Disproving the concept of absolute universal donors and universal recipients in blood transfusion and haematological procedures.
The presence of certain sugar residues on the surface of the red blood cells of an individual accounts for certain characters exhibited by such individuals' blood which distinguish them from others, peculiar features can also be seen in others and this forms the basis of blood grouping, blood groups are hereditary and obeys the Mendelian inheritance theories.
Even if you couldn’t pick anything from today’s class, just remember that group O are universal donors and group AB are universal recipients, other aspects of this class will be made clearer to you as we progress in this topic, have a nice day!... Lol Part of this article was culled from my previous work as it perfectly contains the intended information.
I could recall these lines from our everyday advanced hematology classes as the lecturers attempts to clear out misunderstandings of the blood group concept and also enhance our knowledge on what actually goes of intracellular which manifests extracellular as a difference in reactive capabilities and characteristics of our blood.
credit: <a href=https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1358702 rel=”noopener” title=”This link will take you away from steemit.com”>pxhere. CC0 creative commons license.
One’s genotype is a very important aspect of his/her life as this not only explains his origin but is also important in pathology as individuals with a certain genotype for a given character are more prone to some diseases or infection than others. Mutation of these genes due to biochemical changes accounts for many pathological and non-pathological deviation of the offspring’s genotype and phenotype from the parents’.
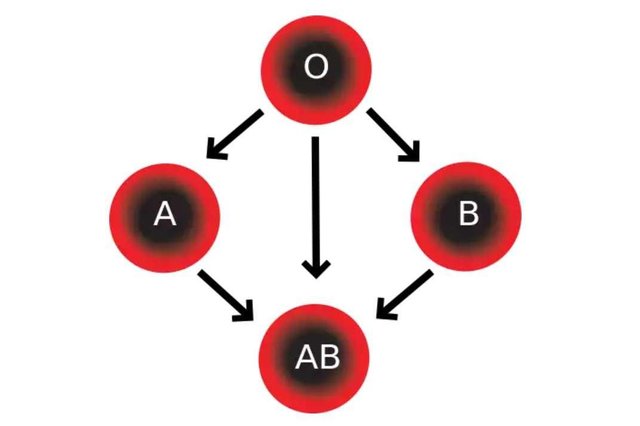
The blood group compatibility sketch. Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license.
Blood groups presents a deviation from the traditional orientation that the inheritance pattern of a particular character is dependent upon a pair of allelic genes at a specific locus. The locus of a gene is its location. Blood group inheritance is controlled by three popular alleles, A, B, O located on chromosome nine(9) and two less popular in alleles H and h located on chromosome nineteen (19). The A, B and H genes are dominant and are expressed in heterozygous conditions, while the O and h genes are recessive and are expressed only in homozygous condition. Individual with blood groups A or B shows characters of blood group A and B, but their genotype consists of blood group AO and BO.
How the Erythrocytes developed antigens
The blood groups develops biochemically, this is largely controlled by genes which determines the direction of the synthesis; the products of this process and also the differentiation into several products; genes also determines how this specialized products influences the body, the impairment of these genes accounts for most of the defects seen in synthesis procedures and products in the body, these defects may be fatal or relatively manageable to an extent by natural or medical enhancements and adjustments.
As already stated, the genes located at chromosome nine (9) controls the ABO blood group system while the H and h gene are located at chromosome nineteen (19); the A, B and H genes encodes transferase enzymes, the O and h genes do not encode the transferase enzymes and are recessive and thus not expressed in heterozygous inheritance, but are expressed in in homozygous inheritance. The H and h genes controls the production of H antigen.
The formation of these antigens occurs at the membrane of red blood cells. The Red blood cells membrane consists of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates, these lipids maintain the fluidity and are attached to proteins to form lipoproteins, the proteins maintain flexibility. Red blood cells membranes are structured to be able to squeeze through tiny vessels without being ruptured and this stresses the importance of the fluidity and flexibility provided by the lipids and proteins respectively.
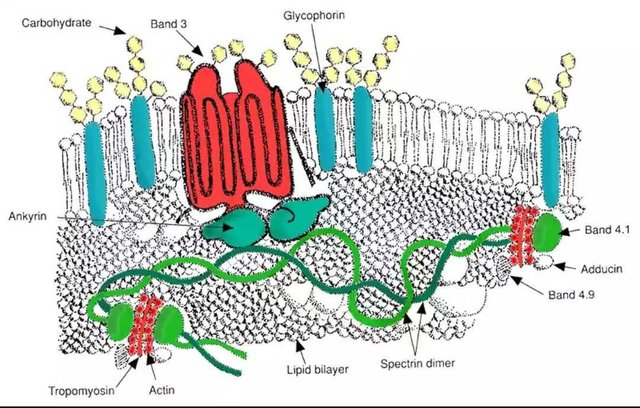
structure of Red blood cells membrane. Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author:
The red blood cell membrane contains proteins, namely ankyrin, actin and band 4.1, the red blood cells membrane also contains another protein known as precursor substance. A specific fucosyltransferase which is a product if the H gene converts the precursor substance to H substance. The formation of specific antigens follows the addition of certain sugar units to the H substance. The A gene encodes enzymes which catalyze the addition of N-acetylgalactosamine to the terminal galactose of the H substance and this leads to the formation of antigen A and subsequently antibody B which consists the blood group A; the B gene encodes enzyme which catalyze the addition of galactose to the terminal galactose of the H substance, this follows a similar route as the blood group A formation via the formation of antigen B and subsequently antibody A which consists the blood group B.

The presence or absence of certain sugar residues confers certain features to erythrocytes which distinguish them into groups. Credit: <a href="https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_type>wikimedia" CC3.0 license. Author:
In contrast, the O gene lacks the ability to encode the transferase and as a result do not add any sugar unit to the terminal galactose of the H substance, thus no H antigen is produced and there is a resultant synthesis of the A and B antibodies which defines the blood group O. In the AB blood group; these two antigens are produced due to the co-dominance of the two genes (A and B) and as a result, the body produces no antibody, this is to prevent probable auto immunity. This H substance/antigen is never completely converted however as they can be detected in the blood groups A, B and O.
These antigens displayed by the blood cells controls the development of antibodies related to them as the immune system develops complementary antibodies to prevents fatal immune reactions in intercellular interactions; blood group A showed antigen A while blood group B showed antigen B, blood group O showed no antigens and hence the ‘O’. These antigens would react with a similar antibody, thus the body develops complementary antibodies to these antigens, an individual with blood group A; has antibody B and vice versa; however, there are important deviation in blood group AB and O as individuals of blood group AB posses both A and B antigens, the body thus develops no antibody. Individuals of blood group O in contrast develops both antibodies A and B as they posses no antigen. The absence of blood group antibodies in group AB individuals and the absence of antigens in form of sugar residues on the cell membrane of the red blood cells of group Of individuals attracts a popular title for these blood groups as the AB individuals are dubbed Universal recipients and the Other individuals are dubbed Universal donors.
Hence during blood transfusion, patients of group AB are eligible to be transfused with blood from any of the blood groups while the Other individuals can donate to patients of any blood group provided their Rhesus antigens are also compatible. This concept have heralded the spheres of preliminary hematology lessons and I could remember my high school teacher saying
Unarguably this concept isn’t so flawed, the blood groups AB and O are the most flexible blood groups having much bigger applications than other blood groups, though there still remains some aspects of disparity, the universal recipients AB can only donate to fellow group AB individuals even though they can be transfused with blood from any other blood group, but the presence of antigens A and B would cause reactions if they are transfused to any other blood groups apart from themselves, group O blood also exhibits similar trait as they only accept blood donation from corresponding O individuals with compatible rhesus antigens.
But wait! Our ship just hit a rock!
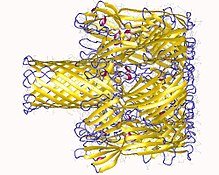
its not a rock! It's just an alpha haemolysin. Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author:
Yes, the concept of universal donors is presently a relative term which only entails that all things being equal the group O blood has the widest range of application in blood donation and blood group AB has the widest range of acceptance in blood transfusion.
Unfortunately, the incidence of haemolysins changed the course of this concepts and ushered in secondary and confirmatory tests before any blood from the ‘universal donors’ can be transfused to anyone including the ‘universal recipients’, this the concept of Dangerous universal donors, haemolysins are proteins and lipids which damaged red blood cell membrane leading to the Lydia of the blood cells and a resultant death of the affected cells, presence of haemolysins causes a chain of blood destruction, an untimely detection and halt of such reactions progresses to fatal destruction of red blood cells and secondary conditions such as intravascular clumping, thrombosis and thromboembolism which occurs rapidly and can lead to the death of the patient within an hour of transfusion with such blood.

microbes such as staphylococcus aureus produces haemolysins and these causes lysis of red blood cells. Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author:
Haemolysins are produced by microbes such as staphylococcus aureus and exists on different structures which also enables their actions and also defines the type of blood cells they attack, this property is also employed in microbiological diagnosis as the haemolytic ability of staphylococcus enables their growth in blood agar and the chocolate agar which is also a modification of the blood agar by heating at 70oc, the staphylococcus with the aid of the haemolysins breaks down red blood cell membrane and obtains nutrients for its growth, these activities also takes blood place in vivo as haemolysins are also produced by these microbes inside the body, presence of the haemolysins in blood group O makes them dangerous for transfusion to any other blood group, however they are still fit to be transfused to fellow group O individuals with matching rhesus antigens.
As already stated, differences arises as regards the structure and mode action of these haemolysins, α-haemolysins usually secreted by staphylococcus aureus forms a homo-heptameric β-barrel in biological membranes and causes complete Lysis of blood cell m by binding with the membrane of the blood cells and forming and oligomeric structures with the water filled channels of the blood membrane and it’s monomer, this result in a disruption of the osmotic system of the blood cells, loss of vital organelles and depolarization of the red blood cell’s membrane and hence the cell dies off, the α-haemolysins attacks the A antigens of the blood cells and hence blood group O with α-haemolysins is unfit for individuals of blood group A or AB.
Β-haemolysins causes hydrolysis of sphingomyelin, phospholipids which accounts for about 45% of the red blood cell membrane, there’s also a release of organic phosphorus from the hydrolysed sphingomyelin, this causes a rise in phosphorylcholine a constituent of platelet activation factors, and also a damage associated molecule which makes the blood cells recognizable by the immune system, and may also lead to the activation of platelets and hence intravascular clumping and immune reactions ensues, the β-haemolysins reacts against the β-antigens of the blood cells and causes incomplete lysis of the blood cell membrane, and present fatal complications and hence universal donors with these sort of haemolysins are not fit to donate blood for transfusion into patients of blood group B or A.

Adverse transfusion reactions results on transfusion of blood with incompatible haemolysins . Credit: wikimedia CC3.0 license. Author:
Pore formation and enzymatic clipping of cell membrane phospholipids are the chief mechanism of haemolysins and this menace has been curbed greatly through cross matching techniques and enhanced immunological diagnosis to ensure that the effect of slow reacting and clandestine effects of antigens are detected and either controlled or prevented before the transfusion commences. No blood group is an absolute universal donor of recipient as the haemolysins when present makes them unfit for transfusion into corresponding blood groups.
References
Haemolysins~wikipedia
Haemolysins~UPEI university
Haemolysin test for characterization of immune ABO antibodies
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! We encourage and support quality contents and projects from the West African region.
Do you have a suggestion, concern or want to appear as a guest author on WAfrica, join our discord server and discuss with a member of our curation team.
Don't forget to join us every Sunday by 20:30GMT for our Sunday WAFRO party on our discord channel. Thank you.
Great post! I was just asking about this topic last week.
Wow, I hope it's answers every question you have regarding this topic, thanks for coming around
This is an enjoyable read as well as being educative. Human blood group and genotype is an aspect that always interests me. I have to bookmark this and re-read later.
Glad to hear this!, thanks for coming around
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail in collaboration with @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing then consider voting both projects for witness by selecting stem.witness and curie!
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!