The National Aeronautics and Space Administration 🚀
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration
I recently published an article about Elon Musk's rocket (https://steemit.com/space/@lndesta120282/flacon-heavy) and I wondered about NASA.

NASA is the government agency responsible for most of the United States civilian space program. Aeronautical research is also NASA's domain. Since its creation in the late 1950s, NASA has played a dominant role in human space flight, solar system exploration and space research. Some of the agency's most outstanding achievements include the Apollo Manned Space Programs, the US Space Shuttle, the International Space Station, Space Telescopes such as Hubble, Mars Exploration by the Viking and MER Space Probes, as well as Jupiter and Saturn by the probes Pioneer, Voyager, Galileo and Cassini-Huygens.
NASA was created on July 29, 1958, to administer and carry out civil astronautics projects, which were previously supported by the various branches of the United States Armed Forces, in order to catch up with the advance taken by the United States Army Soviet Union. NASA takes over at this time the research centers of NACA, previously focused on research in the field of aeronautics. It now has a budget of approximately $ 18 billion and directly employs approximately 17,500 people and a large number of subcontractors located in ten space centers located mainly in the states of Texas, California and California.
Florida, Alabama, Virginia and Washington. Ongoing milestone missions are the completion and operation of the International Space Station, the use and realization of several space telescopes including the James Webb Space Telescope, the OSIRIS-REx space probes, Mars 2020, New Horizons and Mars Science Laboratory already launched or about to be launched. NASA also plays a key role in ongoing research on climate change.
NASA's manned space program has been undergoing restructuring since 2009 following the withdrawal of the US space shuttle scheduled for 2011 and the challenging of the Constellation program, which faces design and funding challenges. The Obama administration, following the recommendations of the Augustine commission, has decided to abandon the plan to return astronauts to the lunar soil by 2020 in favor of a more progressive exploration process that must be preceded by extensive research especially in the field of propulsion.
With this in mind, the development of the Space Launch System heavy launcher and the associated Orion capsule is under way. To compensate for the lack of a space station service system following the withdrawal of the Space Shuttle, NASA relies on during the 2010 Decade on the private sector, which must support the low-orbit service of the space station
History

In 1956, the United States and the USSR each announced that they would launch an artificial satellite as part of the scientific work planned for the International Geophysical Year between July 1957 and December 1958.
In the United States, the development of the satellite and its launcher is supported by the Vanguard program, entrusted to a team of the US Navy, but the project launched late and too ambitious chained failures. On October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union was the first country to orbit the Sputnik 1 satellite. This is a shock to US officials and public opinion, who until then had been convinced of their technical superiority. The Air Force and the US Army at that time also have space programs that exploit the work done on intercontinental ballistic missiles: it is the team of Wernher von Braun, working on behalf of the Army, which finally manages to launch the first American satellite, Explorer 1, on February 1, 1958 thanks to the launcher Juno I improvised from a Redstone ballistic missile.
Although reluctant to invest heavily in civil space, US President Dwight D. Eisenhower decided by a decree dated July 29, 1958 the creation of a civil space agency. This one, baptized NASA, must federate the American efforts to better counter the Soviet successes: the race for the space is launched.
NASA takes over the research centers of NACA, until now turned to research in the field of aeronautics but who for some years also work on launcher projects developed by the US Army in particular in the field of aerodynamics and propulsion. Military projects and their teams, including engineers commissioned by Wernher von Braun, are quickly transferred to NASA. The first manned flight project developed by NASA is the Mercury program, started in 1958 even before the creation of the agency, which should allow the launch of the first American in space.
On May 5, 1961, Alan Shepard made a first flight of fifteen minutes in the capsule Freedom 7: but it is only a simple suborbital flight because NASA did not have at the time of a sufficiently powerful rocket. President John F. Kennedy announces the launch of the Apollo program on May 25, 1961, essentially to recapture the American prestige undermined by the successes of Soviet astronautics, at a time when the cold war between the two superpowers is in full swing. NASA mandated by the president, must put a man on the moon before the end of the decade. It was not until the Mercury-Atlas mission 6 of February 20, 1962 that John Glenn became the first American astronaut to orbit the earth. Three other manned flights took place in 1962 and 1963.
Organization
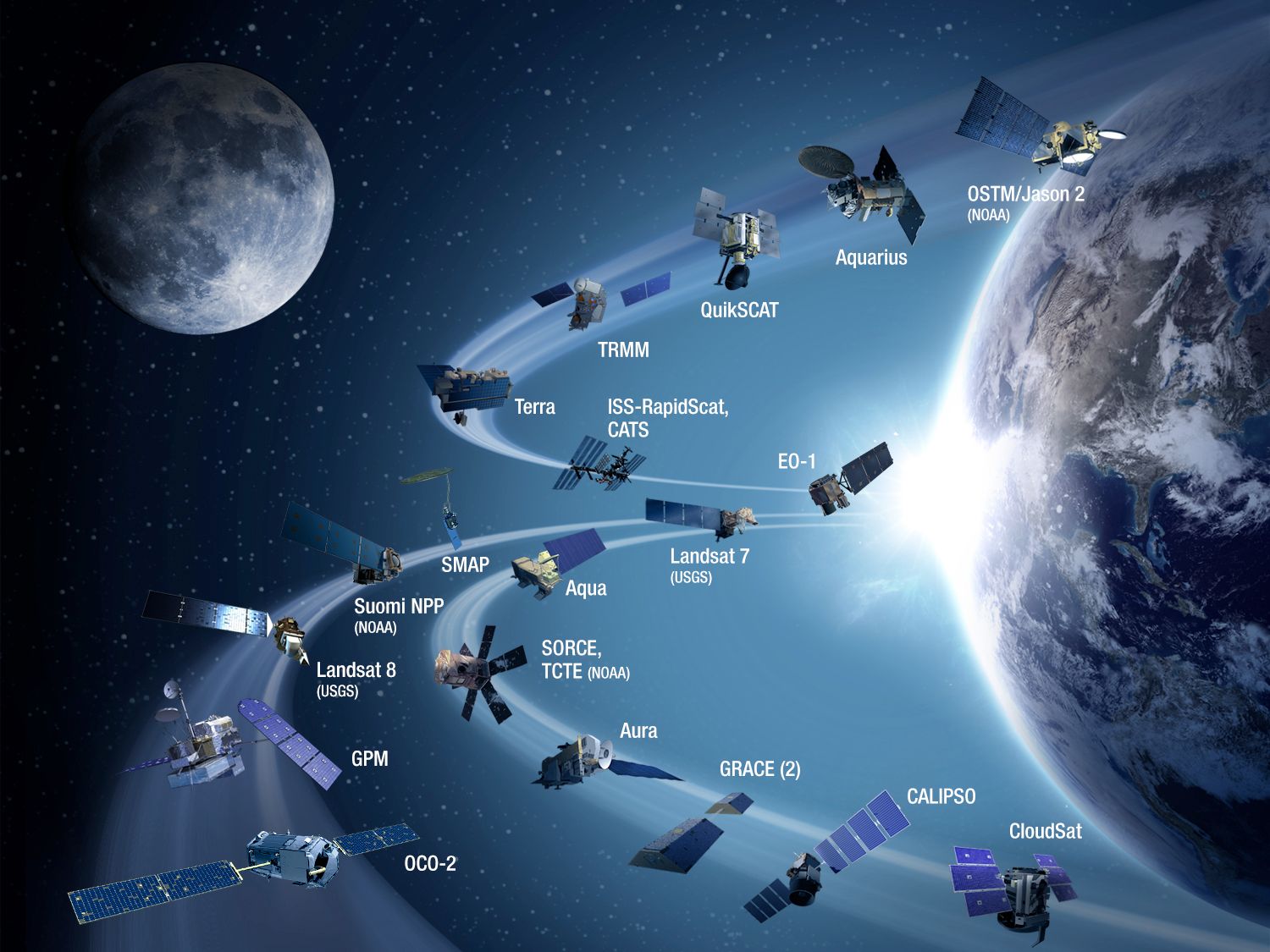

The NASA Administrator is appointed by the President of the United States, after consultation and approval of the US Senate. NASA's headquarters are in Washington. Four directorates are responsible for defining the space policy and controlling its implementation by the various NASA centers: the Aeronautical Research Directorate, the Science Directorate responsible for the scientific exploration of the Earth, the Solar System and the Earth universe, the direction of the Exploration Systems that carries out the necessary developments for human and robotic flights and finally the direction of space operations responsible for launching and monitoring missions.
US space policy and NASA
NASA spends about a quarter of its financial resources on purely scientific activities. These are divided into four themes which in decreasing order of budget are :
• Earth sciences that bring together the study of different atmospheric layers, the Earth's surface and the space environment from space.
• The study of planets and other celestial bodies of the Solar System using space probes.
• Astrophysics dominated by the realization and exploitation of space telescopes.
• the study of the Sun.
About 20% of the budget is devoted to support activities : management of space centers, maintenance and construction of equipment. Aeronautical research, the original activity of the agency, weighs relatively little. Finally, almost 50% of the budget is spent directly or indirectly on manned spaceflight. This part of the activity is particularly fluctuating.
Study of planets
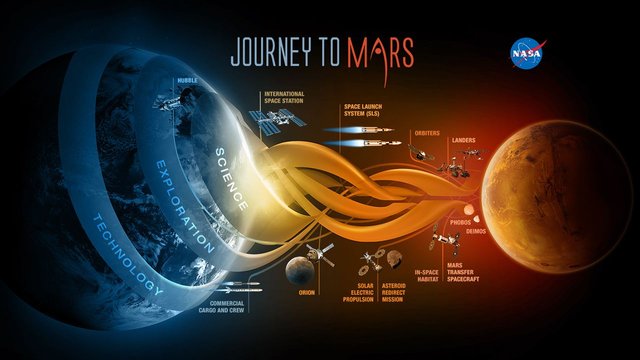
The planet Mars is the subject of a separate program. No less than five missions are in progress. Mars Odyssey is an orbiter who studies since 2002 the geology of Mars and seeks in particular the presence of traces of water. Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is a heavy orbiter of more than 2 tons, carrying a particularly powerful camera, which entered service in 2006 and whose main mission is to establish a detailed map of Mars.
The MER, Spirit and Opportunity rovers are continuing their ground exploration mission that began in 2004 and has been extended many times. Mars Science Laboratory carries the 775 kg Curiosity rover that has been surveying the Gale crater since 2012 with 70 kg of scientific instruments. This is the most complex and expensive project ($ 2.5 billion) of the last decade. It must help scientists to determine whether life could have existed on Mars and to refine the study of the climate and geology of the planet. MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN) is an orbiter in orbit around Mars since 2014 to study its atmosphere.
The March 2020 rover, which incorporates the Curiosity architecture, is to be launched in 2020. Its mission will be to select and collect samples for a future sample return mission currently neither planned nor budgeted.
The New Frontiers program includes ambitious missions whose cost is nevertheless less than 700 million USD. The first mission of this program, New Horizons, was launched in 2006 to study Pluto, which it reached in 2015, before flying over a Kuiper object on the edge of the Solar System. Juno, whose launch took place in 2011, must be placed in a polar orbit around Jupiter to study its magnetic field. OSIRIS-REx asteroid sample return mission was launched in 2016.
In addition to the complex, costly and time-consuming missions that are rare, NASA is developing missions under the Discovery program that cost less than US $ 425 million and whose development time should not exceed 36 months. The number of scientific instruments is reduced and the development is entrusted to a single team.
The operational Discovery missions are the MESSENGER probe, launched in 2008, which completed its mission around Mercury in 2015, Dawn launched in 2007 which successively placed itself in orbit around the asteroids Vesta then Ceres to study them and the lunar orbiter LRO launched in 2009. The missions under development are the Martian lander InSight which was launched in 2016 and surveyed the interior of this planet and the STROFIO instrument aboard the spacecraft space probe BepiColombo of the Space Agency European Union to Mercury.
NASA is the most famous and technologically advanced space organization. Few people who have never heard of NASA and what they are doing. News headlines often tell us about the next success or achievement of NASA.
This space agency has often gained popularity thanks to the films. Most of the films about space are somehow connected to NASA. I think their fame is well deserved and justifies itself.
I am impressed by their further plans for space exploration and data collection. These are multimillion-dollar projects - but they are beneficial for all of humanity. Their cooperation with Ilon Mask says that in the future, the expenses for flights to space will be reduced - this will allow us to save money and expand our own programs.
Thanks for the interesting post @lndesta120282
nice article
It has Increased the personnel of work since 2009 I guess NASA is really improve and have been bettered since inception making progress when it comes to the development of humanity.
Wow, this is great, what a comprehensive review on NASA , it's origin and function. Thanks for educating us on this subject matter. It's very informative
Hi, I found some acronyms/abbreviations in this post. This is how they expand:
thanks for sharing ... I know more about NASA now
Nice poste ..bravo
I absolutely love the theme of space, excellent content very successful @indesta120282
NASA is the best institute for intending aeronautics.. Have a cousin there.. Had a little idea about its operational details as listed on this post... Thanks for sharing mate
Well written. Time to go check out the post about the Falcon-Heavy now