Importance of Hashing Algorithms and Why should we Ask Ourselves if Cryptography and Encryption are Safe from the latest development of Quantum Computers
Rise of Quantum Computers
Quantum computers would be exceptionally fast at a few specific tasks,
but it appears that for most problems they would outclass today’s computers
only modestly.
This realization may lead to a new fundamental physical principle
Some Question we need to ask Ourselves
Suppose such a Quantum Computer were constructed tomorrow - what would this mean for Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
How close we are to Quantum Computers that could crack Cryptography?
Well, as for now we can assume that Quantum Computer are not going to pose any threat's when it comes to Cryptology & Encryption, where high data processing power may have the ability to breach and manipulate information by solving algorithmic hashes to manipulate a blockchain.
We should be aware that recent advances in the field should make us worry about future-proofing systems being built today to protect critical infrastructure that will be in service for perhaps decades.
It's not just about Cryptocurrencies, but Online security is at risk because Quantum Computers are so powerful that they can put an end to outdated Encryption, through brute force of computing power. Banks, Governments and pretty much everything we interact on the World Wide Web, should have some sort of Security Protocol based on Encryption, so please get rid of the idea that data can be 100% safe from Hacks.
Cryptocurrency Protection Against Quantum Computing
Post-quantum cryptography refers to cryptographic algorithms (usually public-key algorithms) that are thought to be secure against an attack by a quantum computer. This is not true for the most popular public-key algorithms, which can be efficiently broken by a sufficiently large quantum computer.
The problem with the currently popular algorithms is that their security relies on one of three hard mathematical problems: the integer factorization problem, the discrete logarithm problem or the Elliptic-curve discrete Alogarithm problem. All of these problems can be easily solved on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer
Basically, ECDSA is compromised, But Hashing isn't. With a quantum computer, you could easily deduce the private key corresponding to a public key. If you only have an address, which is a hashed public key, the private key is safe. Anyway, to spend a transaction, you need to send the public key. At that point you are vulnerable, but the attack is not straightforward.
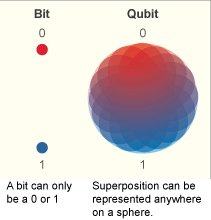
Quantum Computers are made up of devices called Qubits. Researchers expect that some chemistry simulations and machine-learning problems can be taken on with just hundreds or thousands of Qubits. Cracking a Cryptographic key of the kind used commonly today would require hundreds of millions of Qubits.
IBM has announced to release a 5-qubit Quantum Computer to the general public Source
So it will take reasonable amount of time for Quantum Computing to Develop to a stage where it could solve any Encryption Protocol but Did you know that the NSA outlines the switch for NSS (National Security Systems) from Suite B cryptography to the CNSA (Commercial National Security Algorithm Suite). Just to prepare themselves from Quantum computers.
Please be aware that there is already a number of interesting Quantum resistant public key algorithms have been proposed. However the NSA expects that NIST will play a leading role in the effort to develop a widely accepted, standardized set of quantum resistant algorithms alongside the general public.
Please Watch this Educational Video Above, this is somehow related to Steemit Keys
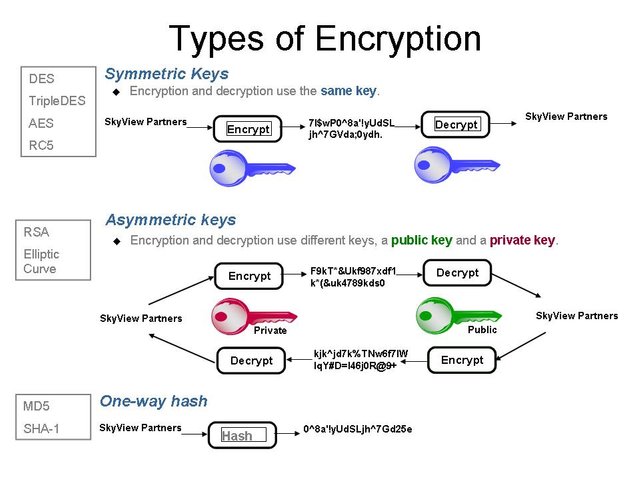
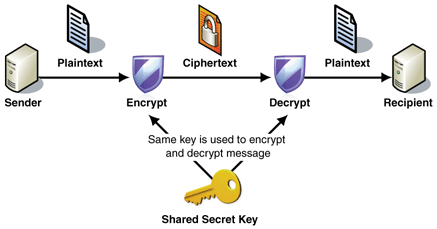
We already have Symmetric-key algorithms which are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both encryption of plaintext and decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys.
The NSA remarked that “The AES-256 and SHA-384 algorithms are symmetric, and believed to be safe from attack by a large quantum computer.
According to the NSA, the following Algorithms aren't safe from Quantum Computers:
- ECDH and ECDSA with NIST P-256
- SHA-256
- AES-128
- RSA with 2048-bit keys
- Diffie-Hellman with 2048-bit keys
Art of Hashing
Let's try to learn some basic important technological terms here, so you get the idea of what hashing is all about?
A Hash is basically a method for guessing the combination of a lock, by turning a random large number into a smaller number by taking certain actions.
For example let's say you randomly pick a large number and pick the 1st, Middle and Last No. to try to solve the remaining numbers, keep in mind that computer have a much more complex way of solving calculation, the idea is that you decide the certain method of guessing until you get the answer.
Let's Highlight SHA-256 Algorithm, The SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) is one of a number of cryptographic hash functions. A cryptographic hash is like a signature for a text or a data file. SHA-256 algorithm generates an almost-unique, fixed size 256-bit (32-byte) hash. Hash is a one way function – it cannot be decrypted back.
Here are some Cryptocurrency coins that use SHA256 Algorithm
- Bitcoin (BTC)
- 21Coin (21)
- Peercoin (PPC)
- Namecoin (NMC)
- Unobtanium (UNO)
- Deutsche eMark (DEM)
- Betacoin (BET)
- Bytecoin (BTE)
- Joulecoin (XJO)
- Devcoin (DVC)
Perhaps a Solution for Bitcoin?
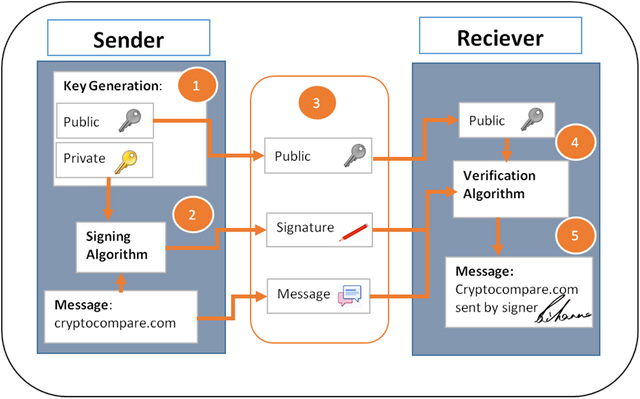
A Bitcoin digital signature and its verification is one of the main key secrets behind the Bitcoin protocol.
It allows non-repudiation as it means the person who sent the message had to be in possession of the private key and so therefore owns the Bitcoins – anyone on the network can verify the transaction as a result.
“So in other words, Bitcoin can’t adopt a quantum-resistant signature scheme at the moment if we want to scale beyond present capacity.”
There are other options like. NTRU, McEliece, and even Fawkes signatures.
Especially Fawkes signatures are incredibly simple and works perfectly with Bitcoin except for the enforced delays – it’s based on a commitment chain.
Together with a secure timestamping mechanism that allows you to prove which message is the oldest – and that’s EXACTLY what Bitcoin is thanks to it’s blockchain! – Fawkes signatures are secure.
My personal possible Solution, visit this source for more Information
Source
Conclusion
Rumors of bitcoin’s demise have been greatly exaggerated. According to a site tracking “bitcoin obituaries,” the media has proclaimed the seven-year-old cryptocurrency dead more than 100 times, yet a recent resurgence has led to a tripling in bitcoin’s price over the last year. It has survived price crashes, cyber heists and community infighting, but bitcoin’s biggest threat may still be lying dormant: quantum computers.
Cryptography is prevalent everywhere and is used for encrypting messages, emails as well as other forms of data. Banks use cryptography as well, although in a centralized manner.
Hence if quantum computers capable of breaking Bitcoin are indeed developed, they would also be a risk to banks and would have far reaching consequences. Which may also suggest our cryptography may be undefeated for a while even after the quantum computing era properly arrives, perhaps giving us enough time to update it. However, many computers and software in use today aren’t patched against even known security problems for which fixes are readily available. We can probably expect a considerable Quantum Security hangover even if the NSA does manage to come up with a quantum-resistant cryptography standard.
Bitcoin is not Doomed nor are all Alt-coins, so ignore any Article which claims Quantum Computing will end all Cryptology and Encryption, this is nothing more than personal opinion.
Sources
Bitcoinmagazine.com: Bitcoin is not quantum safe and how we can Fix it When Needed


Any citations for your images? Thanks!!
My 2-cents. I think no crypts are not unbreakable. Yes, I agree with @steevc that it's about how long you need it for. Was NSA the one who invented SHA256? And I read that btc = SHA256^2 Is it something to lessen worries on encryption safety due to ^2... or is it stressful since it's by NSA? I don't know which or how to decide.
China claims:
source
They are referring to their communication systems being "spy-proof". Any thoughts on this?
Hashing is not the answer to all the problem. I mean we can't prove they are good, we can only try. And by definition they cannot be perfect since the set of possible inputs is way bigger than the output. You didn't mention security levels in your article. To have the security level we have today (2^80) we need hash functions of size at least 240 bits so 256 is good. But since no one can accurately guess the speed up we will get with quantum computers in classical computing settings, this margin is thin. It is safe to assume that we would need SHA3-384. source: Grover BHT hash function