Clinical Characteristics of Lung Abscess
Next, the next topic to be treated is one of the complications of ill-treated and unresolved respiratory processes, such as the formation of Lungs Abscesses, which corresponds to those limited collections containing pus, odorless or foul-smelling, developed in full pulmonary parenchyma.
Lung abscess is described as a suppurative process. Well defined radiologically, usually product of poly microbial organisms, it progresses over time to central necrosis and may compromise one or more areas of the pulmonary parenchyma.
Anatomy lungs breathing human health respiratory. Public domain image. Source Pixabay
Causal Agents
As described above, most abscesses are of Polymicrobial Etiology, with 95% of cases by anaerobic microorganisms. Gram-positive cocci such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumonia may also be involved.
In immunodeficient patients, the agent Mycobacterium tuberculosis, capable of causing bronchiectasis, infected cysts and even pulmonary infarctions, has been isolated very frequently. In its evolution, it forms a cavity that later fills with infectious liquid known as "abscess". As for the anaerobic microorganisms (Clostridim perfringens, septicum and peptostreptococcus), however, there are frequent mixed infections in which microorganisms of the oropharyngeal flora participate. Finally, the most frequently found aerobic germs are staphylococcus, hemolytic and non-hemolytic streptococcus and E.coli.

Micrograph obtained from TEM of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Public domain image. Source Wikipedia. Author: Elizabeth "Libby" White (PHIL # 8433). CC BY-SA 3.0
Physiopathology
The microorganisms have the capacity to reach the lung by four possible routes, or also called entry doors and these are: post-pneumonic (subsequent to respiratory process type pneumonia), by hematogenous dissemination, by direct extension or by contamination. The bacterium most frequently responsible for lung abscesses is staphylococcus, which presents as pneumonia accompanied almost always by pleural effusion.
Two mechanisms are recognized in the pathogenesis of lung abscess:
The hematogenous dissemination as a result of septic processes, originating septic thrombus, coming from infected peripheral veins; usually the most frequent germs are the coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative coagulase-staphylococcus and enteropathogens.
By direct secondary extension to infectious processes such as hepatic abscesses that can be bacterial, amoebic or mixed. The oropharyngeal aspirational etiology is more common in adults, where the aspirated material, by gravity reaches the lung, and the affected lobe depends on the position and time of aspiration. In the supine position, the posterior segment of the upper lobes and the apical segments of the lower lobes are the most severely affected.
Classification
Lung abscesses can be classified into primary and secondary.
Clinical Manifestations
Initial manifestations depend on the patient's immune status and the causative agent, which may be expressed by fever, productive cough, generalized weakness, and anorexia.
This symptomatology progresses and is associated with a state of bedriddenness with very high fever and pleuritic pain that is more intense on the side of the lung lesion, as well as weight loss and anemia. Finally, the patient refers cough with hemoptoic expectoration, vomica type and halitosis.
Diagnosis
Laboratory
Blood cultures: May be positive in patients with Staphylococcus Aureus infection and gram-negative bacilli, which are suspected by hematogenous dissemination.
Sputum culture, with gram, Bk and KOH coloration, both for aerobic and anaerobic germs and gram positive and negative.
Pleural Liquid Culture may be requested in those patients with Lungs Abscesses associated to Pleural Effusion, which by means of diagnostic and/or therapeutic thoracentesis can isolate the causal agent.
Imaging studies
The diagnosis is confirmed by X-ray and chest CT scan (Rx Tx, TC Tx).
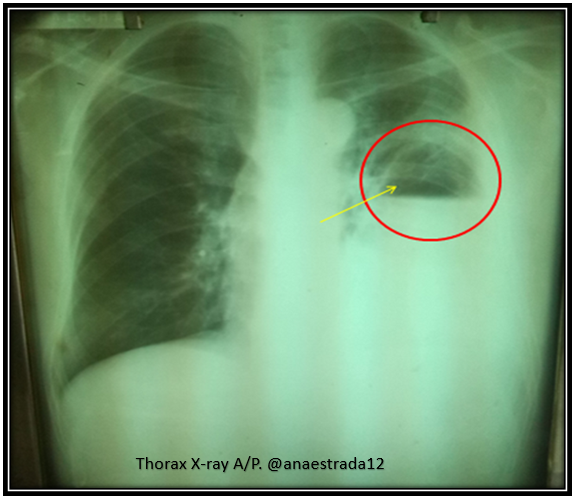
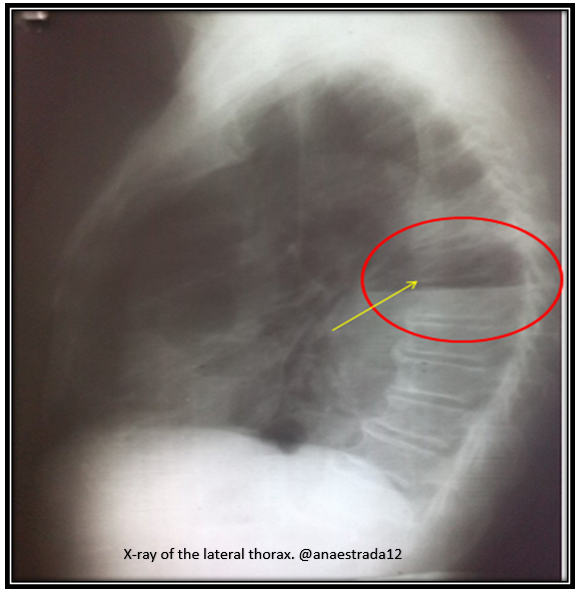
Where the pathognomonic sign of this entity in the chest X-ray is the presence of a cavity with hydroaeréo level.
Fibrobronchoscopy (FBC) with bronchoalveolar lavage (LBA) is indicated in cases of torpid evolution or suspicion of an underlying neoplasm. There are currently no guidelines to support its routine use in diagnosis.
Treatment/Conclusions
The medical treatment has its strong base in antibiotic therapy, preferably combined where the most frequent is the use of Clindamycin is the most recommended antibiotic associated with a broad-spectrum antibiotic, where the common is the use of Cefalospirin 3rd generation, or in certain opportunities is accepted the use of an Aminopenicillin with an inhibitor of betalactamase, thinking of gram positive agents.
Metronidazole is usually another good alternative associated with third generation Cephalosporins such as Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone. There is controversy about the duration of treatment some literature recommend a minimum of three weeks and others are based on prolonged treatment of 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the patient's clinical response, radiological evolution and resolution.
The indication for surgical drainage is due to the failure of medical treatment, which may be associated with neoplastic process more frequently.
Sources of support in the publication

steemSTEM is a project of the chain of blocks that supports the scientific content in different areas of science. If you want to know more about this wonderful project you can join the server in discord
This article will be published at https://www.steemstem.io/
I hope you enjoyed my content.
Muy buen artículo, gracias por compartirlo Dra! Entonces, un Rx lateral sería el ideal para ver la cavidad y lograr un diagnóstico preciso, más que uno A/P o P/A?
Posted using Partiko Android
Once again a very nice and an easy-to-read article.
Thanks for this and Steem on!
Thank you very much @chappertron for the support, the idea is simple! that all people who are not familiar with this area can understand very clearly the content
Mission successful!
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @utopian-io.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness and utopian-io witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Thanks for having added @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post. This granted you a stronger support from SteemSTEM.
Thanks for having used the steemstem.io app. You got a stronger support!
Thanks @steemstem
Hi @anaestrada12!
Your post was upvoted by Utopian.io in cooperation with @steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV
I agree with @chappertron. It is quite easy to follow. Thanks for this!
Thank you @lemouth it's a pleasure for me that this article is to your liking..