What Is Staking and Unstaking in EOS?
Hello, this is Wizpace Ronald.
Today, let's look briefly at the concept of EOS staking.
The EOS coin has the following status and functions.
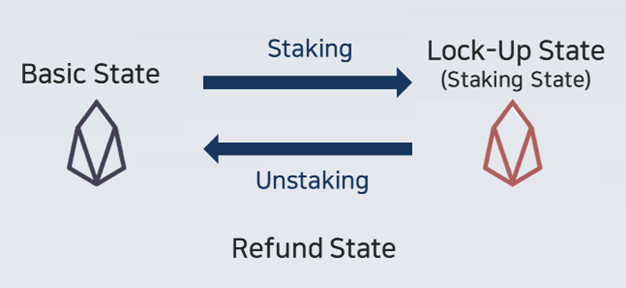
Basic State
- Also known as Unstaking State, it has fluidity and can be traded and transferred.
Lock-Up State
- Also known as Staking State, it cannot be traded or transferred because it doesn’t have any liquidity, but you can use the function of EOS Coin. The staked EOS coin has the following functions.
Resource allocation : You can use as much CPU and network resources as staked.
Voting : You can vote for 30 BPs with 1 EOS.
(Please refer to the following article for an explanation of voting and BP.)
- So, it is said that when EOS staked, resource use power and voting power are generated.
- Several BP and Dapp developers are providing staking and unstaking tools.
Examples: EOStoolkit https://eostoolkit.io , DEXEOS https://dexeos.io , etc
Unstaking
It is a process of returning to the basic state with fluidity from the staking state assigned to the CPU and network resources, and it takes three days (72 hours) to reach the basic state.
Refund State
If you unstake EOS, it will not return to the basic state immediately and will remain in the refund state for 72 hours.
So why did EOS create these staking / unstaking concepts?
This requires complex and profound explanations, but we can state 3 reasons for easy comprehension: 1. Safety 2. Resource Use 3. Voting
1. Safety
It takes 72 hours to get into the unstaked state for transactions and transfers from the staked state. So if someone wants to steal your private key and steal assets, it has to go through 72 hours of the refund state. At this time, the unstaking transaction can be checked by entering the account name or EOS public key at some tools such as https://eosflare.io/, and can be withdrawn at any time before the unstaking is completed. Therefore, it can be said that it is safer from the danger such as hacking.
If you do not need frequent transactions, you can keep your assets more safely by staking.
2. Resource Use
The amount of CPU and Network available for you to use depends on the amount of staked EOS. The concepts of CPU and Network resources of EOS are as follows.
CPU resource : It is the hardware that processes the operation, and is the resource you need to perform all actions on the EOS, such as EOS transfers, account creation, and voting. You can use it in proportion to the amount of staked EOS. It is recorded on the EOS blockchain by measuring the amount of time it has been used, in seconds, in hours, and so on. It does not disappear when you use it, and after 24 hours, the assigned CPU resource is restored and can be reused.
Network resource : It is a network resource used to transfer data regarding EOS transmission, account creation, and voting on the EOS server. You can process data in proportion to the amount of staked EOS. Likewise, it will not disappear and will be restored after 24 hours.
Some services, currently being developed, will allow users to rent CPU and Network resources that they do not use to DApp developers.
3. Voting
People are allowed to vote only when they staked EOS, so that the whole system can fully follow the DPoS(delegated proof of stake). In other words, you have the right to vote as much as the amount of EOS you have. Also, 72 hours of unstaking time make it possible to minimize the impact of those who have short-term dumping and simple trading purposes.
So far, We've been looking at the concept of staking in EOS.
If you have any questions, please feel free to comment!


@dexeosio, you are interesting to read!