The discovery of X-rays / Brief historical review and meaning of X-rays
X-rays have changed people's lives, from their discovery until now, they have been a very useful tool especially for doctors. However, in many other areas such as the science of materials, thanks to their improvement and adaptation have served as an impetus in the creation of techniques for identification and analysis of materials. It also opened a new and vast horizon of opportunities and inspiration in natural science research.
Some people say that Röntgen was not the one who discovered the X-rays, but it's something if we are totally sure and it is the scope of this type of electromagnetic radiation.
This renowned scientist was born on March 27, 1845 in Germany, birthplace of the brightest minds throughout history, specifically in a small town in Lennep located in the west of that country. His family was economically stable, where his parents were merchants. After the growth in the textile industry and due to the creation of the revolution, they moved to Holland in the city of Apeldoorn in the Netherlands, where William spent his studies and much of his childhood. His father's idea was that when he finished high school he took charge of his business, what he did not know was that in a few years his son would be one of the most brilliant minds in science.
Years later he began studying at the technical school to acquire his high school diploma, under the tutelage of a great friend of his father Dr. Willem Gunning. unfortunately Röntgen did not acquire his high school diploma, due to problems with some teachers. However, his interest in the natural sciences had awakened. Although years later, his true love was physics.
After being expelled from the school of Utrecht, Röntgen learned from a great friend who had founded the Polytechnikum in Zurich in Switzerland, immediately Röntgen moved to that country where he presented a simple admission test and was able to enter the school where he finally got his high school diploma.
His love for science had awakened and he decided to study mechanical engineering at the University of Zurich, where he obtained his degree and immediately in 1868 he completed his masters in Physics, thanks to the influence of August Kundt, was the one who helped him to lean definitively for the Physical.
The following years followed the footsteps of Kundt, who at that time was one of the most recognized scientists of the old continent, in his laboratory they began to carry out different investigations. After completing his doctoral thesis in 1870, they were forced to move to different laboratories to reach Strasbourg in the cause of the Franco-Prussian War. Kundt obtained a great position in an elite university in Germany and of course Röntgen followed in the footsteps of his great teacher. Roentgen obtained the "qualification" (an academic degree of higher education in Germany that allows him to accept a university chair.) In the year 1875 he moved to the Hofhenheim University to teach physics and mathematics, but something in him told him that he did not It was his destiny, he realized that teaching was not his passion, he preferred to be in a laboratory doing science, so he returned to Strasbourg and received the title professor position at Ludwig University.
Many remember Röntgen as that lonely researcher, he was also recognized as a very demanding teacher, few students attended his classes especially when it came to experimental physics. those privileged people realized the wonder that Roentgen was as a researcher. But since at that time experimental physics was on one side and only theoretical physics was the one that dominated and the most recognized scientists ruled out that it was a science of the future. Röntgen experimented in his home taking experimental physics as a 2nd option. However, he carried out several experiments that brought interesting discoveries such as: as dielectric convection, a fundamental piece for the theory of electromagnetism that was just emerging.
Röntgen had his peculiarities: he did not like to give lectures and when he imparted it he did not extend much, he did not like to attend meetings with his colleagues either. Many of his publications went unnoticed, the jurors describe him as having little creativity, therefore the receptivity of his writings was very low, but in large part it was because the scientists of that time mostly theoreticians were not of mind open, they were based on what was already discovered and were not open to new advances and inventions in physics.
The discovery
At the beginning of the publication he commented that many people doubted that Röntgen was the discoverer of x-rays, and this is because in the mid-nineteenth century the British scientist William Crookes made different studies of the effects of certain gases by applying energy discharges. These experiments consisted of a small totally vacuum tube containing electrodes to generate current, these tubes were called Crookes tubes. After this process there is a radiation of various particles, which later were called electrons, which traveled from tip to tip inside the tube (cathode-anode). During this process the electrons collided in the atomic structure of the tube, bringing with it a bright light on its surface called luminescence. After all this Crookes came to the conclusion that this type of light was produced by some phenomenon within the tube, specifically that came from the cathode, which hit the glass wall of the tube produced this particular phenomenon that called cathode rays.
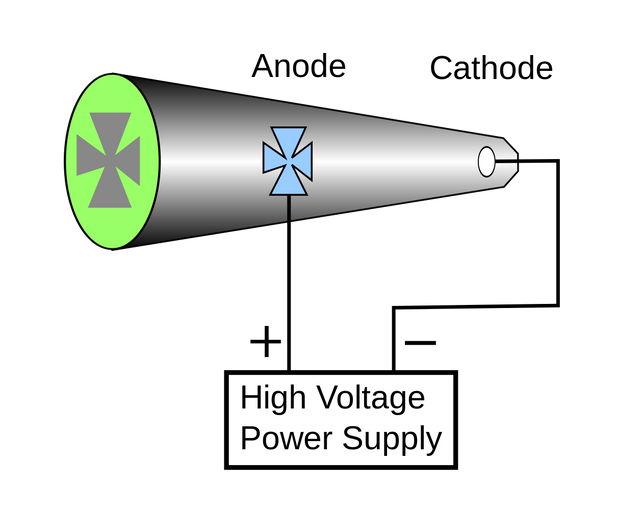
Diagram of Crookes tube, an experimental discharge tube invented by William Crookes around 1875. Licensed CC0 1.0 Wikipedia
After being close to different photographic plates, these could generate a kind of images, but at that time it was not possible to identify what type of image the plate contained. Then Tesla in 1887 decided to continue studies of this effect created by the Crookes experiment, where he could ensure that this type of radiation could be harmful to people, since they could get sick from this radiation when exposed for a period of time determined.
All this aroused the interest of Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen to study why this particular phenomenon occurs. The big question was asked: What was happening outside the tube and being able to check if the cathode rays could get out of it?
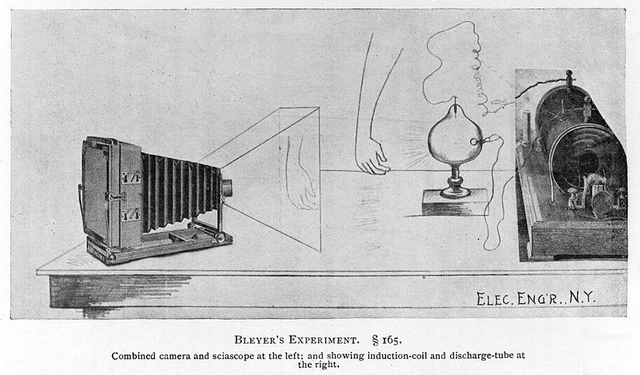
It was in 1985 where Röntgen discovered x-rays, while experimenting with the Hittorff-Crookes tubes and the Ruhmkorff coil to investigate the violet fluorescence produced by the cathode rays.Röntgen while conducting his experiments entered a completely dark room took a tube and then covered it with a kind of cardboard completely black, this to ensure that the cathode rays did not enter the tube. After all this something very peculiar observed a small yellowish green glow that came from a screen with had a layer of platinum-cyanide barium, to check this if it happened constantly turned off and ignited the tube and I could verify that it always happened the same. He was quite sure that his discovery was important and confirmed the experiments of Crookes, since some kind of lightning pierced the cardboard and the tube until reaching the barium plate and after receiving these radiations could emit this type of light.
Before reaching a final conclusion, he decided to continue making experiments to confirm his theory. The first was to place a screen at a greater distance from the tube and perform the same procedure. Immediately observed that the fluorescent light was still there, then he said in his mind that this could be a great discovery because this radiation was very powerful, due to its range.
X-rays. Licensed CC BY 4.0
Then he made the following test in order to measure this wide range of this type of radiation, he could see that it had the ability to cross the air to reach the plate, then asked a new question, And if I put another type of material that is in the middle of the tube and the plates, what could happen ?, Will it have the ability to cross this material that I will place and get back to the screen? Then he placed much denser materials to measure the scope of this type of radiation, the first thing he placed was a book, he observed that the radiation persisted, but with less intensity. He continued to experiment with placing thicker materials and determined that the radiation was still decreasing, but it was still there, until it reached very dense materials such as lead and platinum that completely obscured this radiation.
But the best of his ideas was to come and it was the final thrust to confirm his theory. He decided to use his own hand to see if this radiation was going through him and he could observe very astonished how the bones of his hand were reflected on a plate. It was that the beginning of a new era in science.
He determined that the rays created a very penetrating, but invisible, radiation that went through great thicknesses of paper and even thin metals. He used photographic plates to demonstrate that the objects were more or less transparent to X-rays depending on their thickness and he made the first human X-ray, using his wife's hand. He called them "incognito rays", or "X-rays" because he did not know what they were, only that they were generated by cathode rays when hitting certain materials.
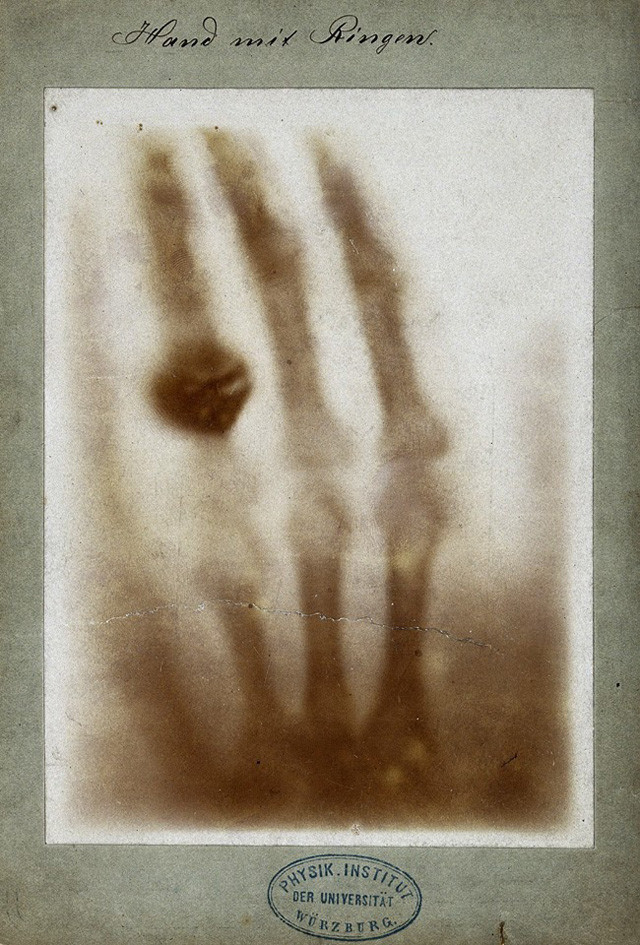
Hand mit Ringen (Hand with Rings): a print of one of the first X-rays by Wilhelm Röntgen (1845–1923) of the left hand of his wife Anna Bertha Ludwig. It was presented to Professor Ludwig Zehnder of the Physik Institut, University of Freiburg, on 1 January 1896. Source Wikipedia. Licensed CC0 1.0
In an interview Röntgen says the following: "I had not revealed anything to anyone about my work. I told my wife that I was doing something that would make people, when they found out, say: 'Röntgen has lost his mind,' "he told Ludwig Zehnder.
After his discovery Röntgen spent several weeks carefully studying the properties of these rays, until finally publishing his great article, in fact his work was so good that it took more than 15 years for other scientists to add data to his discovery, thanks to his work accurate, thorough and dedicated.
One of the most important aspects of his work was that the rays discovered could penetrate practically all the material that he wanted to analyze, it was there where he took his wife's hand you could see all the bones of his hand and also his ring was distinguished commitment, but not the bones (which leave a shadow on a photosensitive plate.) The results of his research were published in the article "On a new class of rays".
He called them X-rays, since in mathematics the X is the representation of the unknown.
The news of the discovery of X-rays spread very quickly in the world. Röntgen was the subject of multiple recognitions: Emperor Wilhelm II of Germany granted him the Order of the Crown and was awarded the Rumford Medal of the Royal Society of London in 1896, with the Barnard Medal of Columbia University and the Nobel Prize. of Physics in 1901.

Exhibit in the Röntgen-Gedächtnisstätte Würzburg - Würzburg, Germany.. Licensed CC-BY-SA 3.0
Now I will focus on talking about what physically means what you discovered Röntgen
X-rays
They are produced by the interaction between matter and electrons that are accelerated at very great velocities. When these slow down or simply stop, the accumulated energy (kinetic) is instantly converted into X-rays. As mentioned in its definition, electromagnetic waves are produced inside a tube containing at one end a plate A and at other ends a plate B, known as (anode and cathode). When emitting the beam of electrons in the first plate, these are accelerated by means of an electrode that generates currents of high voltage between To and B. When arriving at the plate B they are decelerated sharply, which causes that the electromagnetic waves acquire a high frequency and finally X-rays can be produced.
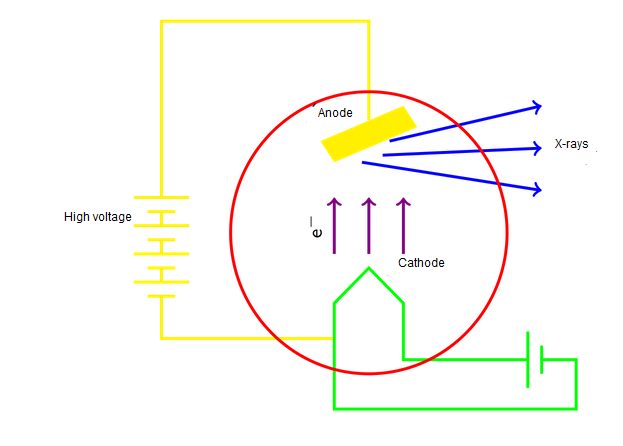
Diagram of production of X-rays in a tube of Crookes. Modified original image. Licensed CC-BY-SA 3.0
It is necessary to take into account certain parameters for the generation of X-rays, such as, for example, the amount of X-rays and the intensity of current must be proportional to the amount of electrons emitted in the tube, which must subsequently be accelerated from the plate higher (cathode), then the number of electrons that go from the first plate must be the same amount of current generated inside the tube.
For the production of X-rays in laboratories and hospitals, X-ray tubes are used, which can be of two types: tubes with filament or tubes with gas.
But first let's explain the composition of an X-ray tube;
These have a valve that is responsible for producing radiation, it must be taken into account that this valve also regulates the vacuum, that is, that no air enters the tube, so that the collision can occur and the entire process involved in the X-ray production. This tube will produce a current that will circulate the current between both poles during a given time so that a potential difference between the cathode and anode can be produced.
Let's talk a little about the Cathode. It contains a filament where it emits the electrons when they increase their temperature, so that the electrons can go from one layer to another, there must be an approximate current of 5 Amps so that they can cross the filament. Something that we must take into consideration is that the current of the tube is totally independent of that of the filament, they are circuits separated one from the other. Another component that has the cathode is the focus cup, its function is to focus the negative charge that must overcome the repulsion of the cathode electrons, so that they can condense in a small area located at the anode.
Now let's talk about the anode. As we all know this is the positive part located in the tube, it is also characterized by two types that are commonly used in the identification of X-rays.
First are the stationary, this requires little current intensity for its operation, and the rotary, are the opposite of the first, can produce high current intensities.
Both have a component in their support called "white", which is the place where the collisions that come from the cathode occur. This component is characterized by having a metal of tungsten alloy which in turn are integrated into the anode with copper. They also have a kind of rotating disc that helps dissipate heat in a certain area, so it is possible to obtain a larger current inside the tube.
The energy with which the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode will give rise to radiations of different frequencies, higher the higher the velocity reached by these electrons. The filament tube is a vacuum glass tube in which two electrodes are located at their ends. The cathode is a tungsten filament and the anode is a metal block with a characteristic emission line of the desired energy. The gas tube is at a pressure of approximately 0.01 mmHg and is controlled by a valve; It has a concave aluminum cathode, which allows to focus the electrons and an anode.
X-ray spectrum
The X-ray spectrum is only the result of the emission of photons inside the tube, which generate X-rays thanks to the energy emitted by said photons.
Within the spectrum of X-ray emission two very important characteristics given by the radiation occurred in this phenomenon.
The first of these is the braking radiation, where the particles that are charged at the anode, tend to experience a very large change in speed, as mentioned at the beginning, they radiate electromagnetic waves in energy packets, necessary to be able to experiment the collisions that finally reach the cathode. This radiation is known as braking or bremsstrahlung. Its application is very important in obtaining X-rays in radiotherapy due to the radioactive collision: with the negative electron of the nucleus.
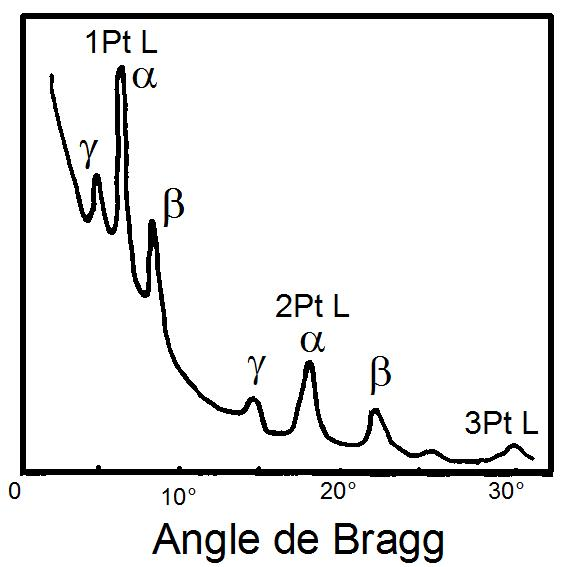
First X-Ray Spectrum recorded by W.H.Bragg and W.L.Bragg in 1913. Source Wikipedia. Licencia CC-BY-SA 3.0
The second one is the characteristic radiation, where the particles have enough energy to be able to go to the inner layers of the atom of the white component. In this type of radiation the electron-hole pair is given, the electrons that come from the surface layers fill these holes with electrons, emitting the radiation of the X-ray spectrum of the material analyzed. The energy coming from this radiation must always be discrete, because it depends exclusively on the energy levels of the atom and the transitions that occur at these levels are exclusive of the inelastic collision of the negative electron of the atom.
X-rays are harmful to the health of people
For anyone is a secret of the side effects that could cause for people to be exposed for long periods to X-rays. Perhaps we know that cause damage but do not know scientifically because ?, I will explain in detail that causes this type of radiation.
We know that ionizing radiation is that energy released by atoms in the form of electromagnetic waves, yes but what does this mean?.
When a kind of disintegration of these bundles or particles occurs, this is called radioactivity and is what we know as the energy released in the form of ionizing radiation, in turn they emit a radiation called radionuclides, which is the substance they use scientists for imaging tests and their treatment.
Exposure to radionuclides is divided into two forms, the first is internal when a person inhales, ingests this type of substance and consequently enters the blood directly, as, for example, when a person is going to receive treatment by means of injections, healing of a wound. It should be noted that the body spontaneously releases this substance from the bloodstream through excrement or simply if you want to do it more quickly and efficiently, an intravenous medical treatment is applied.
The second is externally, which is basically when the substance is in the environment, whether in the air, dust, liquids or any other method. Usually this adheres to people's clothing or any other personal material, so it can adhere to the skin. The recommendation to eliminate this type of substances is that the person cleans properly after being exposed to this type of radiation.
But what are the real risks to health?
When people have the need to perform some type of radiography either, chest, abdomen, bones, among others. In general, they are always exposed to ionizing radiation and receive small doses of this type of radiation. That is why most operators of these long-term equipment have very serious side effects such as hair loss, cataracts and even skin cancer.
A curious fact that is part of my personal experience is that some years ago when I was starting my undergraduate studies I met a boy who works in a radiology laboratory, he told me that he had approximately 15 years working in the area and that Side effects were already present in him. He showed me pictures of the before and after and I could confirm that he had lost much of his facial hair, approximately 70%, in the same way your skin color had a somewhat reddish tone and has many spots all over his body. But the most shocking thing was when he told me to turn off the light and see what is going to happen, turn off the light from the office and amazingly he presented in his dawn a kind of greenish color, I was impacted by the situation, being exposed to so much radiation causes the ionizing radiation in the person will be part of it.
To conclude we must note that X-rays have great advantages, thanks to their discovery provides great advances in medical sciences, so many professionals in the area have made X-rays a fundamental tool to detect diseases and safeguard the lives of their patients. patients However, not everything is rosy, as I have just mentioned being exposed to a lot of radiation causes serious damage to human beings, that is why many companies have taken preventive measures for their employees, creating special suits, medicines that help preserve the health of people.
Great true discovery?.
I hope you have fun with this reading, soon I will publish more content about the great discoveries in the field of physics.
See you soon!
If you want more information about the subject you can visit the following links:
Photon Energies and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Ionizing radiation, health effects and protective measures Production of X-rays X-ray tube APPLICATION NOTES - X-RAY GENERATORS Rontgen, Hounsfield and the History of Radiology Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen (1845-1923) and the Early Development of Radiology Röntgen’s discovery of X-rays William Crookes Crookes tube Cathode Ray Experiment The First X-ray, 1895 The Electromagnetic Spectrum X-ray RADIATION BEAM On the 120th anniversary of the X-ray, a look at how it changed our view of the worldReferences in Spanish:
Produccion de rayos X de rayosxuptm.blogspot.com
Descubrimiento de los rayos X de areaciencias.com
Publish through our official app and you will get an extra vote of 5% https://www.steemstem.io/
 Video credits @gtg
Video credits @gtg
Congratulations @carloserp-2000! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @utopian-io.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the utopian-io witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Thanks for having added @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post. This granted you a stronger support from SteemSTEM.
Thanks for having used the steemstem.io app. You got a stronger support!
Hi @carloserp-2000!
Your post was upvoted by Utopian.io in cooperation with @steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV