Basic concepts in chemical engineering. Part 3. Process equipment, pumps and types of impulse pumps.
Continuing with the fundamental principles of chemical engineering today I will try to explain one of the fundamental equipment in any industry, which is also of daily use in our homes to increase the pressure of the water that we use daily.
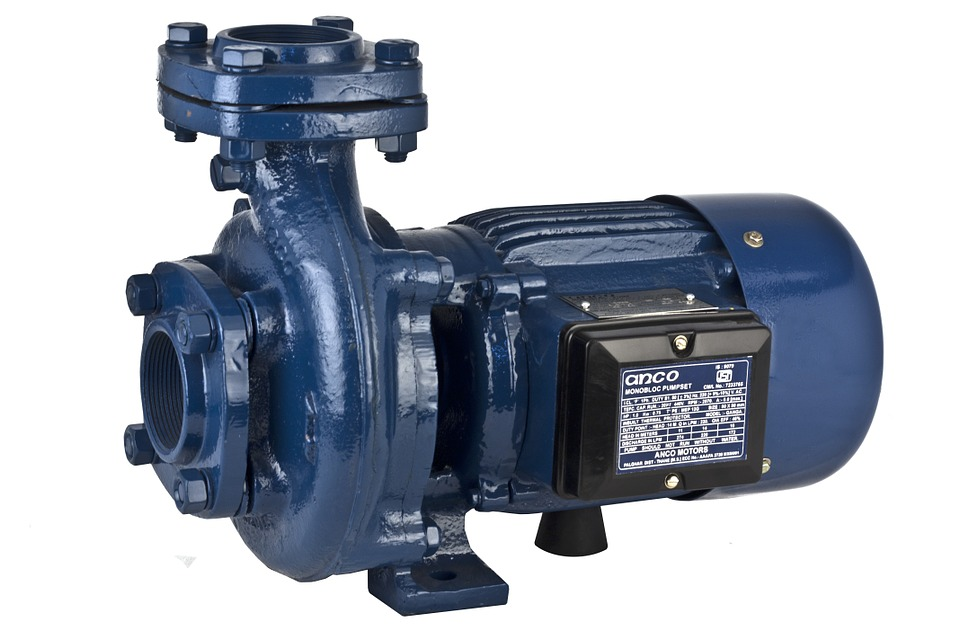

Pump
It is any equipment that supplies energy to a liquid or flow to increase the pressure. The pumping action is the addition of kinetic and potential energy to a liquid in order to move it from one point to another.
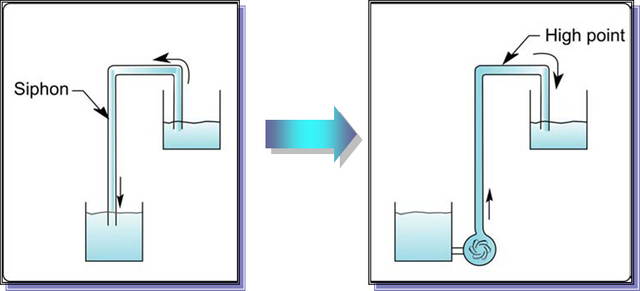
It is a mechanical energy transformer that can come from an electric motor, a turbine and converts it into energy, which a fluid acquires in the form of pressure (eg, aqueduct pumps to overcome losses in pipes), position (eg pumps) deep well) and speed.
The pumps are used to pump all kinds of liquids, (water, lubrication oils, acid fuels, food liquids, beer, milk.
Pumps are also used to pump thick liquids with suspended solids, such as paper pulp, molasses, sludge, waste.
Newtonian fluid:
Fluids where the shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of deformation are called Newtonian fluids. Most common fluids such as water, air, and gasoline are practically Newtonian under normal conditions.
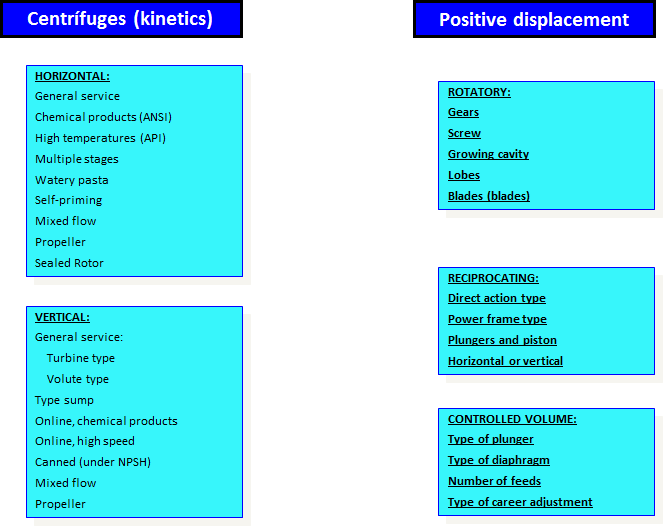
Types of pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps
They are those that supply the same amount of liquid in each cycle or revolution of the pump element, independent of the pressure that the liquid encounters when it leaves.
These pumps guide the fluid that travels along its entire path, which is always contained between the drive element, which can be a plunger, a gear tooth, a blade, a screw, and the housing or the cylinder.
The movement of positive displacement consists of the movement of a fluid caused by the decrease of the volume of a camera. Therefore, in a positive displacement machine, the element that originates the exchange of energy does not necessarily have reciprocating movement (piston), but can have rotary movement (rotor).
In positive displacement machines, both reciprocating and rotary, there is always a chamber that increases in volume (suction) and decreases volume (impulsion), which is why these machines are also called Volumetric.
Reciprocating pumps
They handle a fixed volume of the fluid to be compressed, where a certain amount of it is forced to enter the body of the pump where it is momentarily enclosed, and then forced out through the discharge pipe. From the above it follows that the flow of a reciprocating pump is directly proportional to its rotation speed and almost independent of the pumping pressure. These pumps are not suitable for handling liquids containing sand or suspended matter.
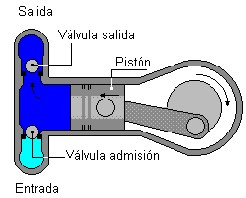
Rotary pumps
The liquid moves in the working chambers, due to the more or less complex rotating movement of the moving elements with respect to the fixed part or stator. In the stator are the suction and discharge cavities; the rotor is the organ of the pump, integral with the drive shaft, which is put into rotation; in addition, in the rotary pump there are one or more mobile elements, which move by making a series of cyclic movements with respect to the rotor

Centrifugal pumps
It consists of a set of rotating blades inside a housing or casing that are used to impart energy to a fluid by means of centrifugal force.
The speed of the fluid is constantly increased through the impeller, then this speed is reduced in the volute or diffuser of the pump, generating an increase in the pressure of the fluid.
It is more suitable for handling large amounts of liquid than positive displacement pumps.
They constitute no less than 80% of the world bomb production.

Advantages and disadvantages of centrifugal pumps
Constant flow, uniform pressure, simplicity of construction, small size, low maintenance and regulation flexibility.
One of its few drawbacks is the need for priming prior to operation, since centrifugal pumps, unlike positive displacement pumps, are not self-priming.
Centrifugal Pumps Components
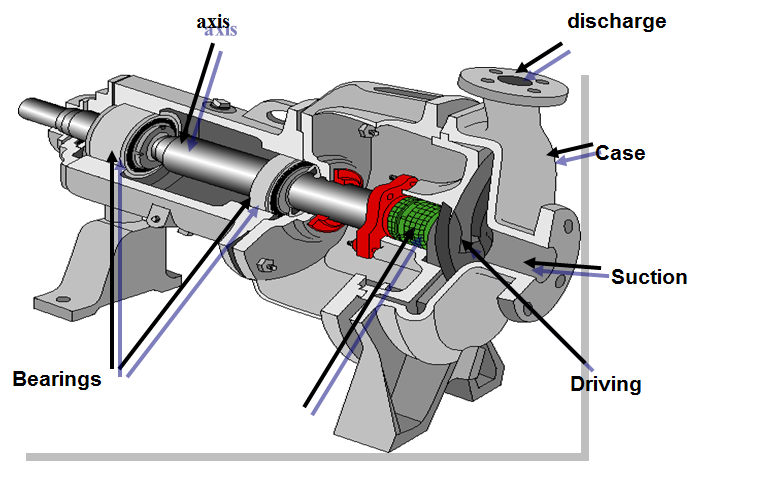
Suction flange
Position: shaft end, side, top, bottom.
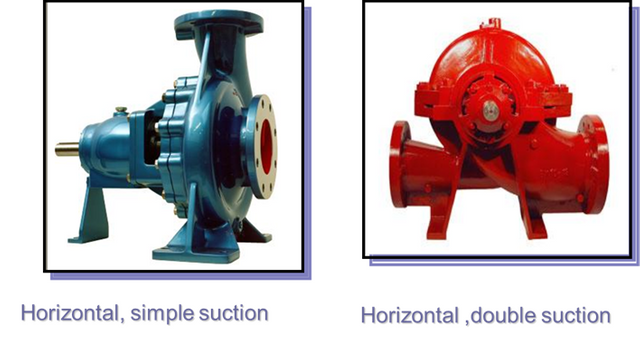
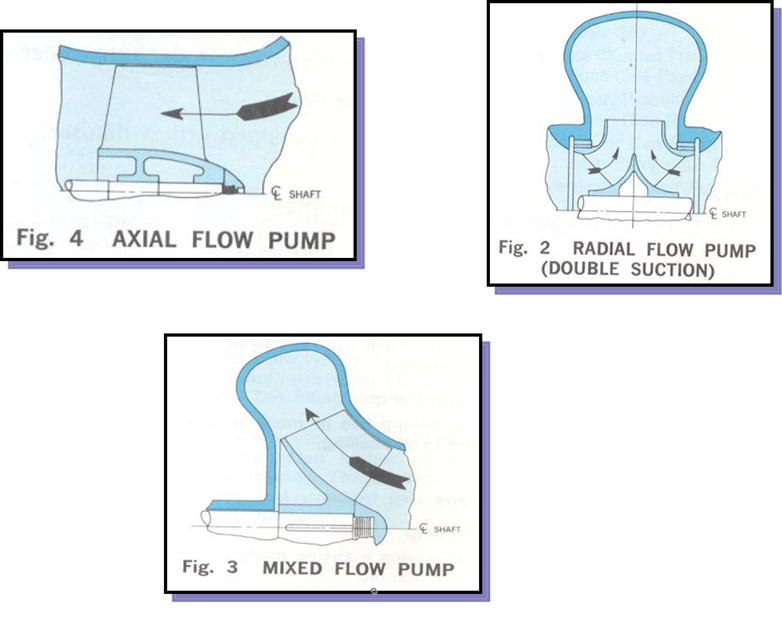
According to the inflow into the intake, the pumps are classified into: single suction and double suction pumps, according to the fluid between one or two sides of the pump.
The double suction is used in order to compensate for the imbalance produced by a single suction.
Rotor or impeller
Formed by a series of blades of various shapes that rotate inside a circular casing.
It is attached to the shaft jointly and is the moving part of the pump.
The liquid penetrates axially through the suction pipe to the center of the impeller, which is driven by a motor, experiencing a change of direction more or less abrupt, going to radial, (in the centrifuges), or remaining axial, (in the axial ), acquiring an acceleration and absorbing a job.
Axis
It is the means by which power is transmitted to the pump boosters.
Assembly with the motive equipment: direct or with the use of mechanical coupling.
- The first critical speed of an axis is related to its deflection (Run out).
Use rigid axles (that work less than their first critical speed and avoid contact with wear rings) for pumps that operate at 1750 r / min or less.
Position of the axis: horizontal, vertical or inclined.
Case
It is the external body of the pump, the fixed or stationary part of the pump. Contains the energy converter element: Volute or diffuser.
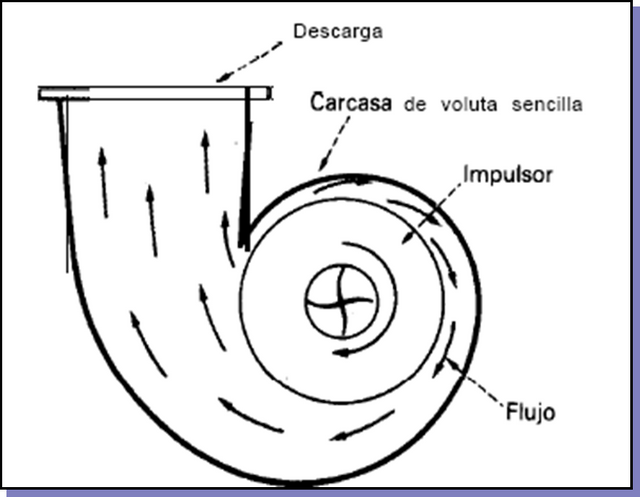
Scroll (Spiral camera or snail)
It is an energy transformer, since it decreases the speed increasing the pressure of the liquid as the space between the impeller and the casing increases. Due to its size it is not practical in multistage pumps. The volute is designed to work with the maximum efficiency flow (BEP); With any other flow rate and due to its asymmetric arrangement, the distribution of pressures in the periphery of the impeller ceases to be uniform, appearing on it a radial thrust.
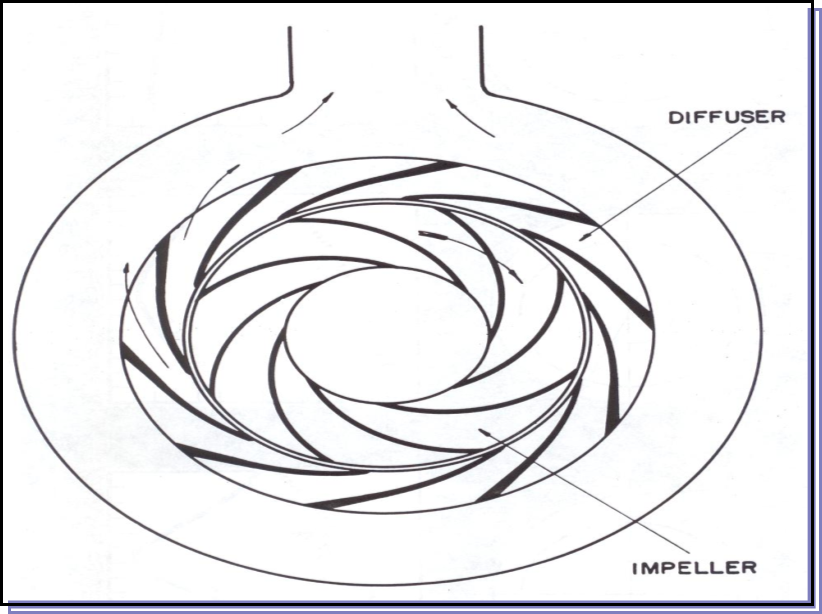
Diffuser (Direct Palettes):
Series of diffuser channels separated by vanes or vanes and placed around the impeller that guide the fluid to the outlet, increasing its pressure. Due to its symmetry, the guide vane diffuser practically does not exert radial thrust on the impeller. Its size is comparatively smaller than that of the volute and this is especially important for multistage pumps. In general, its performance is somewhat higher than that of the volute. The diffuser is used, above all, in mixed and axial flow pumps, in a large number of multistages and in some large single-phase pumps.
Rings or wear ring
Sacrificial element in centrifugal pumps (it is easy and quick to replace). They provide a seal against leakage between the impeller and the housing between high pressure and low pressure zones in the pump itself. A seal that does not have replaceable parts is used only on very small and inexpensive pumps. Mounting type: Stationary (usually on the housing) or rotary (impeller ring).
Bearings
They are the elements that support the shaft, carry the load and avoid friction. Lubricated by different methods, they are classified into two types: slip and antifriction or bearings. They must support axial and radial loads. They require lubrication and in most cases cooling.

For more information visit the following links.
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bomba_hidr%C3%A1ulica
https://prezi.com/i_5oy_-ihgx4/operaciones-unitarias-bombas-y-compresores/
http://boombascbtis213.blogspot.com/
https://books.google.co.ve/books?id=_zrNwOEKfAMC&pg=PA135&lpg=PA135&dq=bombas+operaciones+unitarias&source=bl&ots=z_ZDgn0xEk&sig=MCzq5pE9ynRgL3s3-jyiqEd7xHU&hl=es&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi1oN7Zo-DXAhWFRt8KHeHxDJcQ6AEIezAT#v=onepage&q=bombas%20operaciones%20unitarias&f=false
http://procesosbio.wikispaces.com/Transporte+de+fluidos+y+bombas?responseToken=cbf2db0493aa60f80d2ec3613fada175
https://books.google.co.ve/books?id=XZNYpvnO_V8C&pg=PA71&lpg=PA71&dq=bombas+operaciones+unitarias&source=bl&ots=TvVvixNPMc&sig=MtOzI-ka9G-WrjfsFpyrHBmyBxE&hl=es&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi1oN7Zo-DXAhWFRt8KHeHxDJcQ6AEIjAEwFg#v=onepage&q=bombas%20operaciones%20unitarias&f=false
Congratulations @frankjavier! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP