LEARNING HOW TO PLAY THE VIOLIN PART 1
At the end of the class the student should be able to know what a violin and it's bow is and also parts of the violin.
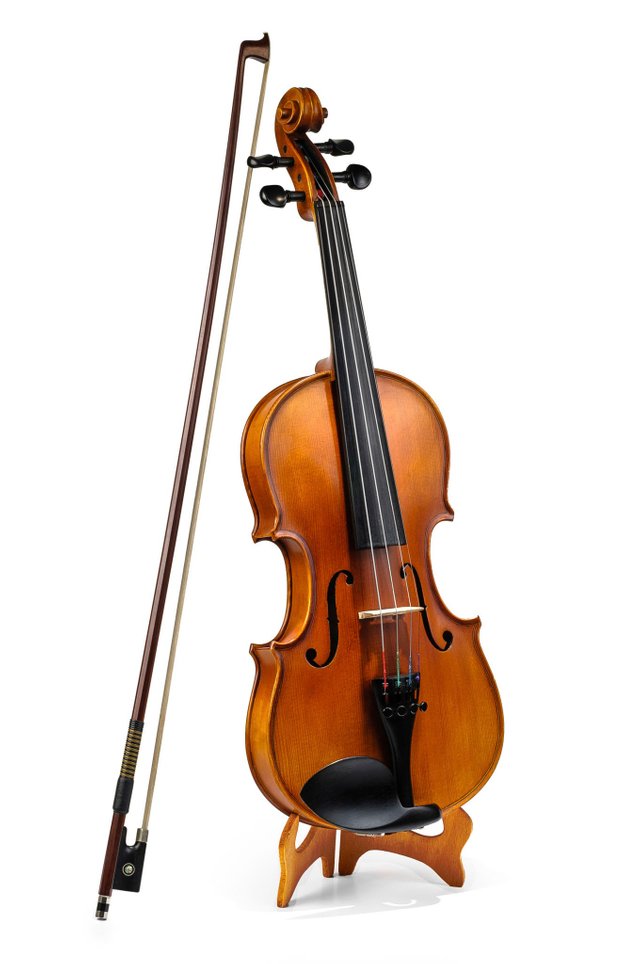
WHAT IS A VIOLIN?
A violin is a stringed musical instrument of treble pitch, played with a horsehair bow. The classical European violin was developed in the 16th century. It has four strings and a body of characteristic rounded shape, narrowed at the middle and with two f-shaped soundholes.
WHAT IS A VIOLIN BOW?
In music, a bow is a tensioned stick which has hair coated in rosin affixed to it. It is moved across some part of a musical instrument to cause vibration, which the instrument emits as sound.
Now knowing what a violin and a violin bow is,let's go into knowing the parts of the violin.
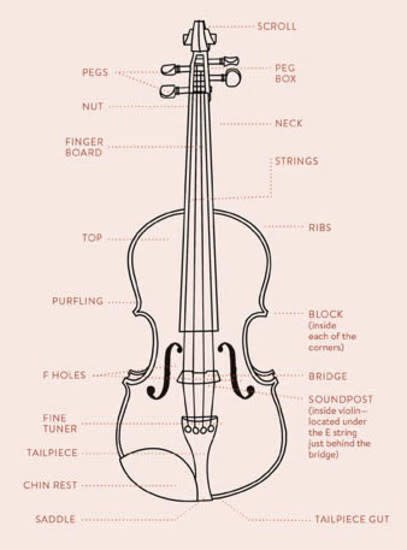
PARTS OF THE VIOLIN
- SCROLL: The decorative top of the violin. It’s most often carved in the shape of a scroll but is sometimes carved in another shape, such as a person’s head.
- PEGS: Four wooden pegs around which the strings are wound. They are used to tune the instrument’s strings. Tightening a string raises its pitch; loosening a string lowers its pitch.
- PEG BOX: The enclosure in which the strings are wound onto the pegs.
- NUT: A small piece of wood between the pegbox and fingerboard. It has four notches, one for each string to emerge over the fingerboard.
- NECK: The part of the violin between the body of the violin and the pegbox and scroll.
- FINGERBOARD: The surface where the fingers press down on the strings. It’s generally made of ebony.
- TOP: The front of the violin. In most violins, the top is made from spruce wood and the back is made from maple wood.
- RIBS: The thin strips of wood that wind around the sides of the violin, connecting the top and the back to form the soundbox of the violin.
- STRINGS: A violin has four strings tuned in intervals of fifths. From lowest to highest (left to right) they are G, D, A, and E. The strings are made from a variety of materials, including steel, synthetic materials and/or animal gut. They are strung over the fingerboard, from the pegs to the tailpiece.
- PURLING: A thin strip of three-ply wood inlaid in a channel around the edge of the violin to protect the instrument from damage. It may look like an outline drawn around the edge of the violin, but its purpose is actually more protective than decorative.
- CORNER BLOCKS: Wooden blocks inside the violin that stabilize the construction of the instrument.
- F-HOLES: The two holes from which sound emerges from the violin. They are shaped like cursive fs.These, combined with the violin’s hollow build, promote resonance.
- BRIDGE: A decorative but functional piece of maple wood that balances underneath the strings and transmits vibrations from the strings into the body of the instrument to create sound. The bridge of the violin is not glued on, it is held in place by tension. The force that the strings exert on the bridge is equal to about 90 pounds.
- SOUNDPOST: A wooden post located inside the violin, under the right side of the bridge. It is crucial for transmitting vibrations of the strings into the body of the violin to create sound, and its placement can change the quality of that sound, in terms of volume and/or tone quality.
- FINE TUNER(s): Small tuners located on the tailpiece. They tune the violin but in smaller increments than the pegs do. Smaller violins often have fine tuners for all strings, but full-size violins tend to have them only for the E string.
- TAIL PIECE: The somewhat triangular piece of wood where the strings are attached on the lower end of the violin.
- TAIL PIECE GUT: The cord that attaches the tailpiece to the violin.
- CHIN REST: A shaped piece of wood or plastic on which you rest your chin and jawbone. It’s attached near the tailpiece.
- SADDLE: A block on the inside of the violin that helps support the tailgut and the tension of the strings.
- PICKUP: Found on an electric violin, a pickup converts the violin’s acoustic vibrations into an electrical signal, which is then sent to an amplifier (much like is done with an electric guitar, an electric bass, or an electronic keyboard).
INSTRUCTOR CHIDIOMIMI (CHIDEX)
If you are ready for part 2 of the class please vote for this and also drop a Hi on the comment box