Different Mechanism and Classification of Automobile Engines #2
I started a series which I would love to continue here, the aim of the series is for those of us who are planning to get a mechanical machine that has an engine and don't know what we are going for and you would want to know what is up in the market and also make the right decision that suit your personality (funny enough a dealer with not go this dip explaining what is inside a car) in one word choose what would work for you. You can see the first part of this series here , in the article 2 Classifications of an engine were discussed which are the Classification by fuel and Classification by Combustion.
On this Post I will be doing justice to the the classification by ignition and the classification by engine strokes.
Introduction
Engines in mechanical machines works differently as I have said in the previous post and the difference here will be based ignition of the vehicle and the stroke of engines, first of all little explanation about ignition, ignition is the process of beginning the combustion of fuel (either diesel or petrol) and engines strokes is the stages or in mechanical terms strokes the engine takes to start (which can be either 2 or 4 strokes in different cases I would explain)

Classification by Ignition
Before I go into the Classification proper, lets see what the meaning of ignition is from Google dictionary.
the process of starting the combustion of fuel in the engine cylinders.source
Engine ignition can be in Spark ignition engines and Compression ignition engine, the Major difference about their two type of ignition Is that Spark ignition engine runs on Otto cycle while the Compression ignition runs on Diesel Cycle, it's not that big of a term Otto cycle is the petrol engine while the Diesel Cycle runs on Diesel engine.
Difference in Spark ignition and Compression ignition
Engine Speed: The Spark Ignition engines are high speed engines because the fuel is burnt homogeneously while the Compression ignition engines are low speed engines because the fuel burnt heterogeneously.
Type of Cycle: The Spark ignition engine works with Otto cycle while the Compression ignition engine works with diesel cycle.
Otto cycle is associated the petrol engine common is most if the automobiles today and it mode of fire uses the SPARK PLUG like the name Spark ignition
While
Diesel Cycle Is associated with the diesel engine, the diesel is ignited by the heat generated when the compression of air in the combustion chamber, into which the diesel is injected.
- Thermal Efficiency: Thermal efficiency of the spark ignition engine is Low due to the lower compression ratio of the combustion process while the Thermal efficiency of the Compression Ignition engine is high due to the higher compression ration of the combustion process
Other difference in Spark ignition and Compression ignition Below
Spark ignition
- Time of Knocking
Knocking happens at the end of combustion
- Type of fuel used
Petrol
- Constant Parameter in Cycle
Volume is constant
- Maintenance cost
Low cost
- Noise Production
Low noise
- Vibration problem
Low
- Cost of Engine
Low cost
- Fuel supply
Carburetor
- Application
light vehicles like motorcycle, cars for commercial use
Compression ignition
- Time of Knocking
Knocking happens at the beginning of combustion
- Type of fuel used
Diesel
- Constant Parameter in Cycle
Pressure is constant
- Maintenance cost
High cost
- Noise Production
High Noise
- Vibration problem
Very High
- Cost of Engine
High cost
- Fuel supply
injector
- Application
Heavy lifting vehicles like trucks and industry generators
Classification by engine stroke
Majorly engine strokes are in 4 strokes and 2 strokes, Engine stroke is the combustion stages for the engine to start, actual term is the strokes taken to start the engine and it is in four stages which are the intake, compression, firing and the exhaust. This stages happen in both the 2 stroke and 4 Stroke but for the 4 Stroke it all happen in 4 Stroke while for the 2 stroke engine it happens in 2 stroke.
A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.source
The 4 Stroke Engines are found in some cars, big generator, and some busses for commercial while the 2 stroke engines are found in the small engines like the little generators used in small apartments and then we can fine the 2 stroke engines in some motorcycles.
How the 2 Stroke engine works
The 2 stroke engine as written above takes 2 strokes to get the engine started. The intake, compression, power and exhaust stroke happen in 2stroke which is the downstroke and Upstroke.
(1) Downstroke:
The downstroke is the stroke where air and fuel mixture is sucked into the combustion chamber for combustion and it takes place when piston move from the top dead center to the bottom dead center along side with the crankshaft rotating 180o
(2)Upstroke:
The upstroke is where the remaining stages happens starting from the Piston moving back to the top dead center from the bottom dead center with the help of the flywheel momentum for the compression of the mixture(air and fuel) and at that same time the spark plug is fired for power known as the power stroke and when the mixture expands the piston moves down from the top dead center to the bottom dead center also the waste gas is been given off through the outlet valve. At the end of this stroke the piston must have made a rotation of 360o.
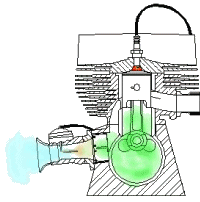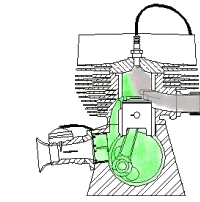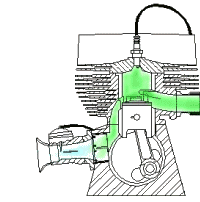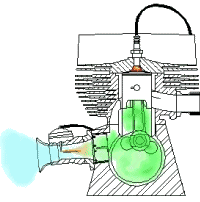
How the 4 Stroke engine works
As written above, it all happen in 4 strokes which are Intake or suction, Compression, power stroke and exhaust stroke.
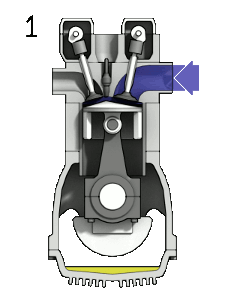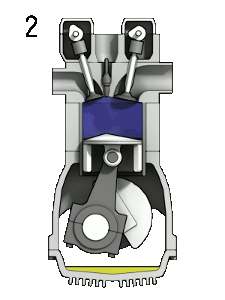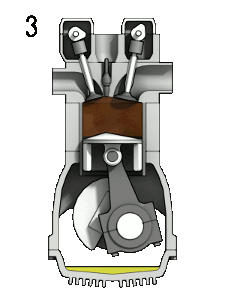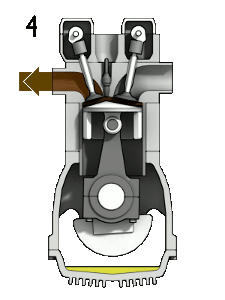
gif credit: Zephyris CC3.0 Licensed
(1) Suction Stroke:
The suction stroke is the stages where the air and fuel enters the combustion chamber. For this to happen there is an inlet value as well as the outlet valve. It's starts by the opening of the inlet valve with the 180o rotation of the crankshaft, the piston moves from TDC to BDC (Top dead center to Bottom dead center) and also the outlet valve stays closed for the fuel and air to enter into the combustion chamber.
(2) Compression stroke:
At this stroke the piston moves again from the bottom dead center to the top dead center with help of the momentum from the flywheel and the crankshaft completes a 360o rotation to compress the mixture (air and fuel) and for the compression to take place the inlet valve and outlet valve stays closed.
(3) Power stroke:
The stroke is the part where power is been generated, the inlet and outlet valve remains closed, the piston rotates another 180o that makes a total rotation is 540o. The expansion of the mixture (air and fuel) is ignited with the help if the spark plug to produce a spark that produces the mechanical work.
(4) Exhaust stroke:
The exhaust stroke is where the waste gotten from the combustion process is been pass out as waste gas. Here the outlet valve opens and the inlet valve closes with the help of the momentum from the flywheel in other to move the piston from bottom dead center to top dead center so as to move out the waste through the outlet valve which is the exhaust. For all that to happen the crankshaft makes another 180o rotation making a total of 720o.
Conclusion
Spark ignition engine and Compression ignition engines are aimed at producing mechanical work but works differently and obeys different principles, personally I would always pick the spark ignition for personal and commercial use unless I want to get a truck for heavy lifting then the compression ignition is much needed and also with the explanation above about the 2 and 4 Stroke Engines I want to believe most of us thinking most automobile engines have the same principles have a better understanding now because they all have the same outcome does not mean they have the same mechanism like all generators produce power but some of them have 2 stroke engine and some 4 Stroke engine.
References for more information
Comparison of Spark Ignition (SI) and Compression Ignition (CI) Engines
ignition
Differences Between SI Engine and CI Engine
spark ignition and Compression ignition difference
Different Types of Engine
How does 2 Stroke engine works
How does the 4 Stroke engine works
Internal combustion engine
Thanks for your time
@osariemen

Well done for your effort. However, I noticed something about the comparison of S.I and C.I engines, Time of knocking was a criterion. But since knocking is supposed to be a malfunction in engines, does the time if its occurrence qualify to be a criterion used in comparison?
Yea it matters
Depending on what u r using the engine for... Take for example you are using a grinding machine and the time of Knocking is at the end what would be d case what you are grinding.... I don't know if u get me
Or a generator to power an industry... During production it knocks.... There will be loss
I think you need to check the technical and correct meaning of Knocking in engines first.
Really???
I reserve my comment
Seems you're not getting the point. You may want to know that knocking happens in many engines while they are still functioning. In fact if some engine runs for 24 hrs, you can be sure that knocking has occurred not less than a thousand times, depending on the kind of fuel used.
I'm hoping you're not using the widely used albeit sadly wrong definition of Knocking as used by roadside mechanics in my locality (A Nigerian like me will understand). Please check.
Please let me understand the aim of this argument?
Are you saying me including knocking in engine is wrong? If yes then you are wrong knocking is a criteria to look out for talking about engines.... Explaining all that process is a long comment on its own
You don't seem to know the first thing about knocking, just a Google Search will help you out, just search it online and stop saying what you don't know.
Better still just tell me what you think knocking is, because I don't see what is long about the explanation of knocking unless you've invented another process and named it knocking.
And to be clear, this isn't an argument, I'm asking you to define a term you used in your write-up as I can see that it might have been wrongly used, yet you keep finding one reason or the other to avoid answering, of course for obvious reasons.
Your choice of words makes me sick.... And you are talking like an island of knowledge
What is your aim.... Lemme know what you want me to know
I said time of Knocking is a difference in SI and CI Engine... Do you think others wise...
Probably you need to see Materials about the difference on both engines here...... This is what I heard several times when doing IC engine when I was in school
I didn't disagree with you, I simply asked for clarification to know that we're talking about the same knocking.
Maybe when you read this, especially under "Normal" and " Abnormal" combustion, you'll understand the reason for my first question.
@osariemen Fantastic post i must say.... I learnt a whole lot!
I look forward to reading more posts from you..
Thanks for the kind words man
Congratulations @osariemen! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
To support your work, I also upvoted your post!
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP