A brief overview of the functions of the human brain – Part-2
A brief overview of the functions of the human brain – Part-1
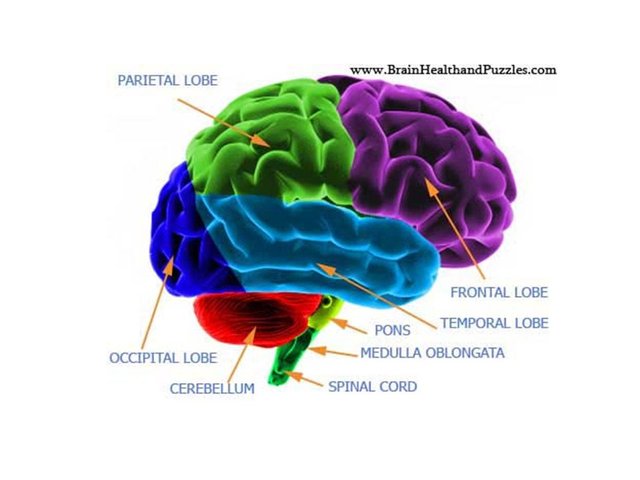
Brain Parts
The basic nervous systems found in the simplest creatures are unbelievable and it is composed of reflex pathways. For examples, invertebrates and flatworms are such living beings, which don’t have centralized brains. The neurons in them are not fixed in place. These are laid out in simple reflex pathways. Neurons in Flatworms are connected together that create a net around the whole animal.
Most invertebrates such the lobster contain common “brains” that is made up of localized collections of neuronal cell bodies known as ganglia. Every ganglion helps organize sensory and motor functions in its section via reflex pathways. The ganglia are connected together to construct a simple nervous system. As the nervous systems grew, chains of ganglia grew into more centralized simple brains.
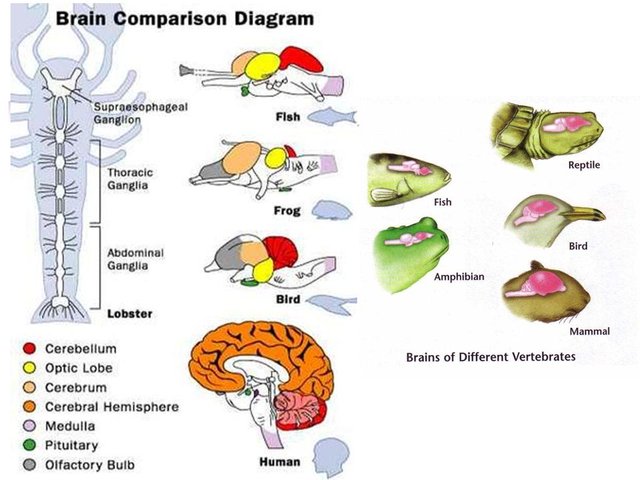
Brains developed from ganglia of invertebrates. Despite being the animal, brain contains several other parts.
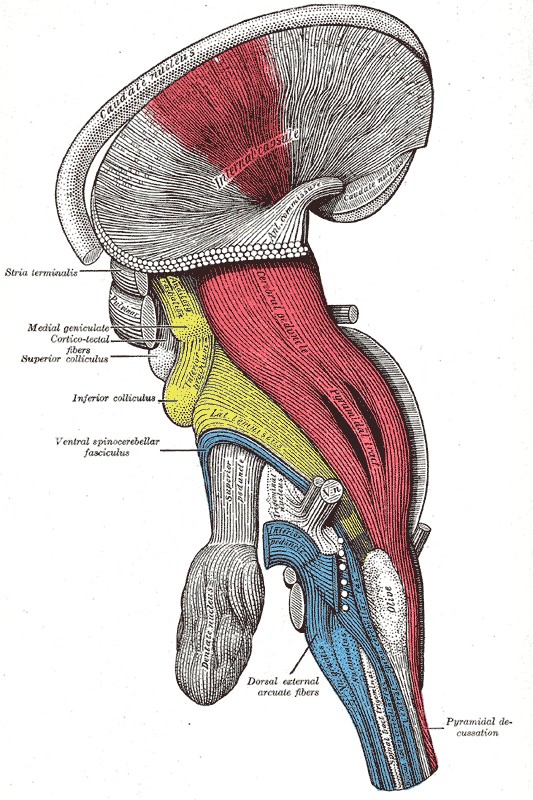
• The Brain Stem
The brain stem is made up of the medulla, pons and midbrain. Medulla is an extended section of the upper spinal cord. The brain stem helps direct the automatic functions (which include blood pressure, heart rate), the reflexes, limb movements and visceral functions such as urination, digestion.
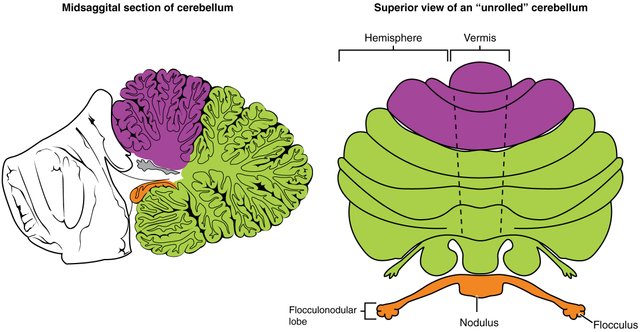
• The Cerebellum
The cerebellum adds all information from the vestibular system that contains the indication of movement and position. This information is utilized to organize limb movements.
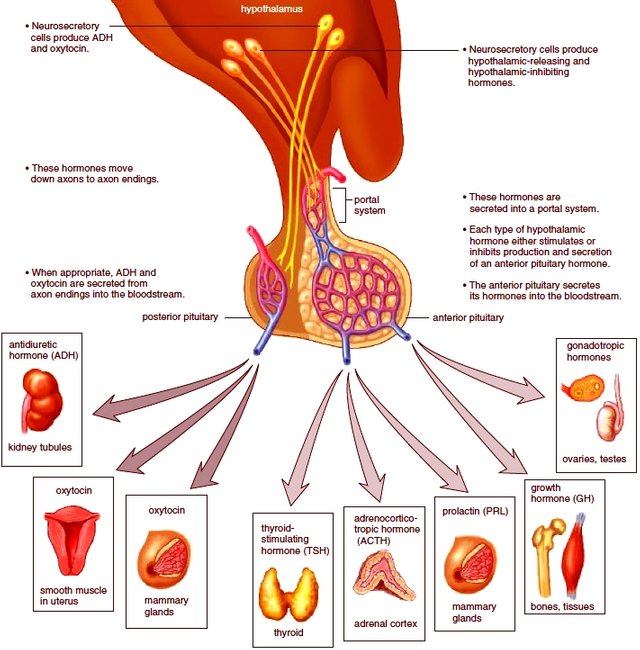
• The hypothalamus and pituitary gland
These both brain parts control visceral functions, body temperature and behavioral responses like drinking, feeding, sexual response, pleasure and aggression.
• The cerebrum or the cerebral cortex or the cortex
The cerebrum is composed of the cortex, large fiber tracts known as corpus callosum, and some deeper structures which include amygdale, basal ganglia and hippocampus. It adds the information from the different sense organs, starts the function of motor, manages emotions and holds on memory and thought processes
Brains for Instinct
There are some lower animals such as reptiles, fish, amphibians and birds, which don’t think or imagine very much but they concern for their daily requirement like accumulating food, drinking, eating, sleeping, reproducing and protecting themselves.
These are called instinctual processes. So their brains are placed with the major centers that manage these functions.
The same functions are processed in the human brain as well, so we have the same parts of the brain that are found in a reptilian brain. These parts are called the brain stem and the cerebellum.
Nice post buddy. Very informative and condensed content.
Thank man. Funny removed just for fun.
hmm ..... this article is full of some unknown facts about how brain works.
Thanks for sharing. Upvoted already :)
Thank you very much.