Breakthrough!!! Physicists created a stable plasma ring at atmospheric pressure!
The plasma of atmospheric pressure is a non-thermal nonequilibrium form of plasma, which is used in many fields of science and technology, such as analytical chemistry, material processing, energy, medicine, biology and physics, since it does not require sophisticated equipment for its production. The most vivid example of its occurrence in natural conditions is the lights of St. Elm, and in installations it is created with the help of electromagnetic fields, unstable and has a non-uniform structure. One of the interesting tasks is to obtain small plasma formations in order to study them and possibly use them in future in technological processes.
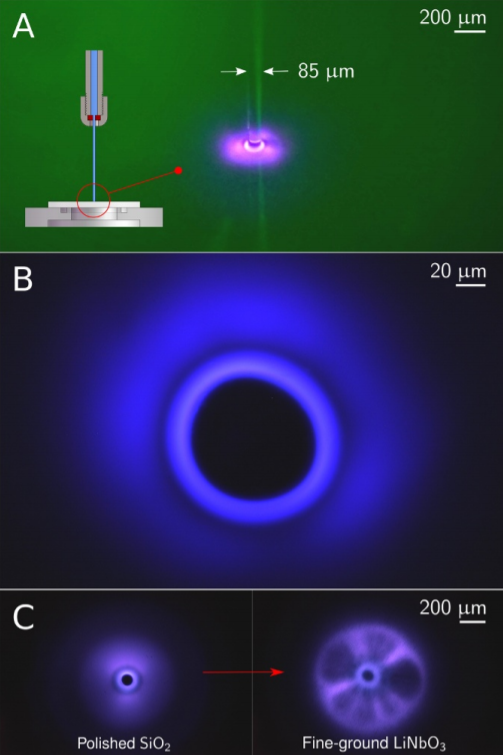
Source Production of the plasma ring: a) the formation of plasma when a laminar jet of water falls on the surface of quartz, b) the plasma ring photographed close-up. The black area corresponds to the diameter of the water jet, (c) photographs of luminescent structures formed when a jet of water falls on the surface of quartz and LiNbO3
Francisco J. Alves Pereira of the California Institute of Technology, along with colleagues from the US and Israel, used an experimental setup that consisted of a ruby nozzle with a hole diameter of 100 μm and a pump that generated a high-speed jet of deionized water that did not contain air bubbles.
A single-crystal quartz (SiO2) or single-crystal lithium niobate (LiNbO3) sample with a polished or fine-grained surface was used as the target. The researchers found that if the water flow rate is more than 200 meters per second, then in the region of the jet collision with the target surface, a luminous ring-like structure will be observed, the intensity of the luminescence will depend on the water flow rate. If the surface of the sample is fine-grained, in addition to the luminous ring, streamers propagating in radial directions will be observed, and the luminescence itself will begin to appear at lower water flow velocities (~ 115 meters per second). Luminescence was not observed with the use of water that did not undergo deionization, or samples with a conducting surface. At the same time, the plasma formation was stable and did not collapse under the influence of an external electric field, generated radio waves in the frequency range from 3 to 40 MHz, and was obtained without the use of external electromagnetic fields.
Physicists explain the mechanism of formation of such a plasma ring as follows. When a water jet hits the surface of the target, a smooth laminar flow of positively charged ions is created along the negatively charged surface (since the silica-based materials acquire a negative density of the surface charge upon contact with water). In the region where a jet of water hits the surface of the target, an electron stream is formed due to a triboelectric effect that propagates to the surface of the water. This electron flow ionizes atoms and molecules in the surrounding air near the surface of the water, forming a corona discharge, the role of the anode being played by the region of the flow of water flowing along the surface of the target, where the positive ions are concentrated. The distance between the "anode" and the "cathode" is estimated at 300-500 micrometers.
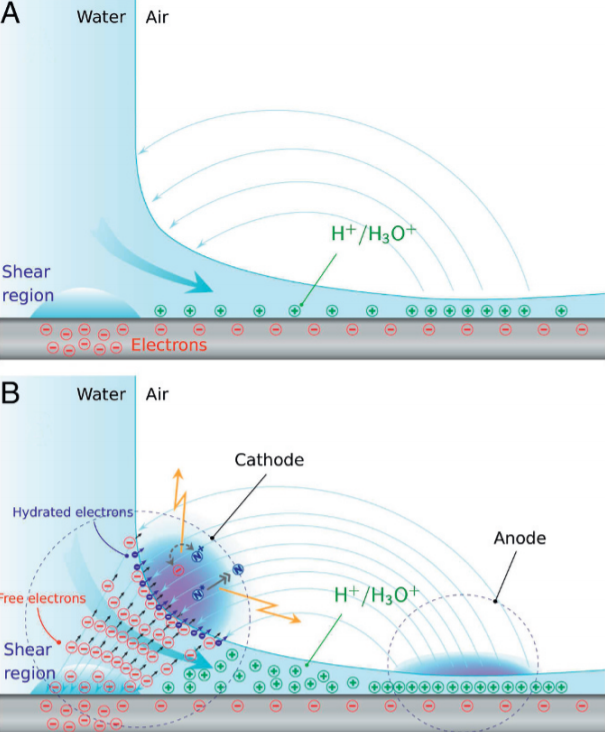
Source The mechanism of triboelectric charging and generation of plasma formations in the air.
Hello @kuku12170 love all your posts, will appreciate if you follow back
@kuku12170 science is changing our world everyday. Glad to see this coming up
Yep!!!