Apoptosis- what is it?
Viable cells can become subject to induced apoptosis or necrosis due to the surrounding environment. A change in acidity can speed up cell death. Apoptosis is an important process for proper cell development, functionality, and chemical-induced cell death. During apoptosis, cells generally shrink in size and form phagocytized apoptotic
bodies. Apoptosis causes the cytoplasm of cells to become condensed and the organelles to be more tightly packed. Apoptotic cells are split into many tiny fragments. Necrosis is the unprogrammed death of cells. During necrosis, cells swell and become inflamed with lysed intracellular components. Cells bud during apoptosis whereas cells undergo a “blebbing” process where cytoplasmic contents are released out of the cell. Acetic acid is a by product of S. cerevisiae during alcohol fermentation and is also used as a preservative for many types of foods. Therefore the presence of acetic acid negatively impacts and restrains yeast performance. The pH level of weak acetic acid compromises the yeast cell’s functionality and promotes apoptosis. Acetic acid causes yeast cells to undergo intracellular amino-acid starvation which then displays the characteristics of apoptosis. Rubbing alcohol, or isopropyl alcohol, contains a certain amount of ethanol. In the journal Ethanol-induced death in yeast exhibits features of apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial fission pathway, a study was done to examine apoptosis of yeast cells with the presence of ethanol. Apoptosis occurred when ethanol levels exceeded a certain concentration typically used during the fermentation process of yeast cells. It was observed that ethanol-induced yeast cells caused apoptosis. The cells underwent
“blebbing” and similar characteristics of apoptosis. 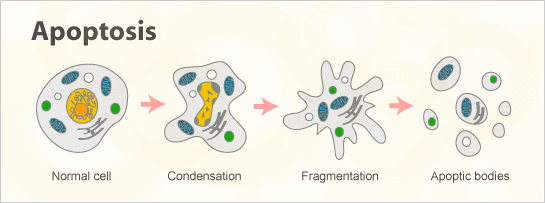
I upvoted You