All you need to know about antioxidants
Antioxidants are a class of vitamins and nutritional ingredients that help the body get rid of harmful action of free radicals, molecules that cause cell oxidation and installation of various types of cancer.

source: drperlmutter.com //Red wine is an excellent source of antioxidants//
The importance of antioxidants is accepted today even among experts in medicine minded conservative being assumed by many people in everyday food choices.
Overview
The role of antioxidants in the body
Free radicals and their effects
Types of antioxidants
Deficiency of antioxidants
The role of antioxidants in the body
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other cells. Thus, antioxidants break free radical chain reactions, sacrificing their own electrons to free radicals feed. For this reason, they are considered and electron donors.
Moreover, antioxidants are part of the natural mechanism of protection of body cells against reactive oxygen species attacks. The body allow the passage of a variety of nutrients with antioxidant properties and produces antioxidant enzymes in order to control the harmful chain reaction of reactive oxygen molecules.
Vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenes and antioxidants lipoic acid are well known in the medical world, with real beneficial properties for the body. The body can manufacture some of the antioxidants essential to health, but not all of them. In addition, the body's ability to produce single antioxidants decreases with age.
The effects of free radicals
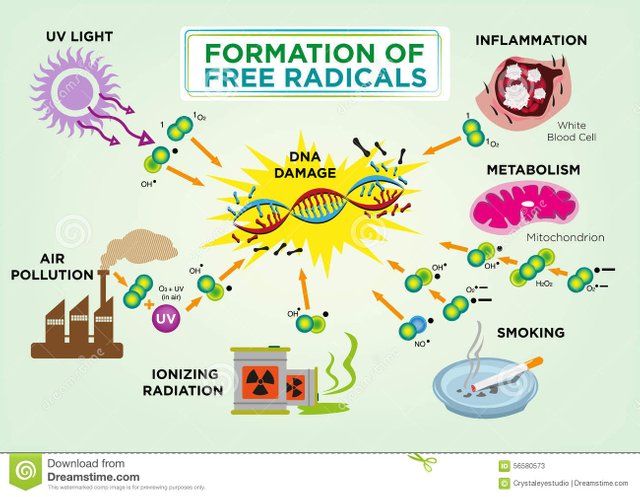
Free radicals are also produced by the body, resulting ago metabolic processes and energy production. Here are a biological response to environmental toxins from polluted air, cigarette smoke, chemicals, ultraviolet rays, radiation or medication. Free radicals also result from inflammatory processes that occur in the body or after filing a sustained physical effort.
A free radical is a reactive metabolite lacks one or more electrons, and this deficiency underlies biological oxidation process. Therefore, free radical will try to replace their lack electrons aggressively attacking the organic molecules.
Free radicals are trying to deprive many proteins in the body electron phenomenon that results in altered DNA and other cellular structures. Moreover, private electron molecules begin to imitate the same action, becoming in turn free radicals. For this reason, the action of antioxidants on these processes is essential for maintaining health.
source: https://www.dreamstime.com
Types of antioxidants
There are two main types of antioxidants
- non-enzyme antioxidants works by interrupting free radical chain reactions. For example, vitamin E can inhibit the activity of free radicals, reducing it to 5 reactions, instead of 100! This category includes vitamin C, polyphenols in plants, carotenoids and glutathione (antioxidant chief that is found in all body cells, enhancing the activity of all other antioxidants)
- enzyme antioxidants works by breaking down and eliminating free radicals. Overall, these antioxidant enzymes in the body oxidative away, turning them into hydrogen peroxide, and water, through a process with several stages that require the participation of other cofactors (copper, zinc, manganese and iron).
Most antioxidants in foods and dietary supplements are non-enzymatic, but strengthen the defense system of the enzyme disarming free radicals and making them more vulnerable, so easily removed.
Another criterion for the classification of antioxidants refers to the extent they are soluble in water (hydrophilic) or fat (hydrophobic). It takes both types of antioxidants for complete protection of healthy cells.
Antioxidants fat-soluble (vitamin E, vitamin A, carotenoids, lipoic acid) are located primarily in cell membranes, while those soluble in water (vitamin C, polyphenols and glutathione) are found in aqueous fluids, such as blood or fluids proximity cell (cytoplasmic matrices).
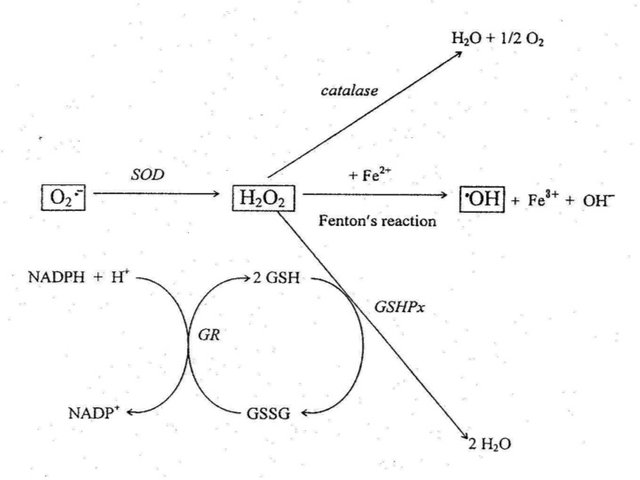
Besides solubility and requirements enzymatic antioxidants and also differs depending on their molecular size. Thus, there are small molecule antioxidants and antioxidant with high-molecular proteins, which have different functions in the body
- Antioxidants small molecule reactive oxygen species destroys and removes them from the body by neutralizing chemical (vitamin C, vitamin E, lipoic acid, carotenoids, glutathione and coenzyme Q10).
- Antioxidant proteins with large molecule proteins and enzymes essential to protect DNA.
source: http://www.desimd.com
Deficiency of antioxidants
Health professionals say that deficiency of antioxidants can cause or favor the occurrence of many chronic diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, cataracts, diabetes, hypertension, infertility, macular degeneration, mental disorders, periodontal disease, respiratory tract infection or rheumatoid arthritis .
Adding sufficient amounts of antioxidants in the diet helps reduce oxidative stress at the cellular level, which means preventing premature aging. In addition, symptoms such as increased susceptibility to infection, skin lesions, slow wound healing or excessive wrinkling of the skin announce necessity to supplement the daily intake of antioxidants in the diet.
Not necessarily the amount of antioxidants in the diet is important, but their diversity, so how they interact and act simultaneously maintaining cellular health of the body. Moreover, best results are achieved through moderate amounts of antioxidants intake diversify.
The best known antioxidants are:
- Vitamin A and carotenoids - found in carrots, squash, broccoli, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, cabbage, melon, peach and apricot
- Vitamin C - is found mainly in citrus like oranges and lemons, but also peppers, broccoli, green leafy vegetables, strawberries and tomatoes.
- Vitamin E - to be assimilated by eating nuts and seeds, whole grains, green leafy vegetables, vegetable oil and liver oil
- Selenium - found in abundance in fish and shellfish, red meat, grains, eggs, chicken and garlic.
- Berries - These juicy fruits, not only taste good, but also help in fighting disease. Although blueberries are small, the benefits it provides for health are enormous. They can boost cognitive function and will strengthen immunity.
- Artichokes - Not everyone knows, but the artichoke has a high content of antioxidants and provides an increased intake of vitamins body
- Grapes and red wine - Grapes are a good source of antioxidants, especially dark ones. They are rich in flavonoids and polyphenols that contributes to maintaining heart health. To enjoy the positive effects of red wine is enough that it be consumed regularly in small quantities.
- Beans - Beans are a very healthy food for the body because it contains not just fiber and antioxidants. Red beans contains the highest amount of antioxidants.
- Beta-carotene - carrots, oranges contain beta-carotene, which helps the body produce vitamin A and combat cancer. Add in your diet foods that contain beta-carotene
- Apples - Apples are a perfect snack can satisfy your craving for something sweet and will give your body the vitamins and antioxidants that help maintain health.
- Potatoes - do not have to abstain to consume by eating potatoes because their body will be doing a favor. Baked potatoes are a good source of antioxidants, unless it will be fully mixed with butter and sour cream.
- Dark chocolate - What they say about dark chocolate is perfectly true. Dark chocolate contains powerful antioxidants and can lower blood pressure. However, there will be abuse of this food. Studies suggest that antioxidants from dark chocolate reduce the risk of outbreak of diseases, including cardiovascular disease and some cancers.
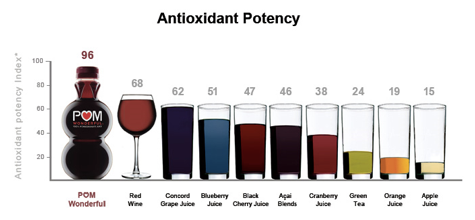
source: http://www.chasingthekenyans.com
Although nothing can guarantee the prevention of cancer or other diseases by following a diet rich in antioxidants, the body better fight against these diseases. Each person owes front of his body, she would do everything in his power to keep him healthy and consumption of antioxidants can do this.
WOW! In terms of nutrition, all hydrogenated vegetable oils are true radicals bombs exploding when you eat. These include margarine, bottled salad dressings, cooking oils, creams without milk. Since high temperature accelerates the oxidation process, all foods have long held to the fire particularly high content of free radicals. In the opinion of Dr. Harman and other scientists, the oxidation of unsaturated fats in the human body is the main cause of cellular pathology associated with aging.
I don't agree with this 100% but mostly that's academic. This is overall well written and good advice. I upvoted it for you.