Digital Communication #2: Digital Modulation
OBJECTIVES:
✔ To explain digital modulation
✔ To identify the different digital modulation schemes
✔ To discuss the operations and features of the different modu
KEY TERMS:
🔑 Digital Transmission is the transmittal of digital pulses between two or more points in a communication system
🔑 Digital Radio is the transmittal of digitally modulated analog carrier between two or more points in a communication system.
🔑 Bit Rate is the rate of change in the input of modulator.
🔑 Baud Rate is the rate of change in the output of modulator.
Source
Before anything else, let us first recall or understand the difference between Analog Signals and Digital Signals; and the difference between Analog Radio and Digital Radio.
💡The Comparison between Analog Signals and Digital Signals:
⚠ ADVANTAGES of Digital Signals
⚪Ease of Processing. Rather than being sinusoidal or having a continuous value of signals, the digital signal has a sequence of two discrete values. It can either be 1 or 0 but cannot be in between. These look like square waves.
⚪Ease of Multiplexing. Multiplexing is a method of combining signals so it is easier to combine discrete data than continuous.
⚪Noise Immunity. In [Digital Communication #1: Information Capacity] I explained noise. They are the unwanted signals that interfere with our signals. Because of the type of wave the digital signal possess, it is hard for the noise to penetrate the signal.
⚠ DISADVANTAGES of Digital Signals
⚪Circuit Complexity.
⚪Higher Cost*.
💡The Comparison between Analog Radio and Digital Radio:
⚪In digital radio, the modulating and demodulating signals are digital pulses rather than analog waveforms.
⚪Digital Radios used Digital Modulation Schemes.
💡What is Digital Modulation?
*** Digital Modulation*** is the transmittal of digitally modulated analog signals (carrier) between two or more points in a communication system. It is sometimes called as Digital Radio – Tomasi.
Have you ever wonder how is it even possible to send informations without physical contact? Just like what I did, I typed these informations and sent it here but how? Is it a magic that the messages we send and post online just appear from nowhere? Of course not! And everything we believe as magic can be explained through science. So to correct you and make you understand how things in our electronic communication been possible keep on reading and let us untangle the curiosity in ourselves.
Whenever we send a message from a transmitter, there is what we call carriers. These are the high-frequency signals that carry our informations. They undergo a process called modulation. Modulation is where the carrier signal is changed and serves as the envelope or capsule of the information. Why is it that the carrier must be changed? Well that is the nature of modulation because if ever the information is the one being changed then the text you sent will also be changed. For instance you texted your partner the words”I LOVE YOU” but because of the unwanted changes of information occurred, then he/she may receive ”YOU ARE NOT THE ONLY ONE” instead. It is impractical to use analog modulation so nowadays, we use digital modulation. In the type of modulation we are currently using, the information signal is also digital, which could be encoded or computer-generated but still uses an analog carrier. An Analog-to-Digital Converter is use resulting to a more complex circuit than an Analog Modulation Technique.
Digital Modulation uses bit rate frequency or bf, which is basically the rate of change to the input of the modulator. It is represented by bits per second or bps.
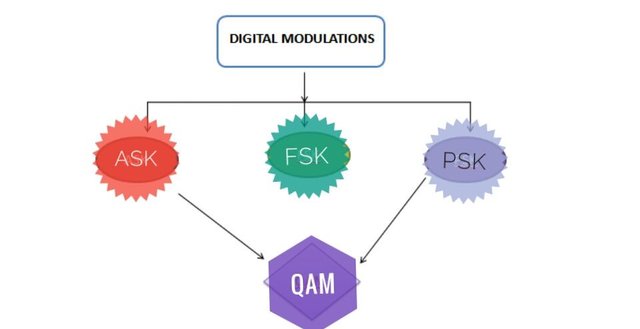
💡What are the Kinds of Digital Modulation?
1. Amplitude Shift Keying
It is simply a double sideband, full carrier amplitude modulation where the input modulating signal is in binary waveform. The output signal is always dependent on its input signal. It is basically an equivalent of an A.M. (Amplitude Modulation) wherein the amplitude of the signal is what being change. It is sometimes called as continuous wave modulation or on-off keying since because it is in binary form, it can only be shifted as on or off.
ASK Operation
If the INPUT logic is HIGH then the OUTPUT is the maximum peak amplitude of the carrier. While if the INPUT is LOW then the OUTPUT is ZERO. It only follows multiplication.
2. Frequency Shift Keying
It is a form of constant amplitude angle modulation that was proved by Emily Baudot, it similar to conventional FM or Frequency Modulation except that the modulating signal is a binary signal. This signal varies between two discrete levels. These levels can either be logic 1 known as Mark Frequency or logic 0 known as * Space Frequency*.
FSK Operation
If the INPUT logic is HIGH then the OUTPUT is the Mark Frequency. While if the INPUT is LOW then the OUTPUT is the Space Frequency.
3. Phase Shift Keying
This is another form of angle modulated, constant amplitude digital modulation --Tomasi
This is basically an equivalent of PM or Phase Modulation but the difference is that its input signal is in the form of binary.
Types of PSK
◾Binary PSK
⚫There are two possible output phases for a single carrier frequency which is either logic 1 or logic 0.
⚫When the digital signal changes it state then the phase of the output carrier shifts between two angles that are 180 degrees out of phase of the carrier.
⚫It is a form of suppressed carrier, square wave modulation of a continuous wave signal.
⚫It is sometimes called as Phase Reversal Keying or Biphase Modulation
◾Quaternary PSK
⚫The angle is being modulated while there is a constant amplitude.
⚫From the its name “Quaternary”, it basically means that there are 4 possible output phases in a single carrier frequency with different input conditions
◾8- PSK
⚫The incoming bits are considered in groups of 3 or known as tribits
⚫The incoming serial bit stream enters in the bit splitter
⚫The I (in- phase) or Q (quadrature) bit determines the polarity while the C (control channels) bit provides the magnitude.
◾16-PSK
⚫The incoming bits are considered in groups of 4 or known as quadbits
⚫The output does not change until 4 bits have been inputted into the modulator.
💫 Additional Learnings:
If you are to combine the Amplitude Shift Keying and the Phase shift Keying, you will be making another form of modulation which is known as QUADTRATURE AMPLITUDE MODULATION. In this form, the digital information is contained in both the amplitude and the phase of the transmitted carrier.
📚BIBLIOGRAPHY
Book: Wyne Tomasi. “Electronic Communication Systems”. Pages 349 and 377.
I hope for those who have been through this topic will kind of remember and add up some informations to themselves and mostly to those first timers in this kind of topic. It is essential to open up our minds to such learnings.
Yours Truly,
SISSY
I am a part of @steemitfamilyph. Join us! Follow - Upvote - Resteem - Comment
.jpg)

This is good information, I like your posts, you are pasting experts in this field, thank you for sharing
This is informative and educative.....
It seems you are vast in knowledge about computers.
Thanks, i have learnt few things though not really cleared.
Will forward my questions soonest
Wow. Nice post 😱😵😊👍👍
Great post.
Well I won't claim I understand everything you said but the post is attractive, well structured, highly organized and nicely packaged. Well done sissy.
Digital communication help people connecting each other and people now not only using it but also living it. Thanks for the post @sissyjill
What about unicorns? Just jokin, I only clicked because I could see your objectives and I was like I don't know what digital modulation is, so why not learn something new. In all honesty I learnt that its something that happens as part of the process to transmit data these days and then I tuned out as I am not a details person. You did make me think about it and that is something I would never had done. :)
I celebrate youd post.nice one