Oil the hydrocarbon mixture that changed the planet
Hello, dear friends Steemians!
Can we live without oil? Crude oil is undoubtedly the most important natural resource of the industrialized countries and it is easy to understand why.
Many of the elements and products that we use today are derived from this non-renewable resource, also known as "black gold". In the first place, it is a source of energy, thanks to which we can use our vehicles and other means of transport because both the gasoline and the lubricants and antifreeze that are used to keep the engine in good condition are derived from it. In fact, our world would stop almost completely without oil. The factories would stop operating, the farm tractors would be stopped. Many houses and offices are heated with oil and without it, they would freeze in the winter.
That is why in this post I will try to explain how such a rich mixture of hydrocarbons changed our lives.
Refinement oil
Refining is the process that is responsible for the transformation of hydrocarbons into by-products. Oil refineries operate twenty-four hours a day to convert crude into useful derivatives. The oil is separated into several fractions used for different purposes. Some fractions have to undergo thermal and chemical treatments to turn them into final products such as gasoline or fats. In the early days, refining was content to separate the pre-existing products in the crude, using its difference of volatility, ie, the thickness of a molecule. It was then when they learned to break them into smaller parts called "cracking", to increase performance, in essence, warning that they and the by-products of their manufacture had "reactive" properties.

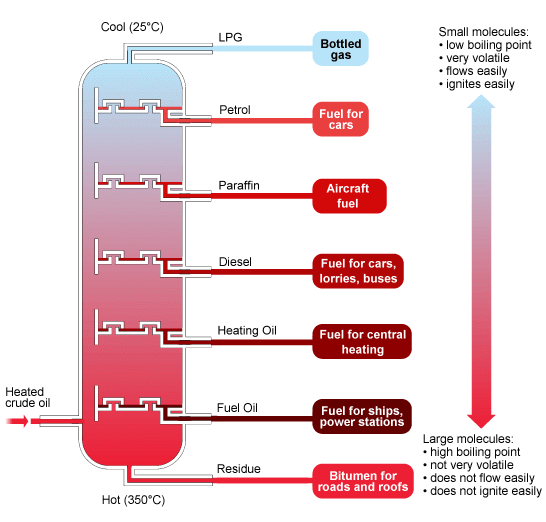
Distillation
Distillation is the fundamental operation for oil refining. Its objective is to achieve, by means of heat, to separate the various components of the crude oil. When the crude reaches the refinery, it is subjected to a process called "fractional distillation". In this, the heated oil is fed to a column, also called a fractionating or distillation tower. The oil passes first through a heater that reaches a temperature of 370ºC and is then introduced into a tower, where it begins to circulate and evaporate. In this way, light products and waste are separated.
Petroleum Distillation
It is done by A fractionating column, also called plate column or plate column is an apparatus that allows performing a fractional distillation. A fractional distillation is a technique that allows a complete series of simple distillations to be carried out in a single, simple and continuous operation. Fractional distillation is a basic operation in the chemical industry and related, and is used primarily in the separation of mixtures of liquid components.
The distillation of oil is carried out through the so-called fractionating towers. In this, the oil rises through the tower increasing its temperature, obtaining the derivatives of this in the following order:
1. Solid waste
2. Oils and lubricants
3. Diesel and fuel
4. Kerosene
5. Naphtha
6. Gasoline
7. Solvents
8. LPG (liquefied petroleum gas)
If there is a surplus of a high molecular weight petroleum derivative, the hydrocarbon chains can be broken to obtain lighter hydrocarbons by a process called cracking.
Oil refining process
The oil finally reaches the refineries in their natural state for processing. Here practically what is done is cooking it. For this reason, oil is also called "crude oil". A refinery is a huge complex where crude oil is first subjected to a process of distillation or physical separation and then to chemical processes that make it possible to extract much of the great variety of components it contains.
The oil has a great variety of compounds, to the point that it can be obtained from the 2,000 products. Oil can also be classified into four categories: paraffinic, naphthenic, asphaltic or mixed and aromatic. The products that are taken out of the refining process are called derivatives and there are two types: fuels, such as gasoline, and petrochemicals, such as polyethylene, benzene. The refineries are very different from each other, according to the technologies and the process schemes used, as well as their capacity. There are to process soft oils, heavy oils or mixtures of both. Therefore, the products obtained vary from one to the other.
Refining is accomplished in several stages. This is why a refinery has numerous towers, units, equipment, and pipes. In simple terms, the operation of a refinery of this type is fulfilled in the following way: The first step of the refining of crude oil is fulfilled in the towers of "primary distillation" or "atmospheric distillation". Inside, these towers operate at a pressure close to atmospheric and are divided into numerous compartments which are called "trays" or "plates". Each tray has a different temperature and serves to fractionate the components of the oil. The crude oil reaches these towers after passing through an oven, where it is "cooked" at temperatures of up to 400 degrees Celsius that turn it into steam. These vapors enter through the lower part of the distillation tower and ascend between the trays.

As they rise, they lose heat and cool. When each vaporized component finds its own temperature, it condenses and is deposited in its respective tray, to which ducts are connected by which the different currents that separated in this stage are collected. At the bottom of the tower falls the "reduced crude", that is, the one that did not reach evaporation in this first stage. The first step of refining is thus fulfilled. From bottom to top have been obtained, in order: gas oils, kerosene, turbine, naphtha and gases rich in butane and propane. Some of these, such as a turbine, kerosene, are products and end. The other streams are sent to other towers and units to submit them to new processes, at the end of which the other petroleum derivatives will be obtained. Thus, for example, the "vacuum distillation" tower receives the crude oil reduced from the first stage and extracts heavy gas oils, paraffinic bases, and residues. The Cracking or Cracking Unit receives gas oils and reduced crudes to produce mainly gasoline and propane gas. The Vapor Recovery units receive the rich gases from the other plants and extract combustible gas, propane gas, propylene, and butenes. The mixing plant is ultimately the one that receives the different naphtha streams to obtain the extra and current motor gasoline. The unit of aromatics produces from naphtha: toluene, xylenes, benzene, cyclohexane and other petrochemicals. The Paraffin receives paraffinic and naphthenic distillates to extract paraffin and lubricant bases.
In summary Petroleum Refining Phases
Crude oil passes first through an oven, where it is heated and converted into steam, then passing to the Distillation Towers
In these Towers, vapors rise from the bottom to reach the trays, located at different levels.
When the vapors rise, they cool down and lose heat. Then they are deposited in their respective trays.
In these trays each substance has its determined place, while the rest of the oil that did not evaporate, remains in the base.

I wish i had seen this before i started my training at the Refinery. Really interesting piece .
Good to be useful, thank you for commenting