Nonlinear Fiber Optics – 1. Introduction-1
Hello everyone. After the Steemit warm-up tours, I will try to help you in the field where I am an expert. You can ask and write as many questions as you want. I believe that it will be a very nice experience for me also, in terms areas that I am missing.
As the title suggests, I will try to give you information about nonlinear fiber optics. I have been working on fiber optic systems for about 10 years as a researcher at a university. When it comes to place, it will be heavy math operations, but I will try to simplify it as much as possible. So let's get started.
1.1 Laser
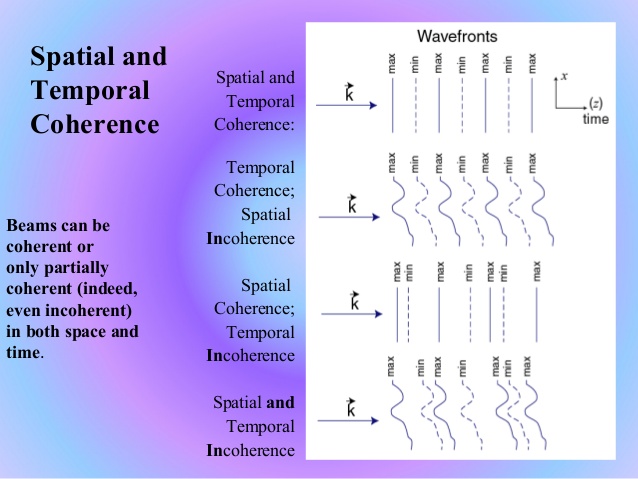
The laser (LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) is a means by which the light is optically amplified depending on the excited emission. The most important difference of laser sources from other light sources is that they are both spatially and temporally in-phase (coherence). Stimulated emission is the key parameter for the coherence. Coherence of light wave is the correlation between the electric field intensities at different locations and times wikipedia. This coherence phenomena makes laser light goes to far away without distortion.
Actually, you know the laser from bars and discos...

giphy
Spatial coherence helps to travel long distances without dispersing light in laser sources. Temporal coherence is effective when the light has a narrow wavelength width. As you see the coherence figure, in time domain temporal coherence is important. For example daily light has a huge spectrum bandwidth so its coherence is so low then we call it incoherehent. But when you start to decrease the spectrum bandwidth of the source then you started get a coherent beam. Besides spatial coherence is about space.
http://keywordsuggest.org/gallery/1292029.html
1.2 Laser Gain
A general laser system has three main components. The first is the environment of the gain, another pump (which may be electrical or light), and finally the cavity. The cavity is designed to be a mirror on both sides. The mirror on the exit side has semi-transparent property to obtain an optical output.
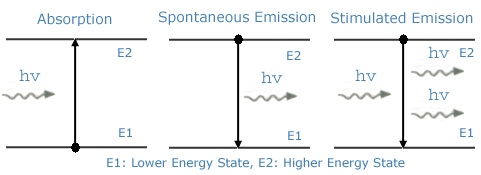
The above components are not enough to form the laser. The gain in the laser cavity also needs to be more than loss. This is called the “threshold value”. In order to exceed this threshold, the light must be examined for interaction with the atoms in the system. In 1916, Einstein revealed three possible interactions. These are “absorption, spontaneous emission and stimulated emission".
http://www.equestionanswers.com/notes/laser.php
If the atom is at the lower energy level, photon absorption can occur. If the atom is at a higher energy level, a stimulated emission can occur which means that a new photon can be formed with the same characteristics as the incoming photon. In the case of spontaneous-emission, the atom in the upper level as energy emits a photon independently of itself.
Upto now, we learnt,
1- what the laser is,
2- what the main condition is to create a laser,
3- What the interactions are needed (Einstein's interaction).
For today this is enough because the second part will contain lots of mathematical equations. I do not want to tighten you so much. From now on, we will continue with levels of the laser systems (2-level, 3 level, 4 level). Then we will talk about types of laser such as solid state, chemical, fiber laser etc.
I hope, this is helpful. I am waiting your comments and questions.
Thanks very much for such an informative post. Looking forward to read the upcoming parts ;)