Real hospital history: "pulmonary tuberculosis"
We know that tuberculosis is one of the oldest infections processes that have affected human health, and despite the fact that we currently have a vaccine as a preventive measure the so-called "BCG" vaccine, which is applied in the early days of recently was born, decades ago was very little information that could be provided to the parents of those grandparents of the elderly who come to the emergency with a series of respiratory symptoms, nowadays although it seems illogical are multiple cases of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults greater.
A few days ago, the emergency of adults of the hospital "Dr Pedro Emilio Carrillo" of the city of Valera Venezuela, an elderly couple between 75 and 85 years, whose clinical condition began more than a month ago, characterized by being lost of progressive weight, non productive cough, nocturnal sweating and feverish peaks not quantified on several occasions associated two weeks ago with dyspnea to moderate efforts and productive cough with mucopurulent secretion, reason why it visits center of its locality that indicates treatment; in view of not seeing clinical improvement and for that day presents a productive cough hemoptysis (search for the meaning) reasons why their relatives decide to take them to the emergency of the hospital during the physical examination the old woman of 75 years in clinical conditions regular dyspnea mucosa oral dry with bilateral sibilants and crackles normotensa with respiratory rate of 28 minutes and saturation 90%. We promptly started treatment with bronchodilators and requested emergency paraclinica and chest X-ray, while the 85-year-old man entered normal clinical conditions febrile to the touch, mild dehydration, hypotension, abundant bilateral crepitants, and secretion mobilization with a respiratory rate of 23 per minute, so it is decided to initiate respiratory therapies, physical and antipyretic means by mouth and paraclinics are requested with chest X-ray.
Hours later and once stabilized by the respiratory part, the results are received that report leucosistosis at the expense of segmented. What was striking in this pair of elders were their x-rays where infiltrates were visualized and the presence of several caverns or cavities of various bilateral sizes characteristic of pulmonary TB, it was decided to start treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, Bk and culture of sputum and assessment by pneumonology who in addition to everything requested indicates ppd and initiates anti tbc treatment in view of the clinical of both patients and radiological findings, currently the prognosis is preserved both are receiving anti tbc treatment and broad spectrum antibiotics. What is suspected in this type of patient without a history of tubercle prices, is likely to have suffered at a certain stage of life that failed to diagnose and treated as a common respiratory picture where their immune system has been enough competent and has remained latent, expressing rather to reactivate at this age where their immune system due to their age is immunocompetent.
Now exposed the case of these people will explain in detail so that you friends of the community understand what this disease is about:
The tuberculosis
It is a disease caused by bacteria that spread through the air from one person to another. If not treated properly, this condition can be fatal. People infected with non-diseased tuberculosis bacteria may need treatment to prevent tuberculosis disease in the future. Find out how to recognize the symptoms of tuberculosis and know if you are at risk.
Causes
Tuberculosis occurs when the healthy person inhales microscopic drops of saliva from the patient (called aerosols), which are generated when the patient coughs or sneezes. These droplets with bacteria have a very small size and reach deep areas of the lung of the healthy person, where they could proliferate giving rise to the disease. Although the lung is the main organ in which the damage develops, there are other locations of the body that can be affected. In the spacious, well-ventilated or outdoors, contagion is complicated. This is because, although tiny droplets can be suspended for some time in the air, they end up spreading and losing their infective capacity.

http://www.webconsultas.com/tuberculosis/causas-de-la-tuberculosis-713
Although there are factors that determine the likelihood of infection, such as the hours shared with the patient indoors, the virulence of the bacterium (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), or the susceptibility of the healthy person, it is accepted that contracting the disease is not easy, and that a prolonged contact is necessary so that there is a real risk of contagion (in a guideline, usually determined about six hours).
Symptom
Tuberculosis bacteria multiply more frequently in the lungs and can cause symptoms like the following:
- An intense cough that lasts 3 weeks or more.
-Chest pain. - You with blood or sputum (phlegm that leaves the bottom of the lungs).
-Other symptoms of tuberculosis disease may include the following:
Weakness or tiredness.
-Weightloss.
-Lack of appetite.
-Shaking chills.
-Fever.
-Sudor during the night.
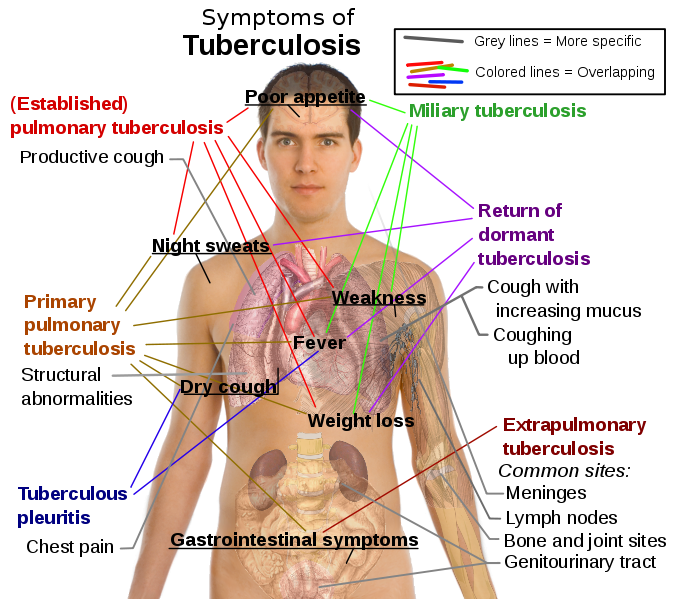
http://tuberculosisomg.blogspot.com/p/sign-symptoms.html
Diagnosis
When the patient visits the clinic with symptoms that may indicate tuberculosis, the doctor will ask a series of questions aimed at knowing the duration of the problem, whether or not the patient has been in contact with tuberculosis patients and for how long. In addition, will commission several tests to corroborate the diagnosis of tuberculosis, none too complex, such as sputum analysis (phlegm) and chest X-ray.
The analysis of phlegm in the laboratory is especially important (phlegm is the mechanism of expulsion of bacteria and, therefore, will appear in it). The X-ray will show the patient's condition. If the gaps in the lung mentioned in Symptoms have already appeared, the disease is considered to be at an advanced stage requiring immediate treatment, and may mean that the patient is potentially contagious.
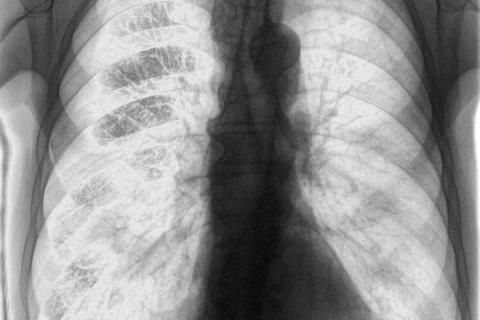
http://www.webconsultas.com/tuberculosis/diagnostico-de-la-tuberculosis-716
Another very common test to detect the spread of tuberculosis is the tuberculin test, which involves injecting under the skin a derivative of a protein from the bacteria, which is harmless, and then study the skin reaction. The interpretation of the result must be done by a professional, since both the positive and the negative can have different interpretations. After the test, you do not have to scratch your arm even though it bites; In that case a cold gauze can be applied to relieve the itching, but without touching the puncture, since it could alter the result of the test.
If the patient has been vaccinated against the bacterium (BCG vaccine), or has been in contact with another mycobacterium of the non-tuberculous environment, it may give positive reaction (False Positive, because it does not actually present the infection). On the other hand, despite having contracted the tuberculosis bacteria, the result may appear negative (False Negative) if the contact has been recent. It usually takes two to eight weeks for the body to react to the test; therefore, it is often repeated at two months, to corroborate the result.
If the doctor concludes that the patient has tuberculosis and that the bacterium has remained in his / her organism an important time, it will be necessary to know the people with whom it has been related, to institute preventive treatment and to try to prevent the disease from developing in they.
Risk Factors for Tuberculosis
Anyone can get tuberculosis, but people with high risk generally belong to these two categories:
- People newly infected by tuberculosis bacteria.
- People with conditions that weaken the immune system.
-A patient with a mouthpiece reading a brochure You have a higher risk of being infected by bacteria from the
tuberculosis in the following cases:
"He's been with someone who has tuberculosis disease.
-It comes from a country where TB is very common or visited.
- Live or work in places where tuberculosis is most common, such as a shelter for the homeless, a prison or jail or long-term care facilities.
- It is a health care worker who cares for clients or patients with a high risk of tuberculosis disease.
You are more likely to have tuberculosis disease once you become infected in the following cases:
-Have HIV infection.
-It's a child under 5 years.
-He became infected with the tuberculosis bacteria in the last two years.
-Have other health problems that make it difficult for your body to fight the disease.
- Smoking cigarettes or abusing alcohol or drugs.
-He was not adequately treated with latent tuberculosis infection or tuberculosis disease in the past.
Treatment
The Koch bacillus has a great ability to protect itself against antibiotics by developing resistance when they are used individually. Therefore, it is always necessary to use combinations of antibiotics. Treatment can be done on an outpatient basis, although respiratory isolation is required, for at least the first two weeks.
Among the first choice anti-tuberculosis drugs are isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol and streptomycin.
International infectious disease associations now recommend starting treatment with three first-line antibiotics for 2 months, followed by two for an additional 4 months.
The most common treatment regimen is the combination of isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide during the first two months to continue for another four months with isoniazid and rifampicin. Depending on the cases, longer-lasting and higher-dose regimens may be necessary.
http://www.3gehealthcare.com/healthy-living/how-to-treat-pulmonary-tuberculosis.html
Prevention
Tuberculosis can be prevented, but it depends, above all, on the patient's attitude. It should always be coughed up in a tissue paper, which should be placed in the trash in a closed plastic bag.
During the first two to three weeks of treatment, the patient should be kept isolated in a room, which should be ventilated several times a day and remain with the door always closed to prevent the spread of bacteria to other rooms of the house . Personal contacts should be brief and limited; and anyone who comes in contact with the patient should wear a mask to avoid inhaling the bacteria present in the air. On the outside there is no risk, provided that a reasonable distance is maintained. The rays of the sun kill the bacteria, so it is convenient that the patient's room is sunny. If patient isolation can not be carried out at home, you should go to the hospital
During this period, the patient will not maintain intimate contacts or sexual intercourse, as he may still be in the infective phase. Only when you have two or three weeks of treatment will you be assured that you can no longer infect anyone. It is necessary to avoid during this time the closed places, with many people, like the public transport.
After this period of two or three weeks, the patient may leave the insulation, and the contacts will not require the use of a mask.

http://www.info.gov.hk/tb_chest/contents/c1212.htm
If a person has been in contact for a long time with a tuberculosis patient, they should go to the doctor and discuss the case. Symptoms (or lack thereof), chest X-ray, and certain simple tests, such as tuberculin, will tell the doctor if you have contracted the bacteria and if you require preventive treatment to avoid infection.
If the contact has been mild, for a short time, or has occurred in an open environment, there is little risk of contracting the bacteria. However, you should consult a doctor if you have doubts about it.
Several studies are currently underway in search of an effective vaccine to protect against tuberculosis, in fact twelve of them have already entered the clinical trial phase. In general they are based on the use of antigens that replace the old BCG vaccine, or that it potencien.
Credits:
https://www.cdc.gov/spanish/especialescdc/sintomastuberculosis/
http://www.who.int/features/qa/08/es/
https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/000077.htm
http://www.cun.es/enfermedades-tratamientos/enfermedades/tuberculosis#tab1
My advice as a practitioner of medicine is very simple, to be vaccinated at birth, to avoid developing this type of diseases in the long term
By: Doctor Johana Albarran
Greetings and have a happy night
Congratulations @joha09sohi! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP