STROKES: The Principle behind every Engine.
Five years of study; excluding the strikes (Internal and External) that every Nigeria University experiences, I got to know a whole lot of things about the Engineering world and the principles that it revolves on.
Mechanical Engineering as my Major, I learn more about Engines. Most (if not all around us) works on the same principles or closely related principles. It may be the Internal or External Combustion engine.
These Engines may work on either Four (4) Stroke or Two (2) strokes principles.
1. The Four Strokes
The four stroke Cycle was invented by a scientist called Nicolaus August Otto, a German. He was born 14th June, 1932. In 1964 he opened his first engine Company.
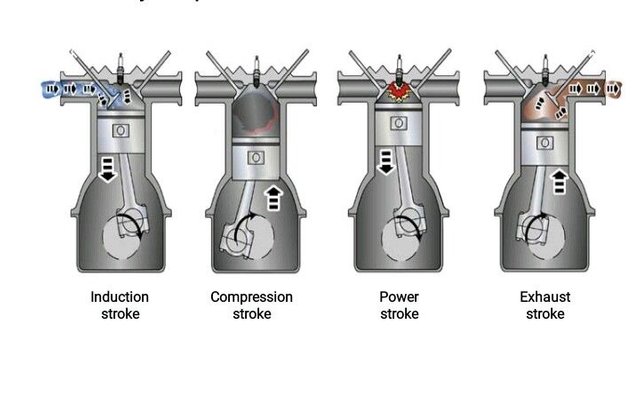
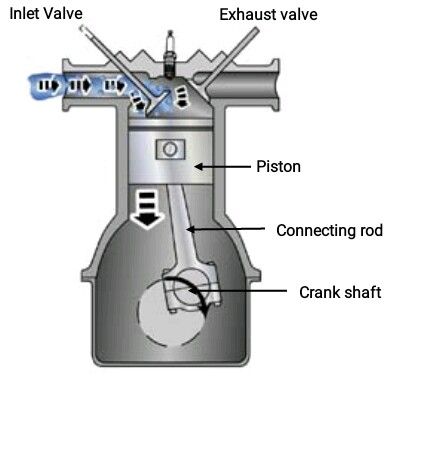
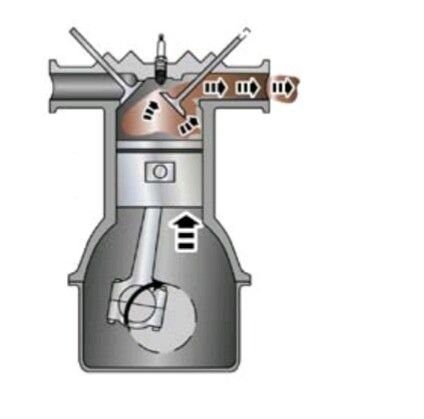
It's called 4 Strokes because it completes it's cycle in four stroke of the piston or Two (2) revolution of the Crank Shaft; the Intake (induction), Compression, Power and Exhaust stroke.
Intake stroke (induction):
This is the first stroke in combustion. In this stroke, the intake value opens as the Piston moves down the cylinder, this down movement allow for suction of air and fuel into the cyclinder.
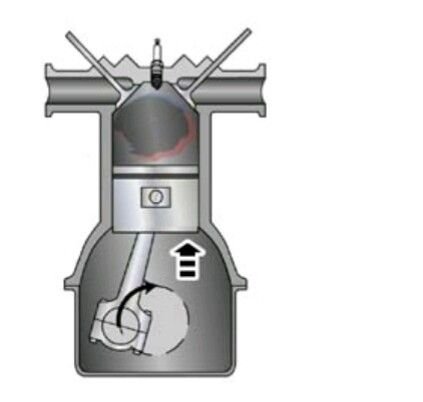
Compression stroke
In this stroke, the Piston moves from the bottom to the top of the cylinder with both valves (intake and exhaust) completely closed. At the air is compressed, it increases the temperature in the cylinder.
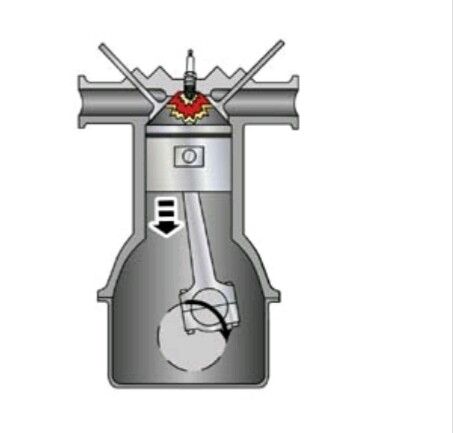
Power Stroke
When temperature is increased due to Compression, a spark is initiated by the spark plugs ( for S.I. Engine) which causes combustion and expansion that forces the Piston to move for Top to bottom of the cylinder. This is the Power stroke.
Exhaust Stroke
This is the final stroke in the cycle. At this stroke, the piston moves from the bottom to the Top of the cylinder, with the exhaust valve open. This forces the combusted air through the open exhaust valve.
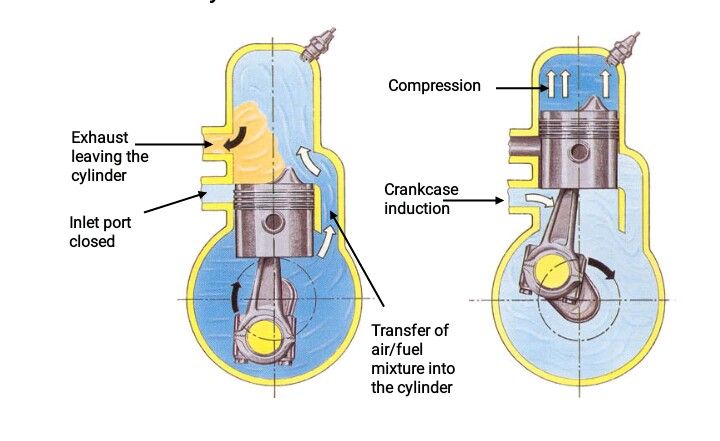
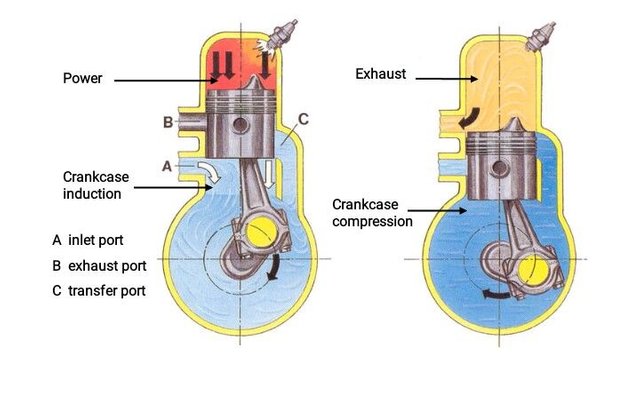
2. The Two Strokes
The two stroke engine was developed by Dugald Clerk; a scotman and modified by Joseph Day. The two stroke engine is not quite different from the four stroke.
It has fewer moving parts.
It has no Valve or Camshaft.
Lubrication unlike the 4 stroke engine is achieved by mixing the oil with the petrol.
The complete cycle of operation is carried out in only two strokes of the piston or 1 complete revolution of the crank shaft.
It's Efficiency is lower compared with the Four Stroke engine.
The four cycle; intake, compression, power and exhaust is completed in one Revolution.
For the 2stroke engine, the angle of rotation of the Cranks shaft for each cycle is less than or equal to 90°; unlike the 4 stroke engines which is greater than or equal to 180°.

Engineer!