Function Of Root Hair And Water Absorption In Plants
The root of the plant is the structure of plants in the soil. Roots as a place of entry of minerals (nutrients) from the soil to the plant part. Root is a continuation of plant axis.
.jpg)
There are two processes that cause water to be sent to the leaves, namely root pressure and transpiration. When many mineral particles accumulate in the inscription, the potential of water will drop so much water enter (terosmosis) into the inscription. The amount of water flowing from the cortex to the stele results in a large impulse that "forces" the liquid into and into the xylem. This event is referred to as root pressure.
During the day, the air outside the leaves is dry. That is, the water content is lower than the water content in the leaves. As a result, the water in the leaves will diffuse out through the stomata. This process is called transpiration. The transpiration process causes the plants to lose water. The existence of the adhesion and cohesion forces that occur between the water and the meso fil leaf tissue cells then this tissue 'draws' water from the tissue beneath it to meet the water requirements in leaves lost by transpiration. The tensile force causes the root water (in the root-pressure process) to fill the xylem rod and keep going up to the leaf. The process of water flow from high potential to low potential because of the attraction of transpiration occurs continuously so that water can reach the leaves.
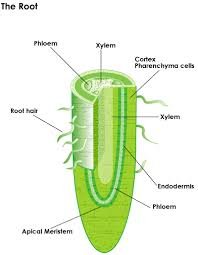
Intravascular transport is rooted from the roots to the top of the plant through a bundle of vessels, the xylem. The transport of water and minerals from root to leaf starts from the xylem root to the xylem rod that leads to the xylem stem and to the bone xylem. The bones contain binding vessels. From the xylem bone, water enters the coral cells of the mesophyll. Salt water and minerals will be used in the process of photosynthesis and transportation. It can be concluded that the transport of water and minerals from the soil to the plant body through: Root hair → epidermis → cortex → endodermis → root xylem → stem xylem → leaf xylem → leaf mesophyl parenchyma.
.jpg)
Root Hair
Root hairs are fine hairs or fibrous hairs on plant roots, usually small and present on the sides of the root or root branches. Root hair is a surface extension of the root epidermal layer that serves to optimize water absorption and nutrient minerals. The more root hairs the root surface area will be greater so as to enable plants to reach water and nutrient minerals in places far from those plants grow.
Root hairs are short-lived. Its life is only two to three weeks and then continuously regenerates through mitotic cleavage. Root hair size is very small (5-17 micrometers in diameter with a length of between 80-1500 micrometers), single-celled, and its length is only a few millimeters from the root. Generally root hair has no cuticle so the movement of water and mineral nutrients from the soil into the vessels will be easier.
Root Hair Function
The main function of root hair is to find the gap between soil particles and facilitate the process of water absorption and nutrient minerals. Water and nutrients that have been absorbed are then taken to other parts of the plant roots. Acid is secreted by this root hair. Acid will help dissolve nutrient minerals in the form of ions so that nutrient minerals are more easily transported and transported within the roots.
Structure of Root Hair
Root hair is located on the sides next to the roots. In general, the root hair consists of several parts, namely the cell wall (the outermost layer of the root hair that protects the root hair), the cell surface membrane, the cytoplasm, and the vacuole.
Vakuola is a temporary storage place. Inside vacuoles are stored water ions and mineral minerals. Before being transported to another root section. Storage of ions in this vacuole also plays a role in supporting the function of root hair in assisting ion exchange in root zone.
.jpg)
Moisturizing Water and Mineral Minerals by Root Hair
Root hair can reach the water and nutrient minerals from the cracks of soil particles. Water and mineral nutrients are absorbed in the form of ions. The ions enter through the cell wall gap, then penetrate the cell surface membrane, then into the cytoplasm. If the leaves require ions, then the absorbed ions are directly transported to the leaves for later use for photosynthesis. If not necessary, the ions are stored in the vacuole.
The ions present in the cytoplasm or vacuole are mobile. Where when the ion concentration outside the cell is lower, the ion inside the cell will come out so that the ion concentration becomes balanced. Vice versa. Absorption of water ions and nutrient minerals is done in accordance with the needs of plants by always maintaining the balance of ions located inside and outside of the root hairs.
Thus the discussion of the function of root hair. From the above discussion, it can be concluded that although there is a root root, but for the absorption process is still needed root hairs. If we pull or remove plants from pots, then the hairs are disconnected root hairs. But do not worry, because the roots will grow back and perform its function. Hopefully my writing is useful.
