Absolute Zero and the Bose-Einstein Condensate🔬
Bose-Einstein Condensate
To understand this theory a bit better, let's start from ZERO... Absolute.
Robert Boyle
Physicist, chemist and inventor.
He was one of the first scientists to discuss the possibility of an absolute minimum temperature in 1665, the concept had good receptivity by the scientific community.
Some argued that this absolute minimum temperature was produced within the Earth, others argued that it was inside water, among other theories. But all agreed that "there is a very cold body that by their participation, all other bodies obtained that quality."
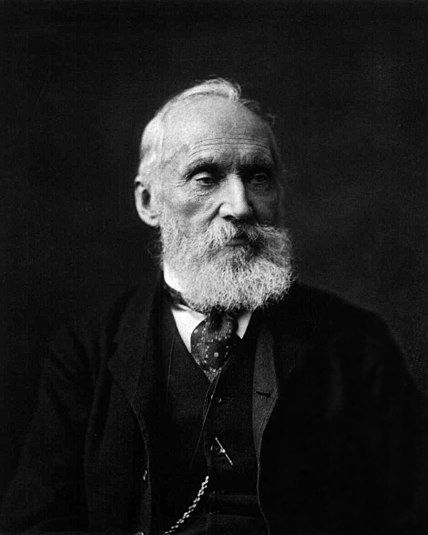
William Thomson (Lord Kelvin)
Physicist and mathematician
In 1848, he devised the absolute temperature scale based solely on the fundamental laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the principles of that scale, he placed zero (0 K) absolute in - 273.15 ° C.
"Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature for matter in the universe, in which the particles of a substance remain motionless". Wikipedia
Absolute Zero
According to the laws of thermodynamics, absolute zero (-273.15 °K) is an unattainable temperature. The largest cold room only reaches -273.144 °K. The reason is that the molecules in the chamber run out of energy before reaching the minimum temperature.
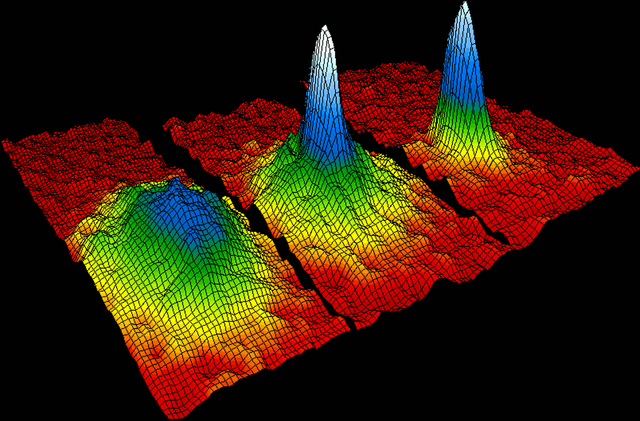
Satyendra Nath Bose and Albert Einstein in the 1920s developed an article with photons of light. Bose describes certain rules to determine if two photons should be considered identical or different, this is called Bose-Einstein condensate.
At present the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) reaches a temperature of 1.9 °K very close to absolute zero.
Some experiments that are performed there require the cryogenization of certain circuits, this is possible with the combination of helium and liquid nitrogen which enters the circuits.
Condensate of Bose-Einstein
When you lower the temperature too much, the quantum properties become very strange, these atoms acquire properties of light waves, instead of points, you have wave packets, moving.
As the temperature decreases, the size of these packages becomes smaller and smaller and if you continue to cool them, they begin to superimpose and when they overlap the system stops behaving as independent particles, but as particles that have lost their identity.
In the Bose-Einstein Condensate the particles are in all places at the same time, they no longer know what they are, they have lost their identity. If one atom is at rest, all others will be at rest. But ... there are no other atoms, they are all a single quantum system.
In this state, matter acquires surprising characteristics such as superconductivity or superfluidity.
Superconductivity
Kamerlingh Onnes
Dutch physicist
In 1911, he discovered the phenomenon of superconductivity when measuring the electrical resistance of mercury under low temperature conditions, to eliminate thermal noise in the movement of electrons inside the conductor.
He determined that for temperatures below 4.5°k the electrical resistance was practically nil.
Superfluidity
Piotr Kapitsa
Physicist and inventor
In 1937 he discovered superfluidity in his quantum hydrodynamic study. Superfluidity occurs at very low temperatures, very close to absolute zero. One of the disadvantages is that, at this temperature, almost all the elements freeze, except Helium.
When helium cools to a temperature of 2 degrees above absolute zero it begins to evaporate. Then a surprising transformation happens. The bubbles stop and liquid is at rest. Then, helium has become superfluid, acquires strange properties.
Superfluid helium does things that are considered impossible. He is able to defy gravity, escaping from a container as we see in the animation to his right.
The superfluid has 0 viscosity, producing a frictionless source. The result is an infinitely narrow horizontal plane; like what happens inside the supernovas when their life span is exhausted and they turn into black holes.
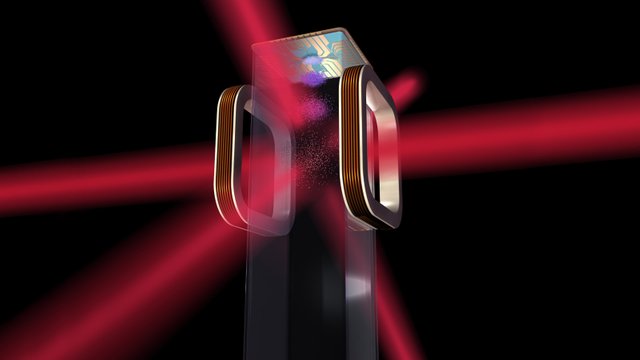
Cold Atom Lab
The search for colder and colder temperatures has been an important topic of physics during the last centuries. Taking us to discover superconductivity and superfluidity. But humanity wants to go further.
On May 20, the Cold Atom Lab was launched aboard the Cygnus spacecraft of the ATK Orbital. This instrument will work from the International Space Station (ISS). Its mission is to reach temperatures millions of times lower than the vacuum of space by lasers, and in this way, to reach absolute zero in gaseous elements from space.
With this, very sensitive quantum sensors could be developed to monitor the Earth's gravity and the search for planetary bodies.
Cold in the Universe
In our solar system, temperatures as low as -240°C have been detected in areas that are in permanent shadow, such as the South Pole of the Moon.
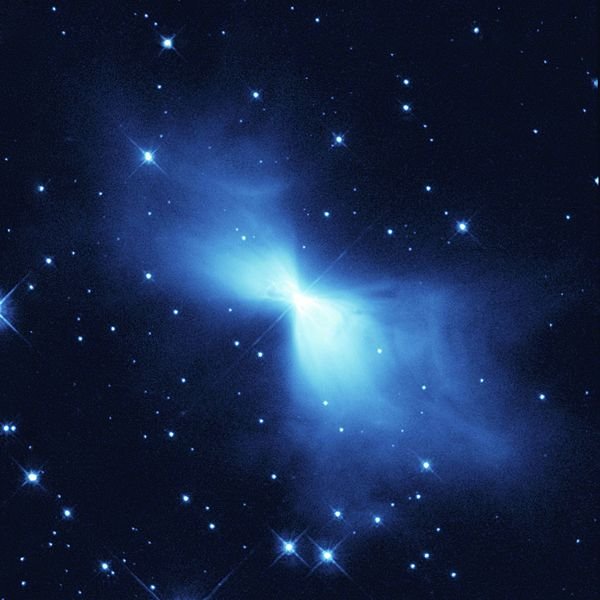
In 1995, at 5000 light years astronomers observed the Boomerang Nebula through a submillimeter wave telescope, they realized that it emitted extremely cold waves, so much that they exceeded the radiation left by the Big Bang, the temperature is only 1 °K (-272 °C).
A degree above absolute zero. It has become the coolest known object in the universe.
Conclusion
I decided to make this publication because it caught my attention when I read a story about Cold Atom Lab and started researching. We have seen how low temperatures can drastically influence matter so that a transformation arises and can be beneficial for humans. The use of the Cold Atom Lab in the international space station will bring new forms of technology.
Our world is vast and mysterious, every day humanity makes surprising discoveries, we go to a world of science fiction, "we are going to the future".
Could there be more states of matter in our universe?
Greetings friends!
References:
- NASA Wants to Create the Coolest Spot in the Universe. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA. MARCH 6, 2017.
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=6765 - Superconductivity. Wikipedia. 5 abr 2018.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superconductividad - Absolute zero. Wikipedia. 4 May 2018.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_zero - Cold Atom Lab. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA. 2017.
https://coldatomlab.jpl.nasa.gov/ - Bose-Eintein Condensate. Wikipedia. 22 May 2018.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bose%E2%80%93Einstein_condensate







This quote, I think you miswrote the reference as "Wikimedia" (I think you meant Wikipedia).
You're right, friend, thank you very much!
How attentive.
regards!
When I started reading I was still in track of the message but when I got to the second quite below I needed to find out what is in this write up
°°°the influential of low Temp on matter and different views from different scientists... Good one mate
I had never known this state of matter, a very interesting subject. What motivates the search for information.
Hi there. I'm a moderator for @steemiteducation @edu-venezuela. Sections of your post were too closely similar to some of your sources. They were borderline considered plagiarized but I could tell you were trying to put things in your own words. In the future make sure the entire post is in your own words. I know that may be difficult with science posts but be careful using someone else's phrasing for sentences. This post wasn't eligible for resteeming but you are welcome to try again with future posts.
Thanks for the recommendation!
The subject was a bit complex and you do not find much information, I tried to write it as understandable. Thanks again, Greetings!