[Great science] Do you know that wernher von braun was the creator of the space missiles and that some of them were used in the Second World War? -Explore his scientific work
Von Braun is a very controversial character, who dedicated his life to the development of rockets for the conquest of space, although he had to offer them as weapons for his development, which he hesitated to do.
He is considered to be one of the most important rocket designers of the 20th century, and was the chief designer of the V-2 rocket, as well as the Saturn V rocket, which brought man to the Moon.

From a very young age he developed his passion for astronomy. On the other hand, the feats achieved by Max Valier and Oitz Fritz in the dangerous field of motorcycle racing propelled by rockets, inspired by a set of toys, several steps and fireworks in a toy cart, which came out with a smile of Street explosion that hit the bones of the 12-year-old in the police station.
In his quest to develop large rockets, he enlisted in the German army to develop ballistic missiles before the arrival of Adolf Hitler to power in 1933, and was later ascribed to the SS in 1940. As his right-hand man (Ernst Stuhlinger) already said. In an interview, Von Braun found it hard to accept the offer to enroll in the SS. While doing his work for the army, Von Braun obtained a Ph.D. in aerospace engineering on July 27, 1934.
The First Test Rocket A-2
The A2 is a German test rocket, built in 1934, in whose design Wernher von Braun participated. It was the first test flight of a whole family of rockets whose development would lead to the creation of V2, the first ballistic missile in the world. They built two A2, which they called Max and Moritz. Both worked well in the tests.
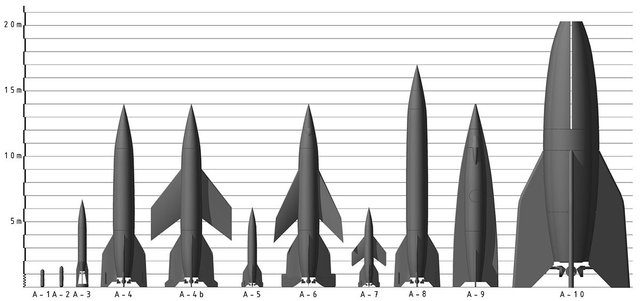

The propellant was formed by 35 kg of liquid oxygen and 75% of alcohol, injected under pressure in the combustion chamber and consumed in 16 seconds. The pressure at the time of launch reached 18 bar at takeoff (producing a thrust of 320 kiloponds), going down to 14 bar during combustion (and lowering the thrust correspondingly to 240 kiloponds). The pressure inside the combustion chamber was 9.2 bar. The flywheel used to stabilize the rocket was moved to the area between the propellant tanks instead of putting it in the nose, as in the A1.
Characteristics
-Push: 3.0 kN
-Mass: 107 kg
-Diameter: 0.31 m
-Length: 1.61 m
-Maximum altitude: 3.50 km
Second world war: the rockets V2
With the beginning of World War II, the German high command commissioned him to design a rocket loaded with explosives in order to attack enemy territory.
The first time a V2 missile was used for military purposes was in September 1944 from day 8, German forces launched V2 against the cities of the Allies, especially Antwerp (Belgium) and London (England). The main advantage of the V2 was that they hit without warning signals (when flying at supersonic speed, they reached their target before hearing the noise of their approach), so there was no effective defense mechanism. As a result of this, the V2 were a factor of terror beyond their actual destruction capabilities, since the guidance system of these missiles was imperfect and, therefore, many failed to reach their goal.
The V2 rocket was a ballistic missile developed at the beginning of the Second World War in Germany, specifically used against Belgium and places in the south east of England. This rocket was the first long-range combat ballistic missile in the world and the first known human artifact to make a suborbital flight, it was the progenitor of all modern rockets, 6 including those used by US space programs. of the Soviet Union, who had access to German scientists and designs through Operation Paperclip and Operation Osoaviakhim respectively.

The German Wehrmacht launched around 3000 V2 military rockets against Allied targets during the war, mainly London and later Antwerp, resulting in the death of an estimated 7250 people, both civilian and military. The weapon was presented by the Nazi propaganda as a revenge for the bombings on the German cities from 1942 until the end of the war.

Wernher von Braun, the German who brought the US to space
One of the bases on which space exploration is based is the use of rockets that are launched to transport people and material to the International Space Station or to any other mission. Since the Chinese alchemists discovered the gunpowder and used the first (and inaccurate rockets), passing through Jules Verne in From Earth to the Moon, the Second World War or the Space Race, the rockets and the desire for their mastery and perfection always has been present. In the development of these devices we find names of famous scientists, however, there is a very special one that went from designing rockets for Nazi Germany (the fearsome V2) to working on Saturn V for NASA.

In 1950, Von Braun and his collaborators worked on the development of the Jupiter ballistic missile and Redstone rockets used by NASA for the first releases of the Mercury program. In 1960, the rocket center was transferred to NASA where Von Braun became the director of the Marshall Space Flight Center of NASA and responsible for the design of the Saturn V rocket that during the years of 1969 and 1972 carried out the Moon.
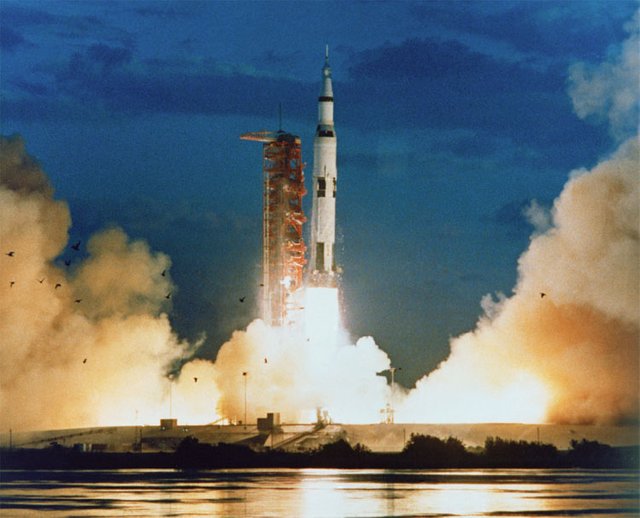
Saturn V
It was a disposable multi-phase and liquid fuel rocket used in NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs. Its design was a burden of Wernher von Braun in the Marshall Space Flight Center and its main builders were Boeing, North American Aviation, Douglas Aircraft Company and IBM. It was the largest of the Saturn rockets family.

In its flights, the Saturn V passed through three phases: S-IC, the first phase, S-II, the second, and S-IVB as the last phase. In all three, liquid oxygen (LOX) was used as an oxidant. In the first phase, RP-1 (refined petroleum) was used as fuel, while the other two phases used liquid hydrogen (LH2). In a mission, on average, the rocket worked for about 20 minutes.
NASA launched thirteen Saturn V rockets between 1967 and 1973 without loss of payload, although Apollo 6 and Apollo 13 had engine problems. The main charge for these rockets were the Apollo ships that took the NASA astronauts to the Moon.
It was used to launch the Skylab space station, but the project to use it as a launch vehicle for probes to Mars was canceled.


Comment and vote if you like this post, Greetings!
For more information, you can visit the following links.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saturno_V
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wernher_von_Braun
https://hipertextual.com/2011/09/wernher-von-braun-alemania-nasa
http://www.cienciahistorica.com/2015/01/13/rocket-man-la-compleja-historia-de-wernher-von-braun/