THE BIOGRAPHY OF THE UNIVERSE - Birth of the Universe (Part 1)
So what actually happened in the beginning? How did we get here? These questions have created a controversy among professional in the fields of religion, philosophy and science. Some people think they are absolutely sure of how and who created the universe, and others are simply agnostic about it. For starters, I do not claim to know how the universe started and since no one really knows what gave birth to the universe, I will attempt to take you back to the time in which the universe was just a baby - because for now, that's how far we can go.
The universe is presently 13.7 billion years old. Since then, it has advanced through different stages. During the early stages of the universe - less than a second old - the universe was said to have gone through its most notorious activities, far notorious than other activities presented 2 seconds to 13.7 billion years later.
Our best theory of how the universe came to be what it is now is 'The Big Bang'. In an attempt to explain what happened let's break down the timeline of the universe into its different stages.
The Plank Era
This is the first known stage of our Universe, beginning from 0 to 1043 seconds old. Our current understanding of general relativity suggests that prior to this time, the universe was a singularity. Everything, all the matter, energy and forces were compressed in a single point of 1035 meters with a temperature of 1032 degrees Celsius.
We have reasons to believe that nature’s four fundamental forces: gravity, the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force all had equal potentials and were unified as one rudimentary force. This idea is called the grand unification. In a time range between 1043 seconds and 1036 seconds, gravitational force is disunited from the others which leads to the generation of the first elementary particles.
Inflation
The strong nuclear force was next to leave the grand unification and this happened within the period from 1036 seconds to 1032 seconds and this caused the very fabric of spacetime to expand at a very alerting rate - this is known as the Cosmic inflation. What happened was that in less than a split second, the inner measurements of the universe expanded from a singularity to the size of a tennis ball - its circumference being roughly 10 centimetres apart. Elementary particles called gluon plasma formed in the unification were then scattered, covering the entire surface of the universe like a very thick boiling soup of quarks.
During the 1930s, astronomer Edwin Hubble found out that the light coming from distant galaxies, which appeared red, shifted when they pass through a prism. As he observed, he noticed that the more remote from us the galaxies were, the redder shifted they appeared. This experiment demonstrated by Hubble meant that the universe is expanding, transporting galaxies and clusters alongside with it, and it still is.
For decades after the time of Hubble, no one knew why or how the universe was expanding exponentially. Today we have evidence that suggests that the reason for this growth is because space itself is expanding.
The sense of distance within the universe is itself changing, although at this time it is far too small an effect to see on less than an intergalactic scale
The Electro-weak force
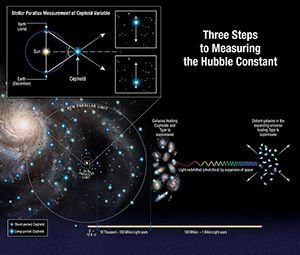
Three steps to the Hubble constant by NASA, ESA, A. Feild (STScI), and A. Riess (STScI/JHU) with Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported license
The Electroweak force is then separated from the grand unification. This caused the process that brought rise to a whole lot of complex particle. Z bosons, W bosons, and Higgs bosons are confederates of the interactions forming what is today called the Higgs field.
I'll take some time to talk about the Higgs field.
What is it, really? This field is one of the most important properties of the fabric of the universe. I came across an awesome representation explaining the Higgs field in the New York Times, they used a short animated comic to compare the Higgs to snow and compared particles to people trying to swim through the snow.
The Higgs is a field of particles called bosons, some particles like light do not interact with this field, therefore, they move with the universal speed constant and other particles like matter interact with this field making them go through space slowly. I like to think of it like swimming, the water molecules make us move slowly when we are in the pool. The universe is a pool of the Higgs field, the stuff that makes us up interacts with this field - if it didn't I probably would be moving through space like my favourite DC hero THE FLASH.
So to break it down, particles that do not have a mass to move with the speed of light for example photons - they do not have mass because they do not interact with the Higgs field. Particles with mass move slowly and have mass because they interact with the Higgs field. The period for this stage of the universe, when the Higgs particles were created is between 1036 seconds to 1012 seconds permitting a universe created completely out of radiation in order to support matter.
Quarks
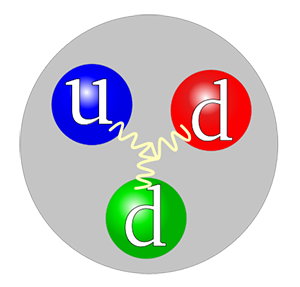
Neutron quark structure by Jacek rybak with Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
These little guys make up the atoms, they are completely massless particles that arrange themselves in a certain configuration which made the atom and essentially all the physical matter in the universe.
Tiny particles that makeup neutrons and protons are known as quarks, when added with electrons, makes up an atom. Before we had the particle accelerator it was commonly accepted that electrons, protons, and neutrons were all unit particles. Unit particles are particles that cannot be divided into something else. We now know that protons and neutrons are composed of quarks bound together by gluons - A gluon is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle for the strong force between quarks.
The different types of quarks are divided into 6 flavours. These different flavours are known as bottom, strange, down, up, charm, and top. Up-quarks, top-quarks, and charm-quarks all possess a charge of +2/3. Down-quarks, bottom-quarks and strange-quarks all possess a charge of - 1 ⁄ 3. Every quark produced is entangled with its antiquark which is opposite in charge- in that way they can cancel each other out; so 0 is also equal to 1-1.
As the quarks and electrons forge in exponential numbers with inflation it causes the universe to cool down to about 1015 degrees and all the forces are separated converging to their present form. This stage of the universe is called the quarks Era. The quarks conquered the universe and ruled the world from 1012 seconds to 106 seconds BC - get it?.
Quarks and antiquarks annihilate each other upon contact, but, in a process known as baryogenesis, a surplus of quarks (about one for every billion pairs) survives, which will ultimately combine to form matter - Physics of the universe.
Hadrons
This stage is characterized as the result of bounding quarks. The force that does this bounding is also responsible for bounding molecules together. It is the electromagnetic force.
There are two types of Hadrons
BARON & MESONS
Three quarks combine to make Barons and two pairs of opposite quarks combine to make Mesons. Protons and neutrons are examples of barons.
The heat density of the universe reduces rapidly down to 1-trillion degrees Celsius . This conversion from heat to kinetic energy permitted quarks to form.
The universe’s temperature decreases to about one trillion degrees, cold enough to permit quarks to combine and make protons that combine with electrons to form neutrons. This entire process results in the production of scattered neutrinos, these neutrinos are still moving through space, even now.
Neutrinos re-combine into new proton-electron pairs. The only rules governing all this apparently random combining and re-combining are that the overall charge and energy (including mass - energy ) be conserved. - physics of the universe.
Apparently, the universe is in the business of recombination. Just randomly trying new things, some fail like failed stars and extinct Animals while other successful atoms like nature itself.
At this stage, the universe is 1-Second old. The Hadron Era took about 106 to one second. Yes, everything that I just explained about the big bang up to this sentence happened in one second. The next article will cover how the universe evolved from this point to when it created the only home we have ever known- the Earth.
References
HOW STUFF WORK | Big Bang Theory


Dear friend, you do not appear to be following @wafrica. Follow @wafrica to get a valuable upvote on your quality post!
Now following @wafrica
There are many accounts of the creation of the universe. I read a very hilarious account (I think the fulani account) that stated that the universe was created out of a huge drop of milk :)
A drop of milk? holy cow, how fascinating.
Sure it is
what the hell. Lol.
little wonder why they're fond of cattle rearing.
Cattle rearing? No be me talk am oo :p
Good read brother, thanks for yesterday, things are all sorted now.
You have to be engaging with the steemstem community if you haven't already been doing so. Votes are weighed by your behavious in the community now. New rules.
How's it going sir?
Glad I could help.
About engaging with the Steemstem community, I seldom do that...but I will put more effort now that you've mentioned it.
And am doing okay...