Deoxyribonucleic Acid
That friends today I will talk a bit about DNA or as few know it as Deoxyribonucleic Acid is a large molecule located in all living cells, which has the genetic data of a living being and certain viruses, considered an accumulation of genes long-term. This keeps for many years and at the same time transmits this data from generation to generation, allowing the development of the functions of the organism, using these data -each gene- for the production of proteins. DNA is a long polymer formed by repetitive units, the nucleotides. A double strand of DNA measures from 22 to 26 angstroms (2.2 to 2.6 nanometers) wide, and one unit (one nucleotide) is 3.3 Å (0.33 nm) long. Although each individual unit that repeats is very small, the DNA polymers can be massive molecules that contain millions of nucleotides. For example, the longest human chromosome, chromosome number 1, is approximately 220 million base pairs.
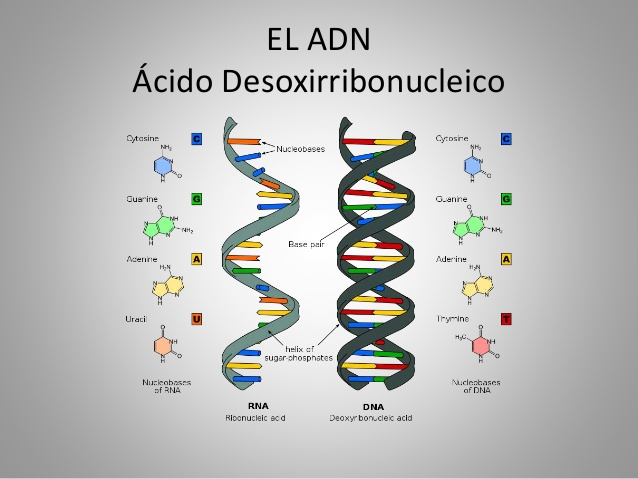
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is made up of alternating units of phosphate and sugar groups. The sugar in DNA is a pentose, specifically, deoxyribose.
Phosphoric acid:
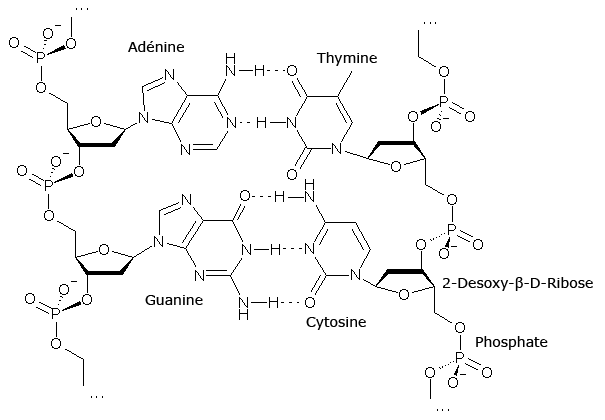
Phosphodiester bond. The phosphate group (PO43-) joins the carbon5 'of the sugar of a nucleoside with the carbon 3' Its chemical formula is H3PO4. Each nucleotide can contain one (monophosphate: AMP), two (diphosphate: ADP) or three (triphosphate: ATP) phosphoric acid groups.Deoxyribose:
It is a monosaccharide of 5 carbon atoms (unpent) derived from ribose, which is part of the nucleotide structure of DNA. Its formula is C5H10O4. One of the main differences between DNA and RNA is sugar because in RNA the 2-deoxyribose in DNA is replaced by a pesto alternative, ribose.
The sugar molecules are bound together through phosphate groups, which form phosphodiester bonds between the third carbon atoms (3 ',' three cousins ') and fifth (5', 'five cousins') of two adjacent sugar rings. The formation of asymmetric links implies that each strand of DNA has a direction. In a double helix, the direction of the nucleotides in one strand (3 '→ 5') is opposite to the direction in the other strand (5 '→ 3'). This organization of the DNA strands is called antiparallel; they are parallel chains, but with opposite directions.
Nitrogenous bases:
The four major nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). Each of these four bases is linked to the sugar-phosphate framework through the sugar to form the complete nucleotide (base-sugar-phosphate).Thymine:
In the genetic code is represented by the letter T. It is a pyrimidine derivative with an oxo group in positions 2 and 4 and a methyl group in position 5. It forms the nucleoside thymidine (always deoxythymidine, since it only appears in the DNA) and the nucleotide thymidine monophosphate (dTMP). In DNA, thymine is always paired with the adenine of the complementary chain by means of 2 hydrogen bonds, T = A. Its chemical formula is C5H6N2O2 and its nomenclature 2,4-dioxo, 5-methylpyridine.Cytosine:
In the genetic code, it is represented by the letter C. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with an amino group in position 4 and an oxo group in position 2. It forms the nucleoside cytidine (deoxycytidine in DNA) and the cytidylate or (deoxy) cytidine monophosphate ( dCMP in the DNA, CMP in the RNA). The cytosine is always paired in the DNA with the guanine of the complementary chain by a triple bond, C≡G. Its chemical formula is C4H5N3O and its nomenclature 2-oxo, 4 aminopyrimidine. Its molecular mass is 111.10 units of atomic mass.
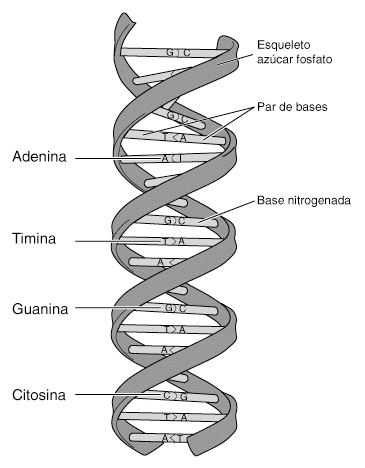
According to its structure, we can find several types of DNA
_
- Chromosomal DNA
It is the one that stores the genetic information of the cell to which it belongs, it is located specifically where the cell is, for example, in prokaryotic cells, it is located in the cytoplasm, and in eukaryotic cells in the cell nucleus. This DNA is represented as a double chain of complementary bases where each chain has a nucleotide. The genome of people has 23 DNA molecules, which have a length ranging between 50 and 250 million bases.
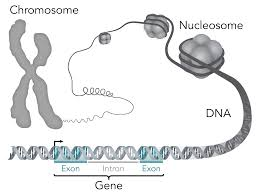
- Recombinant or Recombinant DNA
This DNA refers to the set of techniques used to manipulate DNA molecules, in order to produce them artificially and linked in vitro. The chains that make up the DNA come from two different types of organisms. By adding a new chain to an organism some traits are modified and new traits are created. These combined DNA are very used when creating vaccines, infertility treatments, it is clone experiments.
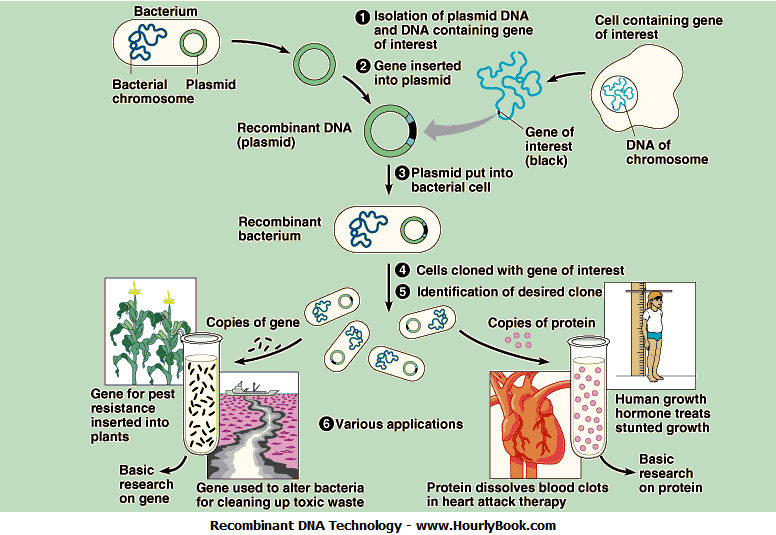
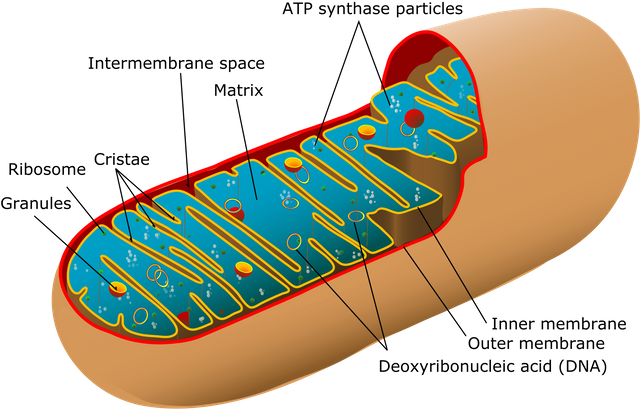
- Mitochondrial DNA
It is the DNA found in cell organelles mitochondria - which provide energy to the cell. DNA is able to reproduce semiautomatically when the eukaryotic cell is divided. This type of DNA passes from the mother to her descendant, only intervening the mitochondria that are contained in the ovum that is released at the moment of the sperm fertilize it.
For more information visit:
- https://www.zmescience.com/other/science-abc/about-mitochondrial-dna-42423/
- http://www.askdrray.com/frail-mitochondrial-dna-equals-frail-people/
- http://weloveteaching.com/0bio105/lectures/genetics/recombinantDNA.html
- https://www.hourlybook.com/introduction-recombinant-dna-suitable-host/
I invite you to comment on this topic, I await your comments
Resteemed your article. This article was resteemed because you are part of the New Steemians project. You can learn more about it here: https://steemit.com/introduceyourself/@gaman/new-steemians-project-launch