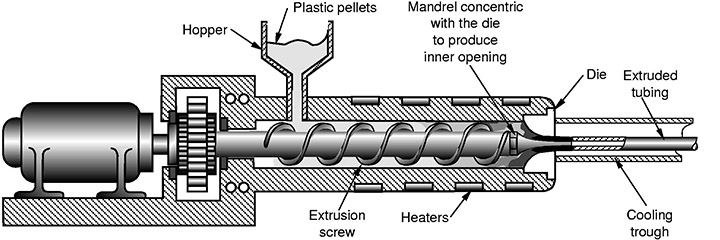
Plastic Extrusion. Process
Extrusion
Extrusion is a continuous process, in which the finished products are obtained by forcing molten material through a forming tool (spinneret, an extrusion head, orifice). The material used in the extrusion process is characterized by a high level of viscosity, and the products are obtained with a cross-section of the desired shape, such as plastic. Extrusion, in other words, can be considered as a complex physical-chemical process that takes place under the influence of mechanical forces, high temperature, and humidity. The processed raw materials are heated by heat, which is released during the process of overcoming internal friction and deformation of the material, and also due to external heating.
The word extrusion comes from Latin roots, from the word "extrusĭo", "extrusiōnis" which means forcing. Other sources state that it comes from the Latin "extrudere" which means to expel. Generally, extrusion is the action and extrude effect; On the other hand, in a more specific way, it can be defined as that process of pressing, modeling and forming a certain raw material to create certain objects with defined and fixed transversal cuts, by means of a continuous flow with pressure, tension or force. This extrusion process was patented in 1797 by a British mechanic and inventor named Joseph Bramah when I try to make a lead pipe. A process that was based on preheating the metal to then pass it through a die through a plunger by hand. But it was not until 1820 that this process was developed by Tomas Burr who built the first hydraulic press, and it was until then that the process was called "squirting". Later Alexander Dick propagated the extrusion process to bronze and copper alloys.
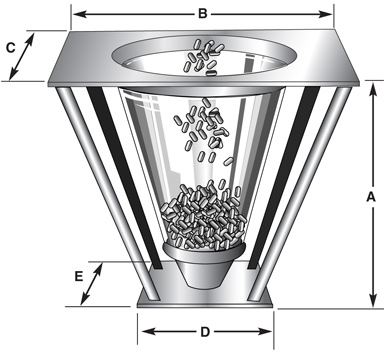
Hopper
The hopper is the raw material deposit where pellets of plastic material are placed for the continuous feeding of the extruder. It must have adequate dimensions to be fully functional; poorly planned designs, mainly in the angles of descent of material, can cause stagnation of material and stoppages in production. In materials that are easily compacted, a hopper with the vibratory system can solve the problem, breaking the bridges of material formed and allowing the material to fall to the feed throat. If the material to be processed is problematic even with the hopper with the vibratory system can solve the problem, breaking bridges of material formed and allowing the material to fall to the feed throat. If the material to be processed is problematic even with the hopper in vibration, the hopper type crammer is the only one that can form the material to flow, using a screw to achieve feeding, Drying hoppers are used to remove moisture from the material being processed, replacing drying equipment independent of the machine. In systems of extrusion with a greater degree of automation, it has systems of transport of material from containers to the hopper, by pneumatic or mechanical means. Other auxiliary equipment is the additive doses to the hopper and the magnets or magnets for the obstruction of the passage of ferrous materials, which may damage the spindle and other internal parts of the extruder.
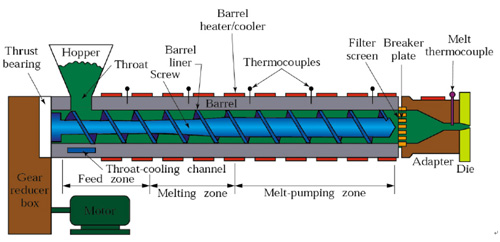
Spindle
Thanks to the intense studies of the behavior of the flow of polymers, the spindle has evolved widely since the rise of the plastic industry to the degree of becoming the part that contains the highest technology in an extrusion machine.
Therefore, it is the piece that in the high degree determines the success of an extrusion operation. Based on the diagram, the fundamental dimensions for a spindle are described below and, in the different designs, vary according to the flow properties of molten polymer that is expected from the extruder. An extrusion equipment can carry from one to 4 screws, the mono-spindle and double-screw configurations being the most used.
Mono-spindle extrusion is one of the main operations in polymer processing and is a key component in many other processing operations. The main objective of mono-spindle extrusion is to form pressure in the molten polymer so that it can be extruded through the die. Most machines are plasticizers (they feed on polymers in the form of granules or powder and melt them into pressure.
On the other hand double screw extrusion is used extensively for mixing, forming compounds or reacting polymeric materials. The flexibility of a double-screw extrusion equipment allows it to be designed for specific compounds since the spindles can be co-rotating or counter-rotating, inter-toothed or non-inter-toothed. In addition, the configurations of the same spindles can vary using transport elements, elements of reverse transportation, kneading blocks, mixing zones and other designs to adapt to the appropriate process of the compound or resin to be processed.
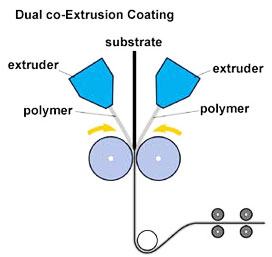
Co-Extrusion
In practice many films, sheets, tubes and other forms are extruded with several layers; this allows the optimization of a wide range of properties, such as oxygen barrier, mechanical resistance, etc. This is achieved by co-extrusion which consists of putting two or more extruders feeding the same die that joins the different extruded layers. The main difficulty of coextrusion is to join the layers to unite their properties, this is achieved by intermediate adhesive layers that join two resins that are not compatible, this is critical otherwise the structure would separate. There are two large types of dice for coextrusion: single and multiple. Both types are based on a separate extruder for each polymer chemistry. In multiple dice, each layer is extruded separately and only combines just before the die lips. This type of dying is expensive due to the complex tooling it requires, but it can mitigate large differences in the rheological behavior between the various layers. Simple dies from multiple layers in a single layer, allowing contact between the polymer layers for a longer period of time. This ensures the optimal bonding, but as a result, greater compatibility between the polymers is needed.