The Light - part 3 - polarization
In previous parts I mostly focused on light vision, espacially colors perception. Now I would like to say few words about the light feature which is not visible for human eye - polarization. But is very important to us. In this article I will answer why.
You remember that light is an electromagnetic wave, so we know that light has electric and magnetic fields which are oscillating. And here we are coming to polarization of light, which is describing how the wave is oscillating.
Polarization definition and types:
According to Britannica
"Light waves are transverse: that is, the vibrating electric vector associated with each wave is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. A beam of unpolarized light consists of waves moving in the same direction with their electric vectors pointed in random orientations about the axis of propagation. Plane polarized light consists of waves in which the direction of vibration is the same for all waves. In circular polarization the electric vector rotates about the direction of propagation as the wave progresses."
In this definition you could already read about types of polarization but here you can see a gif which will help you better understand meaning of above words
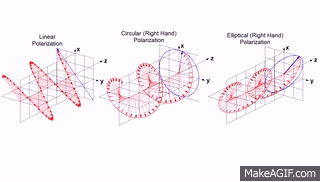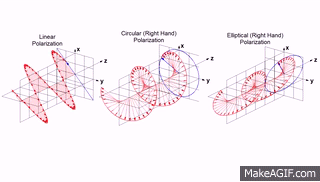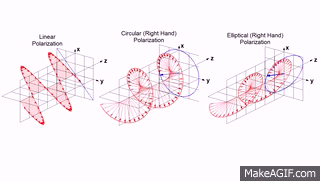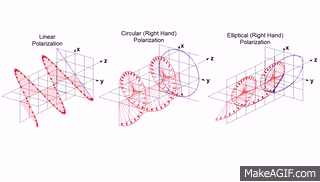
So as you can see we can distinguish three main types:
- linear polarization (plane)
- elliptical polarization
- circular polarization which is actually specific elliptical polarization
Some sources are saying that there is fourth type, which is just unpolarized light where electromagnetic wave consist all, random directions of wave vector.
We do not see polarization but we use it!
Even if our eyes do not recognize polarization, we still widely use this feature of light.
LCD TV sets
Did you know that LCD TV could not work without using polarization properties? Yes that is true, the principle of Liquid Crystal Display is usage polarization of light. Please look picture below:
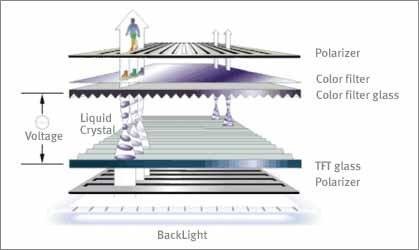
"All liquid crystal displays (LCD) operate on the principle of being able to 'twist' polarized light as it passes through a 'nematic' liquid crystal. The orientation of each liquid crystal in a display is governed by an electric field applied to a transparent electrode, through an array of thin-film transistors (TFT). The liquid crystal is normally 'sandwiched' between two polarizing filters at 90 degrees to each other. Polarized light enters the back of the liquid crystal from the back-lit LED. When the nematic crystal is not energised, it 'twists' the polarized light by 90 degrees so that it passes through the second polarizing filter. When an electric field is applied to the liquid crystal, the light does not get twisted so gets blocked by the second polarizing filter."
*quotation source
Of course there are few types of LCD TFT such IPS ( in plane switching), VA (vertical alignment) and TN (twisted nematic). But the difference between them is inside liquid crystals. Main concept is common for all of them.
3D television
There are TV sets with 3D function which is based on polarization "effect" as well. This kind of solution was highly promoted by LG company, which developed passive glasses for 3D.
How it works then?
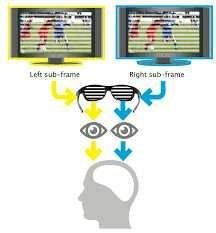
Mainly people can see in three dimensions becuase pair of eyes is used for sight. We can call it stereoscopic vision. Due to fact that each eye looks at object from slightly different angle, our brain interpret incoming 2 pictures as one 3D view. It helps us to understand distances between objects. So how we can see distance in flat two-dimensional screen?
The thing is in glases which cause that 1eye see different picture than second one... We just cheat our brain by showing images recorded from two cameras set in same agles as human eyes.
In passive technology these two pictures are interlaced in odd and even rows. On front of the screen there is attached special polarizer which polarizes odd lines with right circular polarization and even with left direction. Then when you ware glases your left eye can see only left polarization and right eye the oposite one. Just look at picture below:
Polarization in photography
Of course in nature we can have as well polarized light even if sun gives us unpolarized light. Some time ago there was a guy whose name was Brewster. He observed that if the unpolarized light will refract on some object in specific angle (brewster angle) then we will see two rays: one reflected and second refracted, but both will be linear polarized.
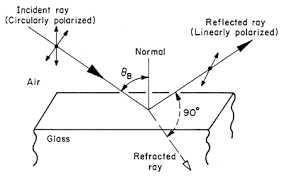
But for you probably more interesting will be how we can applicate this law to common usage. Please take a look at this photography:

You can achieve this kind of effect when you will use polarization filters.
Here you have small explanation from wikipedia:
"Photographs taken of a window with a camera polarizer filter rotated to two different angles. In the picture at left, the polarizer is aligned with the polarization angle of the window reflection. In the picture at right, the polarizer has been rotated 90° eliminating the heavily polarized reflected sunlight."
I have shown you three main application of polarization. As you could read even if we do not see some features of light we can still use them!
I hope that this article was interesting for you, if yes then please vote on it!
Follow , Upvote and resteem
upvote this post then comment your post link which you want should I upvote it
If you not following me you should follow me then do it
https://steemit.com/upvote/@crypto-booster/upvoting-started-followers
Very cool post, like the fact that you show practical examples of how the polarization of the light works - it's way easier to comprehend it that way. Upvoted
Join us on #steemSTEM
Thank you for this very interesting article on light. It has been advertised on our chat channel (and upvoted).
The steemSTEM project is a community-supported project aiming to increase the quality and the visibility of STEM (STEM is the acronym for Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) articles on Steemit.