Chemistry Explanation : Why Methane Gas More Harmful Than Carbon Dioxide in Greenhouse Effect
Gas Emission
Gas Emission
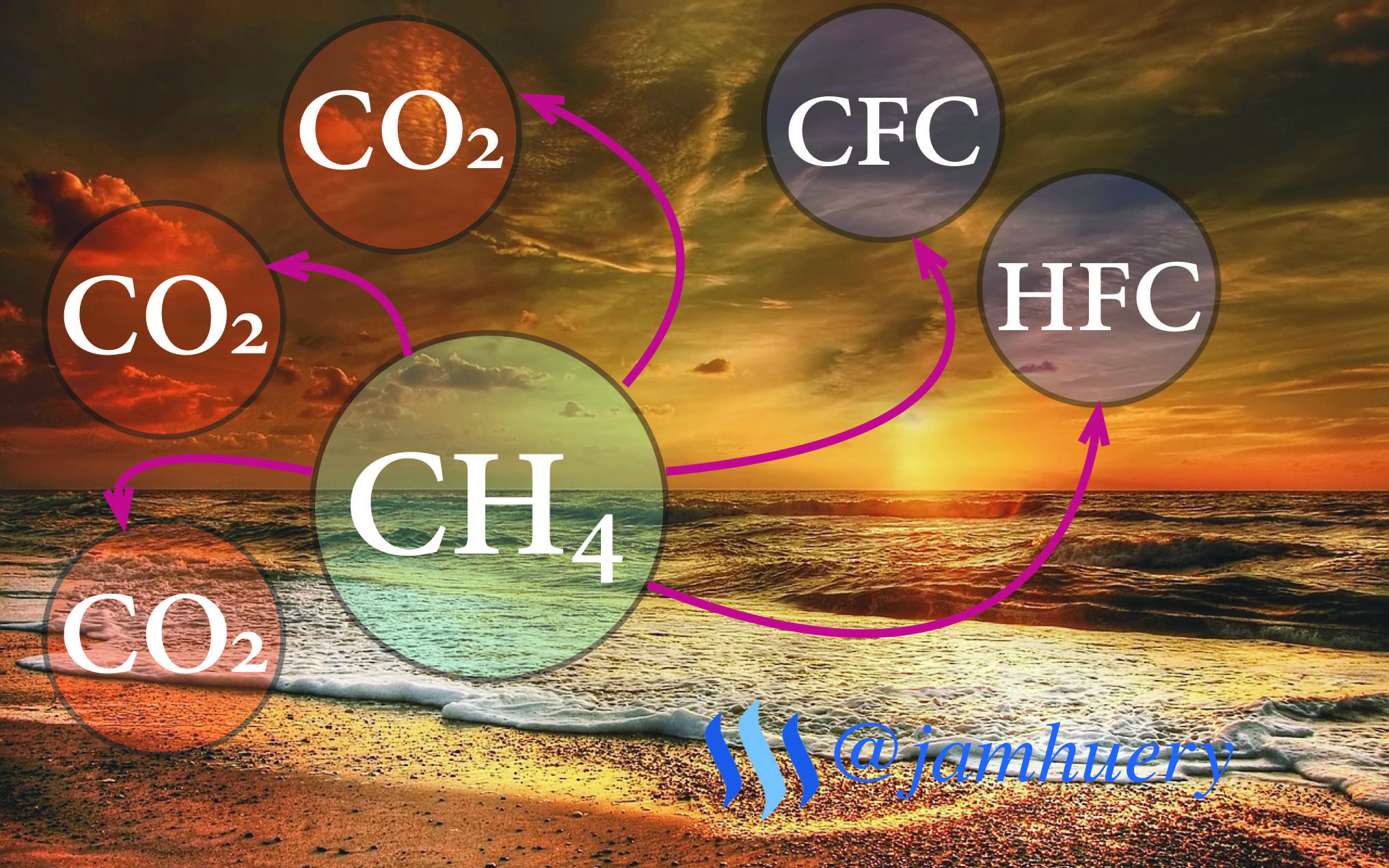
Global warming is temperature rising in the earth's surface caused by increased greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), Dinitrogen Oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons(HFCs), fluorocarbons, and Chloroform (CFC).
Global warming is a process related of rising average temperatures due to trapped greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere, due of accumulation of greenhouse gases such as, carbon dioxide, and methane gas into traps of radiation waves, The gases absorb and reflect back of radiation waves emitted by Earth and consequently the heat will be stored on the Earth surface.
Many sources said the greenhouse (methane) is more dangerous than carbon dioxide, so this post more focused on methane discussions that a result in global warming.
What is Methane ?
What is Methane ?
Methane is a gas formed from covalent bonds between four H atoms with one atom C. The Methane is an alkane derivative. Generally Alkane was difficult to be react (small affinity) and it commonly referred as paraffin, another characteristic of alkene is easy undergoes to complete combustion reaction with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O) gases.
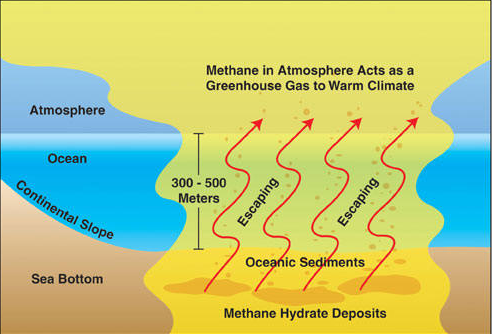
Methane gas formed from natural biomass combustion such as biogenic, and thermogenic processes. this gas trapped in large quantities in ocean sediments, approximately by a depth in 1,000 (one thousand)feet ice, it known as methane clathrate, the clathrate is stable, but at low temperatures (over freezing water temperature) and certain pressure about 5 MPa it will melt quickly and release flammable gases into the air.
The formation of biogenic gas occurs massively in the massed, so it have a large concentration of natural biogas. This gas can be mined like ordinary natural gas, but its main component is methane. Biogenic gas is a result of metabolism from bacteria, So it does not happen at high temperatures. Whereas thermogenic process, the methane gas formed together with oil. The more organic compounds in the rock the more oil produced. In high temperature and pressure the gas will be formed more and more. Chemically, the biogenic process can be formulated :
CO2 + 8 H+ + 8 e- → CH4 + 2 H2O
The methane produced by microorganism naturally, this process called as methanogenesis. It has several steps used by microorganisms as source energy, the methanogenesis is anaerobic respiration used by organisms that occupy of final dumps.
Methane Forming
Methane Forming
The process of greenhouse gas formation in the atmosphere occurs when methane (CH4) reacts with oxygen (O) and Hydrogen (H) molecules called as radicals. The Hydroxy radicals combine with methane and then both molecules elaborated into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). this process was increase CO2 becomes a major role in global warming.
Generally, the releasing of methane frozen from ocean floor to the atmosphere, the cold temperatures and high pressure keeps the stability of methane in seafloor. The scientists think the movement of tectonic plates reduces the pressure on seafloor and releases the methane, the methane releases bubbles into atmosphere. It may be, the atmosphere and oceans begin to heat up and melts more methane than the emits bubbles (gas) out. Many scientists estimate the Antarctica stored approximately 400 billion tons of frozen methane, and this gas will release little by little into atmosphere as the number of ice sections collapses in the Antarctic.
Why Methane More Dangerous ?
Why Methane More Dangerous ?
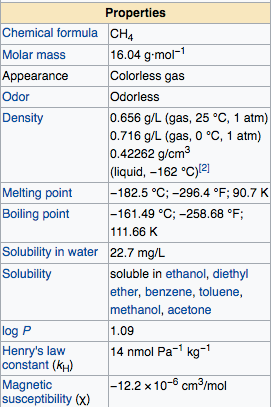
The main reaction of methane is the combustion and re-establishment of steam into synthesis gas and halogenation and it reactions was difficult to control. Extend of Methane oxidation is methanol, but this reaction difficult because this reaction requires a mono-oxygenase enzyme to produce methanol from methane. At standard temperature and pressure the methane colorless and odorless gas, then it boiling point -161°C at atmospheric pressure, this gas only flammable if concentration reaches 5-15% in the air.
Methane is one of the fuels used electricity generation, the combustion methane produces less carbon dioxide (CO2) gas than any other fossil fuel (for each unit of heat produced). The combustion of methane produces 891 kJ/mol of energy. If this energy compared to other hydrocarbon fuels, the methane combustion produces less carbon dioxide gas, but in ratio side from energy generated of methane molecular mass is 16 g/mol, the methane generates the energy (heat) per unit mass (55.7 kJ/mol ) which is larger than any other hydrocarbon.
The Methane combustion takes several stages, the initial result is formaldehyde (H2CO), The formaldehyde oxidation will produce radical formaldehyde(HCO). Which this radical reaction will form carbon monoxide (CO). Chemically, the reaction can be formulated :
CH4 + O2 → CO + H2 + H2O
H2 will oxidize to H2O and released an energy. Usually, this reaction occur quickly, usually even less than a millisecond.
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
Finally, CO will oxidize and form CO2 while releasing energy. This reaction occur more slowly than other stages, usually take several milliseconds.
2 CO + O2 → 2 CO2
The final reaction result of under standard temperature and pressure conditions the above is:
CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O (ΔH = -891 kJ/mol) The methane can also react with halogens by helping of heat energy and ultraviolet, for example, the reaction of methane with chlorine gas (Cl), this reaction will produce dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), chloroform (CHCl3), and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl The initial reaction with radicals Cl+ bond with methane to produce CH3, both molecule combine and form methyl chloride (CH3Cl), This gas was highly reactive with oxidizers and halogens along several chemical contain halogen compounds and it is also an asphyxiated gas that can replace oxygen in enclosed spaces, the asphyxia may occur when the oxygen concentration in the air was reduced below 16%(by volume).
Conclusion
Conclusion
From reaction above, we can see the decomposition of methane gas forms CO2 and the oxidation reaction forms several times of carbon monoxide molecules, and with ultraviolet methane gas will break down Carbon atoms and bind to chlorine, the result of this reaction produces a Chloroform also known as greenhouse effect, so it is clear that methane gas is more dangerous than CO2 gas.
Source :
Support Scientist By Use #science tag or join @steemSTEM
Follow Me @jamhuery

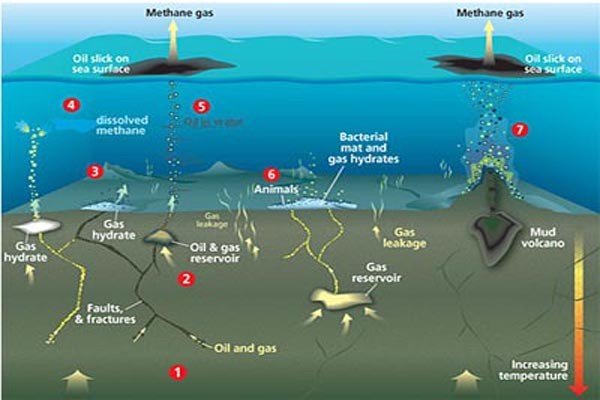
"this gas trapped in large quantities in ocean sediments, approximately by a depth in 1.000 feet ice"
Seriously just 1 feet?
"CO4 + 8 H+ + 8 e- → CH4 + 2 H2O"
Are you sure its CO4 in your equation?
and also CH2 for:
CH2 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Its seems a bit too much typo?
Sorry for my mistake. i wrote formula using html, sometime i confuse to find it after replaced
< sub > 2 < /sub >, after replaced the number sometime i forget to replace it back.wow great education information sharing
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by jamhuery from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews/crimsonclad, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows and creating a social network. Please find us in the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
This post has received a 1.04 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @banjo.