ETHERNET: THE INTERNET AMONG US
I know you might be wondering, what is Ethernet or how does it affect me. Well ethernet is virtually everywhere. If you have made call using an internet protocol phone (IP phone), then you probably have used ethernet technology. If you have gone to cyber cafe to browse either with your personal computer or with shared computer, then you have used ethernet. If you have ever set up hotspot either with your phone or professionally with an access point, then you have used ethernet technology.

credit: acumera
The main purpose of Ethernet is for sharing resources, network resources. Ethernet is a network standard described under the IEEE 802.3 standard working group. It describes how network equipment can present data for transmission to other network devices. It was developed by Xerox in the year 1973 and had since been the most widely used Local Area Networking (LAN) technology the world has ever know.
Initially, ethernet was designed to run only on coaxial cables (those cables used for television connections in the home) but later grew in popularity and was extended to Fiber optical cables, Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) and twisted cable pairs (both shielded and unshielded pairs).
Topologies found under ethernet
As stated earlier, ethernet is a shared media for information interchange. It states how devices can connect and share data within a network. The Topology defines "how" these devices can be connected to make use of ethernet technology. If you are reading this post right now, you are connected to the internet using one or a combination of the topology I will discus below.
The Bus topology
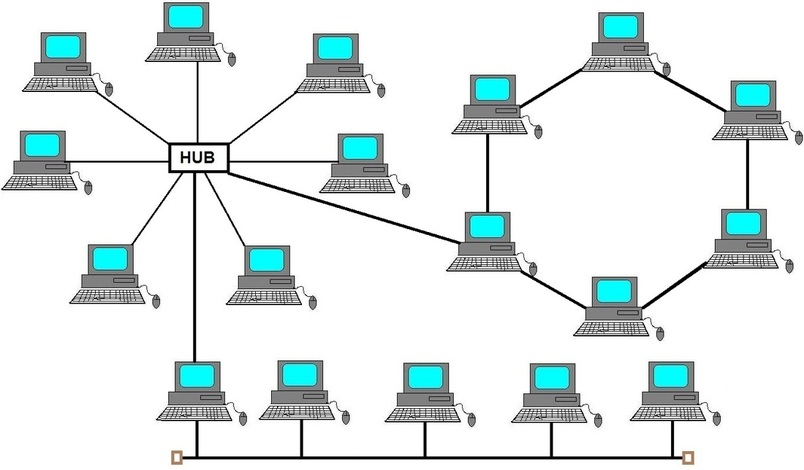
The bus topology was very popular during the time ethernet hubs were predominantly used in the networking field. You can view an ethernet hub as an electrical extension. Yes you heard me right, an extension.It performs no other work on the network other than to replicate the same connection through as many ports available on the hub, just like electrical extension does no other job other than to create more connection point for power usage.
A bus topology is the form of topology in which the nodes (devices) are connected to a singe cable with the end of the cable connected to no other source or device. One of the major characteristic of the bus topology is that the devices connected are usually in half-duplex mode in which only one device is allowed to transmit information at a time. When two devices tries to transmit information at the same time, a situation called collision is said to occur (more on the collision in a moment).
The advantages of bus topology is that it is very easy to setup and also relatively easy to extend if need be. It also has the advantage of being cheap and simple to manage. One of the major disadvantage of this type of topology is that when there is a cut on the bus (the connecting cable), all the devices connected at the far end of the cut is off the network. Furthermore, since the end of the bus is not connected to any device, it must be terminated properly in order to dump signals properly. It is also not suitable for networks that is projected to handle heavy traffic.
What happens when collision occurs....
Ethernet uses what is called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to combat the is issue of collision in a half-duplex communication medium, like the bus topology discussed here.
Carrier sense in this context means to evaluate the transmission medium (usually cable) to see if their is any on-going transmission. If there isn't, transmission is then carried out but if there is the device waits for a period of time before checking again. Multiple access means that this operation is carried out in a shared medium. Hence, many devices are trying to use the medium. Collision detection is a mechanism that is activated once more than two devices tries to transmit at a time (collision).Once collision occurs, all the devices using the medium will transmit what is called a Jam signal. This makes all the connected devices to "back off", once this is done, they will wait for a random period after which all the devices connected has equal right to begin transmission. As stated above the CSMA/CD is used as a form of media access control for the half duplex mode of communication.
The Star topology
In star topology, all the nodes are connected to one central point. Unlike bus topology that has terminal, the only terminal in star topology is the nodes itself. Looking at the star topology, it is almost obvious that more cables will be needed to setup this type of connection but it has one big advantage; it can support heavy network traffic. In fact, among all topology supported by ethernet, the star topology is more resilient and supports more speed. You guessed it right again, when there is a link failure, it only affects the device on that link and not a whole section, hence reducing management overhead.Apart from the cost, since all the devices are connected to one central point, that point now serves as a weak point of the whole setup (bottleneck). This topology also makes use of CSMA/CD for collision resolution but developments have made collision less a problem with advanced communication type, the full duplex communication mode. When star topology is running on half duplex, it will still resolve collisions as stated above.
The Ring Topology
The ring topology looks very similar to the bus topology just that there are no loose ends. the end of the cable is connected to the beginning of the cable, hence no need for termination. The setup hence creates a physical circular path for data transmission. Here, data moves from one device to the other until data reaches the desired node. Some ring networks only allows data to move in one direction and hence termed unidirectional ring network while the setup which permits data to move in both direction are termed bidirectional ring network.The major advantage of this form of connection is that collision does not occur. One of the widely used ring topology is the token ring. Here, a token is passed around the medium, just like an empty basket, and whirls around the medium at a very high speed. Any device that wants to transmit information queries the token to see if there's data in it, if it contains no information, the device then places its own data and the token carries the data to the desired node, if the information is meant for another network, then the node that will receive the token become the gateway.
The collision technology used by the ring topology is the Carrier Sense, Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA). This form of technology is widely used by your smartphone when you setup a hotspot. A token is passed around for all the devices connected to the hotspot, then the operation is as described above. No collision occurs in this setup since the token can be at one place at a time.
The major disadvantage of this method of communication is that the token can only move with much speed, hence the speed of the network is determined by the speed of the token. Thereby limiting the obtainable speed of these form of networks.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology involves the combination of two or more topologies stated above to form a desired network topology. This is the most widely used network topology in modern networks since any of the above mentioned topology hardly meet one's demand during network design. One of the most popular used hybrid topology is the mesh network. The mesh can either be a full mesh or a partial mesh. The full mesh connects every point of the network, hence, redundancy is at its peak but the major challenge is that full meshed networks are always very expensive to setup.
credit: aitkotw
The partial meshed network is similar to the full meshed network except that all the points are not connected but there is at least more than one connection to a node. This is in a move to reduce the financial issues encountered in the full mesh.
Broadcast and Collision domains
The issue encountered above in a half duplex form of communication is due to the fact that the whole nodes in the network is in the same collision domain and the same broadcast domain.In a general term, the collision domain specifies the amount of device that can "speak" at the same time. Hence, the lesser the number of devices that can speak at the same time, the faster a half duplex connection can operate. This was the main reason why the hub could not be used in today's networks because all the ports are practically in one collision domain. The network switch is a better equipment to the hub since all the ports are in different collision domain, hence you can choose to transmit using half duplex or full duplex in a switched environment.
The broadcast domain specifies the amount of device that can "listen" in a network. When a broadcast occurs in a network, all the devices in that broadcast domain must pause its operation and listen (processes the broadcast information) before it can continues its operation. The whole ports on a hub are in one broadcast domain, same with the switch (by default). You can control the amount of the device that can listen to broadcast in a switched environment by creating what is called a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). This is a way of tricking the devices connected to the switch to see ports that are not in the same VLAN to "think" that they are in different locations.
Outside the local area network, the broadcast does not occur. Hence, broadcast are not propagated in the internet (imagine a situation whereby all the devices on the internet halts because I want to check my mailbox). Broadcasts are good because it helps to locate an unknown device in a LAN, but when to many devices pauses their operation to listen to the broadcast meant for one device, then the network will be slow. Hence Cisco recommends maximum of 50 devices in one LAN. If your switch has more than 50 ports, then consider breaking the LAN by creating VLANs.
Ethernet Frames
Encapsulation is the wrapping of a protocol with another protocol in other to safely move data to its desired destination. Encapsulation done at the TCP/IP level is called segment while encapsulation done at the IP or Network level is called Packet. Encapsulation done at the Data link level or ethernet level is called frame. Frames are the last information that is converted into bits (1s and 0s) and then transported by either cable (fiber cables, twisted pair, coaxial cables, etc.) or wireless (Wi-Fi, Li-Fi, etc.).
Frames makes use of addressing scheme called MAC addressing and is a 48-bit hex address used to locate devices on the same LAN. Unlike IP addresses that are assigned to devices and can change at will by the user, MAC addresses are burned to the device by the manufacturer and can never be changed. During data transmission, the source and the destination MAC addresses are allowed to change in the frame but the source and the destination IP address can never change while the packet is on transit.
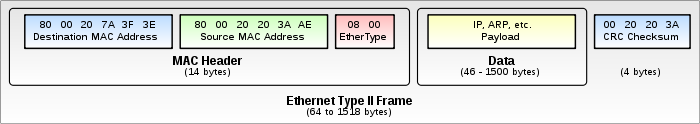
Frames maintain Headers like the IP header I discussed in my post here. The Header contains all the information needed for the transmission of the data and the data itself. It also contains control and error correction information. A frame header is shown (above ) and contains fields, just like the IP header. The functions of the fields is elaborated thus:
The preamble is a 7 byte field used to inform the device receiving the frame the preceding information is the start of the frame help enable data synchronization. The Start Frame Delimiter (SFD) is a 1 byte field used to points out the next byte is the beginning of the Destination MAC address. The Destination MAC address field is a 6 byte field which identifies where the frame is to be sent. If this is absent in the frame a protocol called Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is issued to all the devices on that network segment in search of the destination MAC address.
This is a broadcast used to search for MAC address corresponding to an IP in a packet. The ARP returns with a MAC address and this is used to fill up the Destination address field. Source MAC address field is also a 6 byte field which is the address of the node currently handling the frame. As stated earlier, both the destination and source MAC addresses can change on transit cause any device that receives a frame wipes the source MAC address field and replaces it with its own MAC address, performs ARP and replaces its result with destination MAC address.
The Frame Check Sequence (FCS) is a 4 bytes field containing the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) used to check for errors in the received frame. If the received data is corrupted, the data is discarded and another copy is requested for. The Type field is a 2 byte field layer three protocol used in the logical identification of destination device, this usually contains IP address information (either IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses). Finally, the Data and Pad field contains the data being transmitted and the pad helps complete the size of the data in situation where by the size of the data is not up to the minimum standard frame size (46 byte).
Summary
Ethernet is the mostly used form of Local Area Network because of the speeds it offers and the ease of installation and usage. It is defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard and includes all the LAN operation. Ethernet supports different topologies including bus, star, ring and or a combination of two or more of the the stated topologies. The topology states how the devices involved in the Ethernet are connected. Media Access Control (MAC) is then used to state the information moves from one device to another.
References
Most of the references are already reflecting within the text
- Basics of an internet LAN -lifewire
- Ethernet -arceelect
- collision avoidance -Wikipedia
- Ethernet frames -slideshare
- address resolution -lifewire

))
))
))
))
))
Yeah. Thanks for the educative information, I didn't know about ethernet before now, but as I read your article step by step, I now fully understand it.
I'll take that as a compliment. Thanks bro
Thank you I was finding an article on ethernet frame I got from the link you have given below.