Astronomy of ancient Greeks
We owe the Greeks the creation of mathematical astronomy. Great Greek thinkers rejected mythological beliefs, and the phenomena in the sky tried to explain mainly scientifically. Astronomy has thus been separated from astrology.
The solar system with world at centre
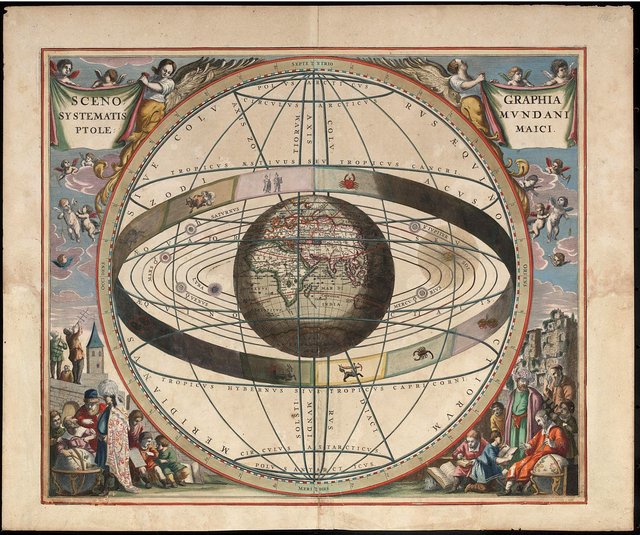
The ancient Greeks, like other peoples of that time, farmed and watched the sky to measure the seasons. Part of their knowledge was borrowed from the civilization of Mesopotamia. Initially, the Greeks' knowledge was saturated with the beliefs of other peoples. In the 6th century BC Greek thinkers began to move away from mythological roots and look for real explanations of the phenomena in the sky. Thales from Miletus traveled to Egypt, where he studied mathematics. He is credited with the thesis about the sphericity of the Earth. Pythagoras, a well-known mathematician, proposed a theory that the cosmos is made up of round spheres surrounding a round Earth. According to this theory, the Sun, the Moon and each planet has its own sphere. Aristotle wrote many works on celestial bodies. He believed that the Earth is a sphere and it is located in the center of the universe. The geocentric model (Earth in the center) of the space construction was widely recognized. In the third century BC Aristarchus of Samos was the first to propose a solar system (the Sun in the center) of the solar system, but he was then ridiculed and forgotten. In the second century BC Hipparchos of Nicaea, a Greek mathematician and astronomer, quite accurately estimated the distance from Earth to the Moon with his calculations. He also created the oldest catalog of stars and a system of magnitude systems for determining the brightness of objects in the sky. His greatest discovery was the perception of the earth axis's precession (the phenomenon of changing the direction of the axis of rotation of the rotating body). Until the year 100 AD The Greeks created the foundations of mathematical astronomy.
Claudius Ptolemy as depicted by a 16th-century engraving

The last great astronomer of antiquity was Claudius Ptolemy. He worked in Alexandria in the second century AD He created an extensive mathematical theory that allowed predicting the movements of celestial bodies. Ptolemy was certain that the objects in the sky could only move around well-defined circles. In its system, the planets roam in a uniform motion on circular orbits. And because even simple observations of the sky show something else, Ptolemy developed the system into small circles that circulate on larger ones. This is shown in the diagram below, where, according to this theory, the Earth is a blue point, and red is the Sun. In addition, it shifted the Earth slightly in relation to the center of the orbits of the bodies around it. The Ptolemy system at that time well described the planet's movements, but today we know that it isn't real, yet we can see clearly how mathematical knowledge and precision of calculations gradually over time has replaced faith in stellar gods.
Greetings to lovers of Astronomy!
References:

This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail in collaboration with @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing then consider voting both projects for witness by selecting stem.witness and curie!
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!