DIGITAL COMMUNICATION # 1: DIGITAL TRANSMISSION
The evolution of technology in todays era is as fast twice and more than enough than the human race. We have beem dominated by evolution of changes in technology allowing ourselves to have a comfortable way of living. As years goes by, technology and many studies have been conducted in order to answer the curiousity of a persons mind to gave answer from possibility. Human has been so eager on change of technology developing it from time to time until one day the idea will be claimed as we do. The age of machines and technology advancement are the key of success for some part of the sector in the industry by competing its updated softwares and tools used in production. Mindset of the individual has been reset to the greatest extinct of being intelligent by conducting a lot of researcg routine in order to acquire the best and nearest possible answers.
The world today is at the peak of innovations and advancement so if you have the idea of changing it by contributing those knowledge paused for a moment and let us connect each other by staying this post of mine. Maybe you'll have the idea you can actually acquire at the end.
KEY TERMS
Digital Transmission – is the sending of information over a physical communications media in the form of digital signals. Analog signals must therefore be digitized first before being transmitted.
Digital Signals – are described as discrete, their amplitude maintains a constant level for a prescribed period of time and then it changes to another level.
Analog Signals – the amplitude changes continuously with respect to time with no breaks or discontinuities.
Pulse Modulation – It is the conversion of information into pulse form for transferring pulses from a source to a destination.
Key Formula
Resolution = Vmax/Dynamice Range
fs=>2fa : where fs=sampling frequency ,fa= fundamental frequency
Objectives of the Study
•Define key terms in digital transmission
•Familiarize the different pulse modulation techniques
•Study the operations, processes, features of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
•Illustrate the highlights of delta modulation
•Elaborate Differential PCM
Advantages of Digital Transmission
•It is more immune to noise
•Digital pulses are better suited for processing and multiplexing
•Digital signals are simpler to measure and evaluate
•Digital systems are better suited to evaluate error performance.
DISADVANTAGES OF DIGITAL TRANSMISSION
•The transmission of digitally encoded analog signals requires more bandwidth.
•Analog signals must be converted to digital codes prior transmission and converted back to analog at the receiver.
•Digital transmission requires precise time synchronization between the transmitter and receiver clocks.
•Digital transmission systems are not incompatible with existing analog facilities.
PULSE MODULATION
Is the conversion of information into pulse form for transferring pulses from the source to a destination.
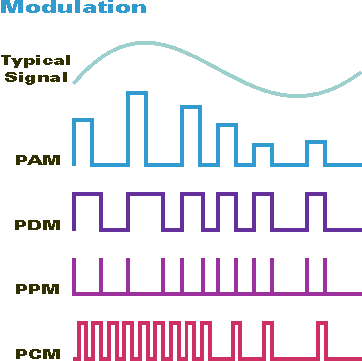
PULSE MODULATION AND ITS METHODS
Basically pulse modulation has four (4) types of methods this are the following;
PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION
Is a method of converting information wherein the amplitude of a constant width, constant position pulse is varied in accordance to the instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal.
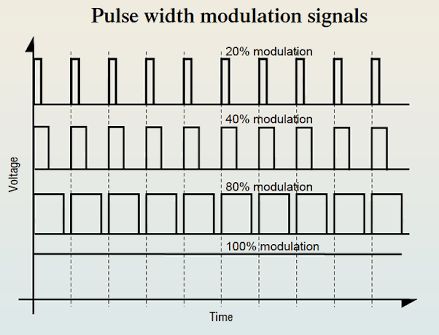
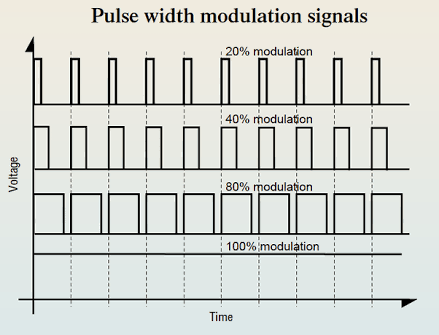
PULSE WIDTH MODULATION
Is the process where the width of a fixed amplitude pulse varies proportionally to the amplitude of the analog signal.
PULSE POSITION MODULATION
Is a form of pulse modulation where the position of a constant widthin a prescribed timeslot is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This method is seldom used in the application of the output.
PULSE CODE MODULATION
Is a sampled and converted to a fixed length, serial binary number for transmission. The binary number varies according to the amplitude of the analog signal. This method is the most widely and popularly used.
MODULATION
PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM) BLOCK DIAGRAM
FUNCTIONS OF EACH BLOCK
BANDPASS FILTER
It limits the frequency of the analog input signal to the standard voice band frequency range of 300GHz to 3000Hz. (antifoldover filter)
SAMPLE AND HOLD CIRCUIT
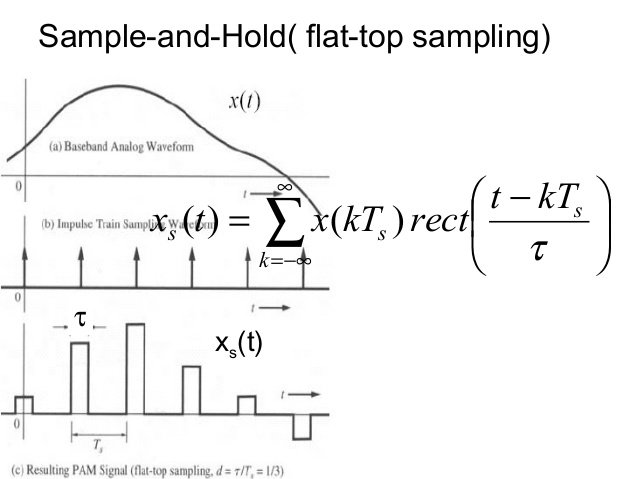
It periodically samples the analog input signal and converts the samples to multilevel PAM signal.
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC)
It converts PAM samples to parallel PCM codes.
DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTER (DAC)
It converts PCB codes back to PAM signals.
HOLD CIRCUIT
It converts PAM signals to its original form.
PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM) PROCESSES
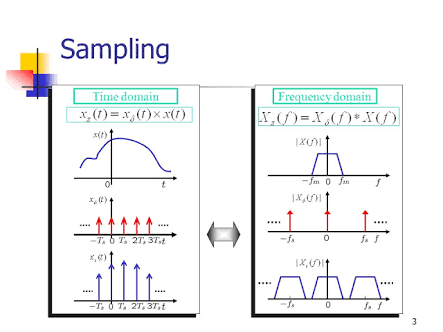
• SAMPLING
Is the conversion of the analog input to PAM signal
QUANTIZING
Is the assignment of the amplitudes to the PAM signals. It is a process of converting an infinite numbers of possibility to a finite number of conditions (rounding off the amplitude of flat – top samples to a manageable number of levels)
• Encoding
It is the assignment of binary codes of the PAM quantized signals ready for transmission.
Sampling Circuit
For the Analog-to-Digital Converter to accurately convert a voltage to a binary code, the voltage must be relatively constant so that the ADC can complete the conversion before the voltage level changes.
TYPES OF SAMPLING
NATURAL SAMPLING
Is when the tops of the sample pulses retain their natural shape during the sample interval.
FLAT-TOP SAMPLING
It is uses sample and hold circuit, the input voltage is sampled with a narrow pulse and held relatively constant until the next sample is taken.
SAMPLING
The Nyguist Sampling Theorem establishes the minimum sampling rate that can be used for a given PCM System.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS ENGR. OBISO, PAGE 29-33
Thanks you so much steemians for giving time reading this information. I hope you'll all appreciated by this. Have a nice day!
Currenly of life,
Benchcarr
I am a part of @steemitfamilyph. Join us! Follow - Upvote - Resteem - Comment
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.png)
.gif)
.gif)
.gif)
.png)
.png)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)