diversity of living beings (classification).

Being alive
It is a set of atoms and molecules that form a highly organized and complex material structure, involving molecular communication systems, which is related to the environment with an exchange of matter and energy in an orderly manner and has the ability to perform the basic functions of life that are nutrition, relationship and reproduction, so that living beings act and function on their own without losing their structural level until their death.
In biology, identification, naming and grouping of organisms in an established system. The many forms of life that exist must be named and organized in an orderly manner, so that biologists around the world can be sure they know the exact organism being studied.
The definition of groups of bodies should be based on the selection of important characteristics, or shared characteristics, responsible for the fact that the members of each group are similar to each other, and different from those of other groups. Current classification methods also seek to group groups into categories, so that they reflect the evolutionary processes underlying the similarities and differences between organisms. These categories form a kind of pyramid, or hierarchy, where the different levels represent the different degrees of evolutionary relationship.
The classification of plants and animals by structural similarities was established on firm systematic bases by the Swedish biologist Carl von Linne or Linnaeus.
Since many structural similarities depend on evolutionary relationships, the modern classification of organisms is at many points similar to that of Linnaeus based on logical structural similarities.
The classification unit for plants and animals is the species. This term is difficult to define but we can approach if we say that it is a group of similar individuals in terms of structural and functional characteristics, which in nature only reproduce each other and have a common ancestor. Neighbouring species are grouped into genera. Gender is a superior unity.
The scientific names of the organisms have two terms: genus and species in Latin. This system is called binomial.
Just as several species are grouped in genera, similar genera are grouped together in families. In turn, they are grouped in orders and these in classes. A group of classes can be called division if we are studying plants or cutting edge if they are animals. The philosophies (or divisions) are the great divisions of the kingdoms.
Today, due to the great development of cell research techniques, it has become apparent that the main division of living beings is not between plants and animals, but between organisms whose cells lack nuclear sheath and organisms whose cells have nuclear membrane. The first are called prokaryotes (before the nucleus) and the second eukaryotes (cores. true).
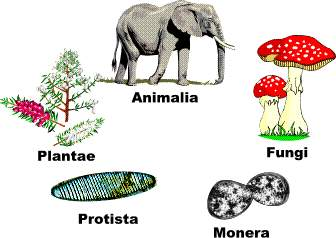
five kingdoms
Advances in science brought new knowledge and in 1969 Robert Whittaker replaced the unmanageable animal/vegetable dichotomy with the system of the 5 kingdoms: animalia (metazoa), plantae (upper vegetables - embryophytes), fungi (upper fungi), protista or protoctista (protozoa, eukaryotes and lower fungi) and monera (bacteria and prokaryotes algae).
This system, due to its great simplicity and usefulness, has remained in force until today, although it is now proving to be completely outdated.
It is based on differentiation by cell characteristics, nutritional requirements, tissue differentiation, etc.
The monkeys
The most primitive organisms, depending on their structure, are grouped in the kingdom of the moneras, divided into bacteria and blue-green algae or cyanophytes, which includes about 10,000 species. Because they lack a cell nucleus, they are called prokaryotes. Many of them are equipped with chlorophyll, a green pigment that allows them to perform photosynthesis, that is, capture light energy and transform it into chemical energy that they use to make their food.
Constituted by a single cell, they are the simplest living beings in terms of their structure; they do not have differentiated organs and in their interior is free DNA, a vital molecule for their functioning
The protists
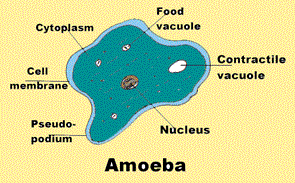
There is a not entirely defined space between the plant and animal kingdom: the protists, unicellular organisms endowed with nuclei, can move freely, which resembles animal species, but they have chlorophyll, which allows them to be nourished through inorganic substances, using sunlight as an energy source, which also resembles plants.
Among the protists, flagellate animals reproduce by cell division. In them, the cell has organelles or differentiated structures with specific functions and can present cilia or flagella, appendages that allow them to move. Until recently they were called protozoa because they had characteristics in common with animals; today they form a separate kingdom, divided into rhizopods, flagellate, hair and sporozoa.
Among these organisms, the best known are amoeba and paramecio. In this kingdom there are also beings closer to plants, the types of algae called pyrophytes and euglenophytes. Green euglena, for example, is one such organism. It lives in fresh water and is equipped with one or more scourges that allow it to move. Pyrophytes are yellow or brown algae, with two flagella. Other unicellular algae such as diatoms, which are endowed with a mineral silica cover, also belong to the kingdom of the protists.
The mushrooms

Another kingdom whose definition is still under investigation is that of fungi. These are heterotrophic organisms, i. e. they cannot make their own food from inorganic substances, as is the case with chlorophyll plants. That is why they must be nourished with substances made by other living beings. They are a clear example of organisms that share the qualities of plant and animal kingdoms.
There is an intermediate form between the mushroom kingdom and the plant kingdom: lichens, which are associations between algae and fungi. Lichens inhabit very varied environments: deserts, higher mountains, tundra, arid terrain of steppes and Antarctic glaciers; they can live in these places precisely because of the symbiosis that exists between the organisms that form them: the fungus provides the absorbed humidity of the air and the algae, which has chlorophyll, makes the starch from which they feed.
Vegetables:

This kingdom, like the animal, is made up of individuals with very different levels of evolution, from organisms of few cells to trees many meters high. The plant kingdom arose when the first pluricellular algae adapted to the mainland about 500 million years ago. The lower floors are grouped into three subdivisions: talophytes (algae more developed than the protists), bryophytes (mosses and hepatic) and pteridophytes (equisetes, lycopodians and ferns). The superior plants are characterized by having flowers and seeds, and are subdivided into gymnosperms, whose seeds are exposed (pines, cypresses) and angiosperms, whose seeds are protected within the fruits (walnut, margarita). Angiosperms spread across the planet 120 million years ago, and constitute the most evolved and numerous subdivision of the plant kingdom, from the simplest flower to the most complex and colorful.
Animals:

In ancient times the first colonies of protists were formed, from which the simplest animals were derived: the poriferous (sponges) and the cnidarian (medusa, hydras and anemones).
Later, flat worms, mollusks (snails, squid), annelids (segmented worms) and arthropods (crustaceans, arachnids and insects). Echinoderms (erizos and starfish) share their origin with cords, or animals with corda or notocordio, a dorsal structure that serves as an internal skeleton. These include vertebrates: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. The first vertebrates were fish that evolved in many species such as sharks, trout and lamprey. Others, some 300 million years ago, originated amphibians and reptiles.
In the evolution of life, from the existence of water and emergent lands, the food chain was already constituted and in equilibrium: primitive animals fed on plants, which in turn were nourished with water, minerals and carbon dioxide. The first vertebrates living outside the water still needed water to lay their eggs. Later, reptiles began spawning and incubating on land, until they were able to reproduce and remain there all the time. Growing in size and evolution, some reptiles returned to the sea, others gave life to the dinosaurs of the Triassic period of the Paleozoic era. It is thought that birds are derived from some reptiles that developed wings and others originated mammals. These last two zoological types survived the dinosaurs, which disappeared at the end of the Cretaceous period, which succeeded the Triassic, because they could not adapt to the changing conditions of the planet.
In the Tertiary era, mammals perfected their metabolism and adaptation to climate change. His brain became more complex and the family of bipedal hominids (which walked on two feet), the direct ancestors of man, emerged.
Unity of living beings
Despite the great variety of living beings that exist in nature, all of them have a series of common characteristics: they are basically made up of the same chemical elements (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus mainly), which are grouped in the same chemical compounds (glucides, lipids, proteins and nucleid acids).
In addition, all living beings are made up of one or more cells. The cell is the unit of structure and basic function of organisms, i. e. it is the smallest part of a living being capable of performing vital functions.
All living beings perform three vital functions: nutrition, relationship and reproduction.
The nutrition function consists of the ability to take substances from outside and, based on them, to renew and conserve the body's structures and to obtain the energy needed to develop vital activity.
The relationship function enables organisms to detect changes in the environment in which they live and develop an adequate response to adapt and survive.
The relationship function is essential to maintain the life of the species, as it allows living beings to form copies of themselves.
.gif)
REF:
http://www.mysciencesite.com/science6LT1.html
https://es.slideshare.net/ParthKshirsagar1/diversity-in-living-organisms-70664453
http://www.learncbse.in/diversity-living-organisms-cbse-notes-class-9-science/