Bacteria present in the peripheral of Santa Bárbara de Zulia - Biological Analysis
Summary.
The population that was taken as object of study was constituted by eighteen (18) workers in the sale of fish in the peripheral. For this, the survey technique was applied, supported by a questionnaire, containing 5 items with alternatives on a Likert scale. In this sense, the data were tabulated in tables using the statistical model by dimension and indicators to be represented in bar-type graphs. The conclusions allowed to determine that: The fish is exposed to inadequate conditions of hygiene on the part of the manipulators, in addition to an incorrect storage and deficiency in the use of the good practices of manufacture on the part of the sellers.

Introduction
Fish is a food that undergoes a series of changes from the moment of its capture due to its composition, a characteristic that makes it a product with a high degree of susceptibility to decay and decay, those responsible for these phenomena are the enzymes that constitute it and the microorganisms that invade organs and tissues as soon as death happens.Source of textual quotation: Manual of quality and processing for retail fish sale of the municipality of Colón, Zulia State - Venezuela
Of the microorganisms, it is the bacteria that most influence the lifespan of the fish. However, not all those that are present at the time of capture or collection are capable of multiplying during storage, only a part of these will end up proliferating in great quantity and becoming responsible for the alteration. The time of year, the characteristics of the diet, the geographical area, the species of fish and the capture system are determinants of the number and type of bacteria present initially, while the handling and storage conditions condition the altering flora.
Obviously, all the manipulations that the fish is subjected to after the capture or collection will significantly affect the microbiological quality of the fish. Bacterial microorganisms that are pathogenic for humans and that are transmitted by this product can be divided into two groups: species whose natural habitat is water (Vibrio cholerae, Aeromonas sp., Etc.) and others that are present in the water due to contamination Fecal origin and are associated with the process of manipulation that subsequently suffers fish (Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp.Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus) Herrera (2005).
The changes that occur from capture to sale alter the physical, chemical and microbiological conditions, making this product a high risk food for the consumer's health, especially through the marketing chain, in which there is a a series of critical points that, if not properly controlled, end up affecting the sanitary quality of the product.
That is why the establishments must fulfill the activity of owning a place in good hygiene conditions, suitable with areas for personal hygiene, for handling and storage, in addition to the necessary clothing for each of the employees who handle the product. .
Why the approach to this problem that afflicts the community consuming fish in the area?
Bacteria can cause well-being or discomfort to humans. Some are allies of living beings and live in harmony while causing or causing diseases such as skin ulcers, nerve damage, skin damage, in the mouth mucous membranes; bacteria also contaminate food such as salads, preserves, sausages among others. For all the above, it can be said that diseases caused by bacteria bring consequences to the body, and according to the magnitude of the population can preserve vomiting, ulcers, bad breath, bad urinary and body odors, inflammations among others.
Such is the case of the peripheral, malecón or sale of fish located on the banks of the Escalante river of the Santa Bárbara municipality of the Colón municipality; state Zulia where the sellers of this product do not take the necessary precautions to prevent the presence of bacteria, bringing this as a consequence that consumers do not feel comfortable doing their shopping, due to the bad odors that come from the place.
For the above, the following questions should be highlighted:
Do fish sellers have knowledge about bacteria?
Do the fish vendors maintain the general hygiene of the food?
Do the fish sellers meet the requirements demanded by the M S A S?
Will the fish that are sold be completely fresh or with a long freezing time?
What type of bacteria exist in the peripheral of Santa Bárbara Municipio Colón in the state of Zulia?
To answer all these questions, a series of actions is carried out aimed at fish sellers, with the purpose of taking the necessary precautions to avoid the presence of bacteria in the fish, taking into account two basic levels, in the biological and social, and in this way raise awareness of the process in the sale of fish focusing on the proper hygiene and handling of fish.
Objectives pursued with this investigation.
Determine the bacteria present in the fish handling areas. With the determination of these bacteria, we can know what actions to take regarding the changes that must be made in the handling of the sale of fish.
Determine the participation of fish sellers in the hygiene and hygiene of the peripheral.
Evaluate the quality of the product (fish) consumed by the population.
Theoretical Bases
Peripherals.
Peripherals are the premises where the fish is displayed for retail sale, attended by fishermen or fisherwomen. Fishmongers are one of the links through which fish passes from being caught in the sea until it reaches the consumer's home. They must be given very specific circumstances so that the product maintains all the safety guarantees and, for this, have hygienic regulations and a guide of good practices. Each of these establishments is responsible for the products being safe. But how should they maintain the fish? What cleaning and disinfection guidelines do they follow? Aspects such as these should be part of a package of good hygienic practices based on hazard analysis and critical control points.
Hygienic handling of fish.
From the moment of capture, in order to ensure good quality and long shelf life. The importance of hygiene during handling on board has been evaluated in a series of experiments where several hygienic measures were used (Huss et al., 1974). The quality and shelf life of fish treated in complete asepsis (aseptic handling) were compared with fish stored in clean plastic boxes with clean ice (clean handling) and inadequately treated fish, that is, stored in ice inside boxes dirty and old wood (normal handling). As expected, the level of bacterial contamination of the three lots presented a considerable difference.
During the first week of storage, no difference was found. Only during the second week the level of initial contamination becomes evident and the fish with the highest contamination presents some days of reduction in shelf life, compared with the other samples. These results are not surprising if we remember that bacterial activity is normally important only in the final stages of the storage period.
Analysis of the investigation
The bacteria present in the fish handling areas in the Santa Bárbara Municipio Colón district of Zulia state are described in the following annex:
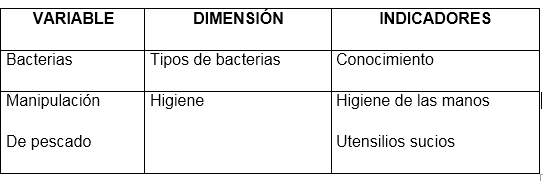
[Table source]: @sandracarrascal
The following questions were asked to the surveyed population:
Do you have good hygiene when handling fish?
[Table source]: @sandracarrascal
[Source of graphic]: @sandracarrascal
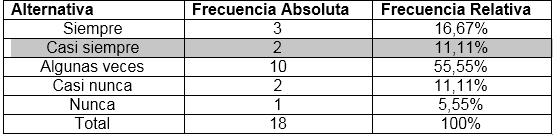
In the graph, the results obtained for item 1 are presented, in which respondents were asked Do you have good hygiene in fish handling?
The values obtained for this item being that 16.67% always chose the answer, while 11.11% said Almost always, 16.67% expressed some times, 55.55% Almost Never, while another 5, 55% selected Never.
This shows that some workers do not have in mind the good hygiene in the handling of fish to keep it away from bacteria since they usually represent the cause that produces the most notable effects in the deterioration of fish.
Do you maintain a good hygienic practice in handling fish?
[Table source]: @sandracarrascal
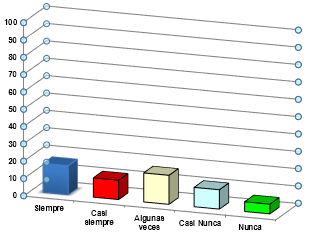
Graphic Source: @sandracarrascal
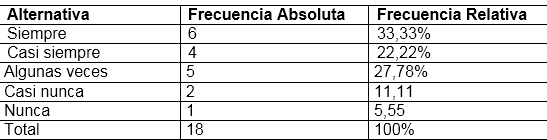
In the previous graph, the results obtained for item 2 are presented, in which respondents were asked: Do you maintain a good hygienic practice regarding the handling of fish?
The values obtained for this item were that 33.33% always selected the answer, while 22.22% said almost always and 27.78% selected some times, 11.11% said almost never and 5, 55% said never. This shows that peripheral workers always maintain good hygienic practices when handling fish.
In the previous graph, the results obtained for item 1 are presented, in which the respondents were asked Do you have a good hygiene in handling fish keeps it away from bacteria? The values obtained for this item being that 16.67% always chose the answer, while 11.11% said Almost always, 16.67% expressed some times, 55.55% Almost Never, while another 5, 55% selected Never. This shows that some workers are aware of good hygiene in handling fish to keep it away from bacteria since these normally represent the cause that produces the most notable effects in the deterioration of fish.
They are naturally present in the skin, gills, and digestive tract, their number and type being a reflection of the bacteria in the environment where the fish is found. Bacteria are the most well-known pathogens in food contamination, they are the most common and the most studied.
Do they maintain good hygienic practices regarding the handling of fish?

Table source: @sandracarrascal
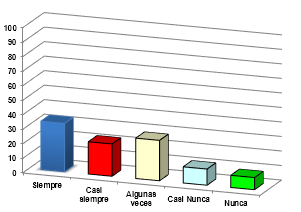
Source of graphic: @sandracarrascal
The values obtained for this item were that 33.33% always selected the answer, while 22.22% said almost always and 27.78% selected some times, 11.11% said almost never and 5, 55% said never. This shows that peripheral workers always maintain good hygienic practices when handling fish.
Do you keep the hygiene of your hands when handling fish?
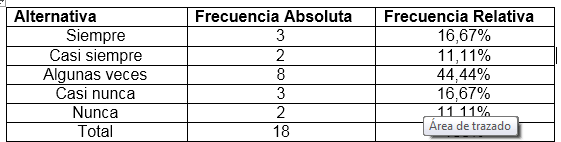
Table source: @sandracarrascal
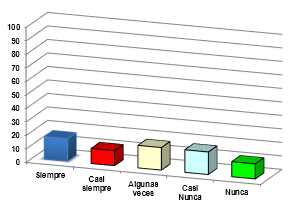
Source of graphic: @sandracarrascal
The values obtained for this item were that 16.67% always chose the answer, while 11.11% said almost always, 44.44% selected some times, 16.67% said almost never and another 11.11 % never selected This shows that peripheral workers sometimes keep hand hygiene for handling fish.
Do you use gloves for handling fish?
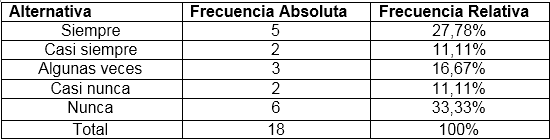
Table source: @sandra carrascal
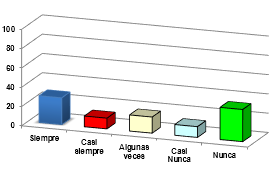
Source of graphic: @sandracarrascal
The values obtained for this item being that 27.78% always selected the answer, while 11.11% said almost always, 16.67% selected some times, 11.11% selected almost never and 33, 33% never. This shows that workers do not use gloves for handling fish. People who work in a fishmonger can contaminate the genus directly. The correct handling of food and the continued application of hygienic habits are the basis for guaranteeing safety.
The worker must wear specific clothing and always clean, light colored and to cover his street clothes. If gloves are used, they should be cleaned frequently, before starting, after handling money or after touching other surfaces. They can not smoke, eat or chew gum while they work, and they can not cough or sneeze near food. It is not advisable to wear jewelry, watches or long nails, as they hinder personal hygiene.
Cutting tools should be cleaned frequently, especially after performing evisceration operations and always before disinfecting them. In addition, once disinfected, they must be kept in a specific container or cabinet to protect them from any contamination. The company must guarantee the training of the manipulator personnel in matters of food hygiene, in accordance with the work they perform. The owner of the establishment must verify that the employees have sufficient and adequate knowledge to ensure the safety and hygiene of the food handled in their establishment.
Annexes of laboratory tests carried out for this investigation

 .
.
Note: The laboratory tests were sent to be performed in a private laboratory, with the intention of corroborating the bacteria present in the periphery (sale of fish) in the locality.
Conclusions.
The fish is exposed to inadequate hygiene conditions by the handlers, in addition to incorrect storage and deficiency in the use of good manufacturing practices by the vendors.
It was possible to identify other types of bacteria belonging to the genera Citrobacter sp., Enterobacter sp., Klebsiella sp. Edwarsiella sp., Proteus sp., Vibrio sp. Staphylococcus sp. and Streptococcus sp., it is important to clarify that the presence of bacteria different from the established pathogens, may represent a risk for Public Health.
Recommendations
• Conserve hygiene.
• Keep food at safe temperatures.
• Use safe drinking water and safe raw materials.
• Remove food products, clean the area of containers, containers, etc.
• Remove the equipment to expose the surfaces to be cleaned. Remove the small equipment, parts and joints that are to be cleaned from a certain area.
• Cover delicate installations to protect them from water, etc. Clean the area, machines and food waste equipment by means of a water jet (cold or hot, depending on the case) and using brushes, brooms, etc.
• Apply the cleaning product and use mechanical energy (for example: pressure and brushes) as necessary.
• Rinse thoroughly with water, until the cleaning substance is completely eliminated, after the appropriate contact time (the residues can completely inhibit the effect of disinfection).
• Cleaning control.
• Sterilization by chemical disinfectants or thermal treatment.
• Remove the sterilant with water after the appropriate contact time.
• This final rinsing is not necessary for some sterilizers, for example: for formulations based on H2O2 that decompose rapidly.
• After final rinsing, the equipment is assembled again and allowed to dry.
• Cleaning and disinfection control.
• In some cases, it will be good practice to re-disinfect (for example with hot water or low chlorine concentrations) just before starting production.
References consulted
ADAMS, M. R. MOSS, M. O. Food microbiology. Editorial ACRIBIA. Zaragoza, 1997.
FRAZIER, W. C. WESTHOFF, D. C. Microbiology of food. 4th edition. Editorial ACRIBIA. Zaragoza, 1993.
ICMSF. Food microorganisms 2. Sampling methods for microbiological analysis: Principles and specific applications. 2nd edition. Editorial ACRIBIA. Zaragoza, 1999.