Separation techniques: Chromatography
Separation techniques: Chromatography
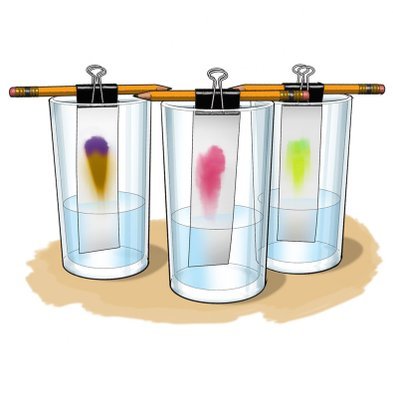
Source
In the study of chemistry and its components is very important the collection of samples as well as their study, since this will allow us to know each and every one of the atoms, materials and various elements of which they are formed.
This is where the chromatography enters the scene, which is a technique used for the separation analysis of mixtures of volatile substances. It also allows a general quantitative analysis of multicomponent mixtures of volatile organic compounds. It should be noted that through chromatography materials are separated for examination by other techniques.
Chromatography, as indicated by its name (comes from the Greek χρῶμα chrōma and γράφω gráphō, meaning respectively "color" and "write, record", literally "color writing", or better "color registration"), was originally used with colored substances. <
Source
Chromatography can fulfill two basic functions that are not mutually exclusive:
- Separate the components of the mixture, to obtain them purer and that can be used later (final stage of many syntheses).
- Measure the proportion of the components of the mixture (analytical purpose). In this case, the quantities of material used are usually very small.
Phases of Chromatography
Chromatographies are done in two phases. One static and another mobile.
Static or stationary phase
The mixture is placed on a fixed support, for example, paper. It is the substance that is fixed in a position in the chromatography procedure. The stationary phase can be an absorbent solid or, more commonly, a film of a low volatile liquid, supported on an inert solid or on the tube wall itself
Mobile phase
In this phase, another substance is moved over the mixture that is already on the support of the static phase, for example, a liquid that moves through the paper with the mixture. In the mobile phase, the process of separation of the components of the mixture will begin when the different components of the mixture move on paper at different speeds through the liquid.
Chromatographic system
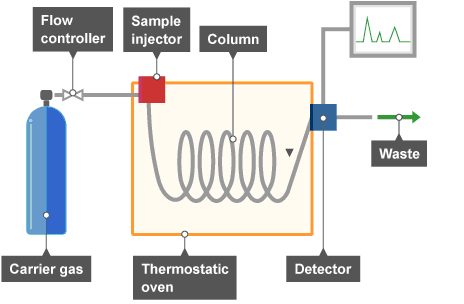
Source
Carrier gas
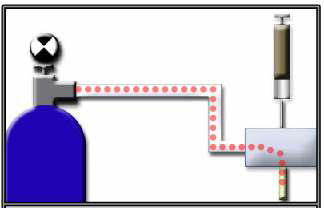
The carrier gas fulfills two main functions
- Transport the sample components
- Create a suitable matrix for the detector
Sample entry system
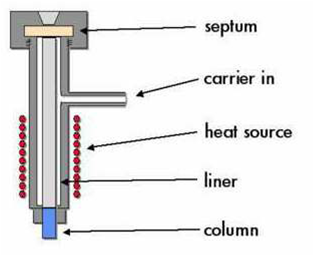
- Injection port, its function is Evaporate the sample and enter it in the column. The injection is done through the Septum,
- The septum, must be stable. It is also responsible for maintaining the seal of the port
- Liner, Provides a volume and an inert surface for the evaporation of the sample. Generally made of glass even when there are metallic ones. They must be replaced or cleaned regularly because over time they present deposits of non-volatile material and degradation products. There are liners specifically designed for each type of injection.
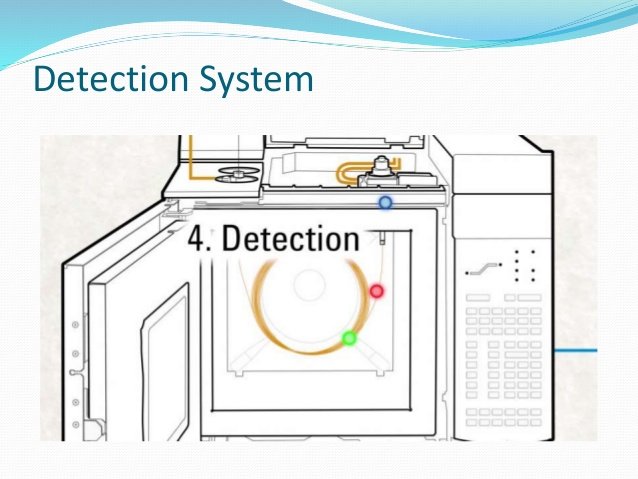
Detection system
Source
For our chromatographic system to be useful, you need a way to measure the components that elute from the column, a detector. Any method that directly or indirectly produces a signal at the output of the components serves as a detector
The fundamental function of the detector is to produce a stable signal when it passes only drag gas (baseline) and produce a different signal when a component of the Sample.
Classification of separation methods in chromatography
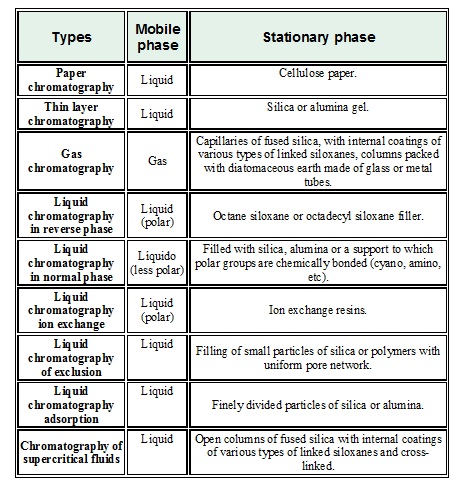
The different chromatographic techniques can be divided according to how the stationary phase is arranged:
Flat chromatography: The stationary phase is placed on a flat plate or on a paper. The main techniques are: Paper chromatography & Thin layer chromatography.
Column chromatography: The stationary phase is located within a column. According to the fluid used as a mobile phase, the following are distinguished: Liquid chromatography, Gas chromatography & Chromatography of supercritical fluids
Gas chromatography is applied to numerous organic compounds. In the case of non-volatile compounds, processes called "derivatization" are used, in order to convert them into other compounds that volatilize under the conditions of analysis.
Within liquid chromatography, highlights high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), which is the most widely used chromatographic technique currently, usually in its reverse phase mode, in which the stationary phase has non polar character, and the mobile phase has a polar character (usually water or mixtures with a high proportion of it or other polar solvents, such as methanol, for example). The name "reverse" is given because traditionally the stationary phase was composed of silica or alumina, of polar character, and therefore the mobile phase was a non-polar organic solvent. An eluotrópica series is a range of substances of different polarities that act like mobile phase and that allow observing a better displacement on a stationary phase.
For more information visit the following links.
- https://www.tplaboratorioquimico.com/laboratorio-quimico/procedimientos-basicos-de-laboratorio/que-es-la-cromatografia.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatography
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5206469/
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/triple_ocr_21c/further_chemistry/chromatography/revision/6/
- https://es.slideshare.net/ferccmx1/cromatografia-definiciones-y-tipos
- http://slideplayer.es/slide/4045049/

Great post, the Chromatography is wonderfull and very interesting
thanks
Wow excelente post, I really learn a lot
I'm glad for you
awesome, I really didn't know about this
Great I'm glad you discover this
wow, is great your post, a recommendation for you to learn to justify the text I'll leave a link link. With this link you will learn how to place the text centered, sideways or justified; among other tips that you can learn. I gave you an upvote. Congratulations
Please that be very helpful