The Air, Composition Of What We Actually Breathe
Every day we get up thanks to the fact that we can breathe, but some of you have asked yourself what it is that we actually breathe, knowing that in the actulity the CO2 gases that we emit to newspapers damage our existence. That is why I will reopen in this post about the air and the chemical elements so this fundamental element of life is constituted.
The air is the mass of gas that surrounds the earth. Formerly it was considered an element, since the four fundamental elements of nature were named: air, earth, fire and water. The first to know exactly the chemical composition of the air were the scientists Lavoisier, Priestley and Cavendish back in the eighteenth century. They checked that it was a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen. Others later discovered that there was ammonia and carbon dioxide (CO2). At the end of the 19th century Ramsay and others discovered the presence of rare or noble gases in very small proportions.
Air
Air is called the mixture of gases that make up the Earth's atmosphere, which remain around the Earth by the action of the force of gravity. Air is essential for life on the planet, is particularly delicate and is composed in slightly variable proportions by substances such as nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), water vapor (variable between 0-7%), ozone, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and some noble gases such as krypton or argon, that is, 1% of other substances. Its physical properties are: it is lighter than water, it has a lower density than water, it has no defined volume, it does not exist in a vacuum, it is a transparent, colorless, odorless and tasteless fluid.

Components of the air.
The components of air can be divided into constants and variables. The constant components of air are around 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and the remaining 1% is composed of gases such as carbon dioxide, argon, neon, helium, hydrogen, other gases and water vapor. The variable components are the other gases and vapors characteristic of the air of a certain place, such as, for example, the oxides of nitrogen coming from the electric discharges during the storms or the carbon oxide that comes from the exhausts of the motors.
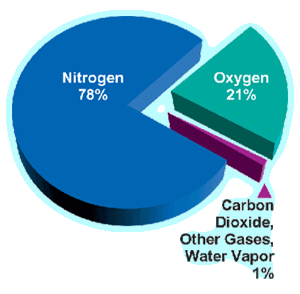
Oxygen and nitrogen: Abundance and Natural State.
The Oxygen.
It is the most abundant element of the earth's crust, both in mass and in number of atoms. The oxygen atoms are more numerous than those of all the other elements put together. Normally it is in a gaseous state. It constitutes 21% by volume or 23.15% by mass of the atmosphere, 85.8% by mass of the oceans (pure water contains 88.8% oxygen), 46.7% by mass of the earth's crust (as a component of most rocks and minerals). Oxygen represents 60% of the human body. Is present in all live tissues. Almost all Plants and Animals, including humans, require oxygen, either in a free or combined state, to stay alive. In living matter, oxygen is combined with the elements Carbon, Sulfur, Nitrogen or Hydrogen.

Nitrogen
In the natural state it appears as a diatomic gas, it constitutes approximately four fifths of atmospheric air, although it does not intervene in combustion or in respiration. Nitrogen is present in all organisms, mainly in amino acids and also in nucleic acids. The human body contains approximately 3% by weight of nitrogen.

Importance Of Air in the Chemical Industry
Obtaining Oxygen From The Air.
The oxygen is extracted by liquefaction and subsequent fractional distillation. The air as mentioned above consists of 21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen and 1% Argon, Neon, carbon dioxide and water vapor. Industrial level First these two last compounds are separated from the air; it is then compressed, cooled and allowed to expand, until liquefaction occurs and liquid air is obtained. Then, it is allowed to partially evaporate, which vaporizes the nitrogen, whose boiling point is lower, leaving a residue enriched in oxygen. By means of a cyclic repetition of this process, an oxygen of 99.5% purity is obtained. The main applications of oxygen in order of importance for the industry are:
- Casting, refining and fabrication of steel and other metals;
- Manufacture of chemical products by controlled oxidation;
- Rocket propulsion;
- Production and manufacture of stone and glass products.
In the chemical and petrochemical industries, oxygen is used as a reagent to improve the performance of a large number of processes. In metallurgy and steel, it is also used for combustion and for adjusting the carbon content of steels.

Obtaining Nitrogen from the air.
Nitrogen can be obtained from the air by simple removal of oxygen. In the laboratory, by passinge air above heated copper, it seizes the oxygen to form solid cupric oxide, CuO. If phosphorus is burned in an inverted bell over water, solid pentaoxid phosphorus is formed, which dissolves in the water and leaves a residue that is mostly nitrogen. Another method of obtaining is to make air bubble in an alkaline solution of pyrogallol, which absorbs oxygen. In industry, nitrogen is obtained from liquid air.
Many industrially important compounds arise from nitrogen, such as ammonia, nitric acid, organic nitrates and cyanides, which contain nitrogen. The extremely strong bond in elemental nitrogen dominates nitrogen chemistry, causing difficulty for both organisms and the industry of converting N2 into useful compounds, but at the same time, causing the release of large amounts of useful energy often when the compounds are released. burn, explode, or decay back into nitrogen gas.
For more information visit the following links.
It is an honor for me your comment. Thanks for the support