Google releases "Talk to Books", an AI search engine. "Keyless books" can be used without keywords

As a technology giant started as a search engine, Google has launched many interesting search tools. Yesterday, the company’s research organization released a search engine based on artificial intelligence, which allows ordinary people to feel the power of the latest semantic understanding and natural language processing technologies: they are important for the development of artificial intelligence technology. direction.
It is worth mentioning that the author of the book "The Singularity Approaching," and Ray Kurzweil, Director of Engineering at Google Research Institute, also participated in this work.
This project currently includes interactive AI language tools, and the main artificial intelligence technology it presents is the "word vector." Word vector is a form of natural language processing. Some geometric properties of vectors can well reflect the syntax or semantic meaning of a word.
For example, the difference between two word vectors corresponds to a word relationship, and the word vector distance corresponds to a word's relevance or similarity. For a selected set of words, its vector is projected into space. Word vectors with similar meanings show interesting clustering phenomenon in vector space. For example, national nouns are grouped together, and university names form another cluster.
Natural language understanding has developed rapidly in the past few years, partly due to the development of word vectors. Word vectors enable the algorithm to understand the relationship between words and words based on practical examples of actual language use. These vector models map semantically similar phrases to neighboring points based on equivalence, similarity, or relevance of concepts and languages. Last year, Google used the language's hierarchical vector model to improve Gmail's Smart Reply. Recently, Google has been exploring other applications of these methods.
Today, Google shared the Semantic Experiences website with the public. There are two examples on this website that show how these new methods drive previously impossible applications. Talk to Books is a new way of exploring books. It starts at the sentence level, not the author or theme level.
Semantris is a word association game supported by machine learning, in which you can type the words associated with a given prompt. In addition, Google also published the paper "Universal Sentence Encoder", which describes in detail the models used in these examples. Finally, Google provided the community with a pre-trained semantic TensorFlow module that allows the community to experiment with their own sentence or phrase code.
Modeling method
The method proposed by Google extends the idea of representing language in vector space by creating vectors for larger chunks of language (such as full sentences and small paragraphs). The language is composed of the hierarchical structure of the concept, so Google uses the hierarchical structure of the module to create vectors, and each module must consider the features corresponding to the sequences on different time scales.
Associations, synonymous, antisense, partial relationships, overall relationships, and many other types of relationships can all be represented using vector space language models as long as we train in the right way and ask the right "problems." Google introduced this method in the paper "Efficient Natural Language Response for Smart Reply".
Talk to Books
Through Talk to Books, Google provides a new way of book search. When you state something or ask a question, the tool will find out in the book that you can answer your sentence. This method does not rely on keyword matching. In a sense, you are “talking” with the book and the answers you get can help you determine if you are interested in reading them.
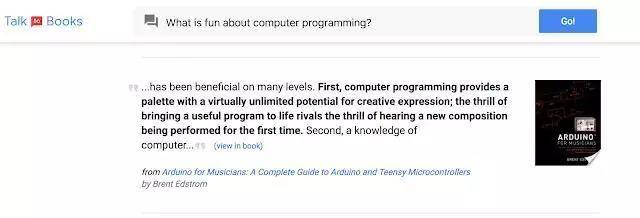
The model is trained on one billion chat sentences and learns to identify which ones might be good responses. Once you ask a question (or make a statement), the tool searches for all the sentences in the 100,000 book, finds the content corresponding to the input sentence according to the semantics of the sentence level; there are no preset rules that limit the relationship between the input and output results.
This is a unique ability to help you find interesting books that keyword search may not find, but there is still room for improvement. For example, the above experiment has a role at the sentence level (instead of being at the paragraph level like Gmail's Smart Reply), then the sentence of a "perfect" match may still be "out of context." You may find that the book or article you are looking for is not what you want, or the reason for selecting an article is not obvious. You may also notice that well-known books are not necessarily ranked high; this experiment only observes the matching degree of a single sentence.
However, it has the advantage that this tool can help people find unexpected authors and books, as well as surface book.
Semantris
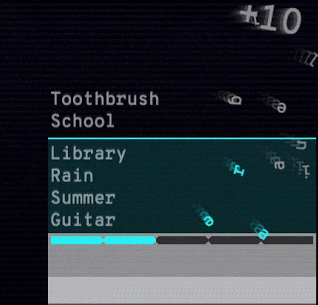
Google also released Semantris, a word-association game supported by the technology. When you enter a word or phrase, all words are arranged on the game screen, and the sorting is based on how well the words correspond to the input. Using this semantic model, synonyms, antonyms, and neighboring concepts are all under control.
The time pressure of the Arcade version (see the figure below) allows you to enter a single word as a reminder. The Blocks version does not have time pressure, you can try to enter phrases and sentences.
The examples shared in this article are just a few of the possible ways to use these new tools. Other potential applications include classification, semantic similarity, semantic clustering, whitelisting applications (selecting correct responses from multiple scenarios), and semantic search (such as Talk to Books). Look forward to the community for more ideas and more creative applications.