 kilograms = 1 metric ton (t) |
The weight
The weight is the measure of the attraction between two objects produced by gravity. Gravity is the force of attraction. The intensity of gravity between objects depends in part on the distance between them. The greater the distance, the lower the force of gravity. Your weight is the measure of the force of gravity exerted by the Earth on you.
The basic unit of weight of the metric system is the newton (N), named for Isaac Newton, the discoverer of the force of gravity. Newton is used because it measures force, and weight is the intensity of the force that Earth's gravity exerts on an object. An object with a mass of 1 kilogram is attracted to the Earth with a force of 9.8 newtons. Then an object with a mass of 50 kilograms is attracted with a 50 x 9.8 or 490 N. What is its weight on Earth?
As the force of gravity changes by distance, your weight can change depending on how far you are from the center of the Earth. And although there is not much difference, when you are on the top of a mountain, you weigh less than when you are at sea level.
Now, given that the distance between an astronaut and the center of the Earth is enormous, the gravitational force of the Earth is smaller and although it seems that the astronaut weighs nothing, it is not so because despite the distance they are attracted by the Earth by the force of gravity

Image Pixabay
The force of gravity not only changes with distance, but also changes according to mass. An object that has a large mass, such as the Earth, exerts a force of enormous gravity on other objects. (That is why we stay close to the earth and we are not flying through space). But any object with mass exerts a gravitational force, and that includes you.
The density
Sometimes, scientists must compare substances according to their mass and volume. The relationship between mass and volume is called density.
Density is the volume of mass per unit that a substance has. That is not as complicated as it seems. This formula, which shows the relationship between density, mass and volume, can help you understand it:
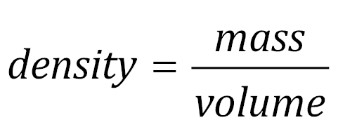
The density of the water is 1 g / mL. Objects that have a density lower than water float. Objects that have a higher density will sink.
Temperature
And in the metric system, the temperature is measured in the Celsius scale. On this scale, the temperature freezes at 0 ° C and boils at 100 ° C. It is not a coincidence. The metric temperature system was created in such a way that there is exactly 100 degrees between the freezing point and the boiling point of the water. To get an idea, the normal temperature of the human body is 37 ° C and the ambient temperature is about 21 ° C.
With this I hope you have learned to use the basic units of metric measurements. For a future publication I want to focus on the measuring instruments. Thank you for reading this far!
References used
http://www.profesorenlinea.cl/fisica/MedidasSistema_internacional.htm
https://www.montereyinstitute.org/courses/DevelopmentalMath/TEXTGROUP-1-8_RESOURCE/U06_L2_T1_text_final_es.html
https://definicion.de/sistema-metrico/
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sistema_Internacional_de_Unidades
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Velocidad_de_la_luz
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/TRAPPIST-1
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alfa_Centauri
http://www.bbc.com/mundo/noticias-39059047
https://www.vix.com/es/btg/curiosidades/2011/06/16/que-es-un-ano-luz

@steemstem animation by the awesome @foundation



nice post
Tus explicaciones son muy didácticas, seguro q eres un buen profesor
Gracias me alegra que te gusten @orgaescola
great post!!
good information, i am civil engineer , and this post is very good
Very good post, I did not know about the light years, very interesting.