Toward Space, Reach the Stars: Space exploration ...(1)
The dream of space and space exploration has existed for thousands of years, the advancement of science and technology, the dream of exploring space and reaching for stars can be achieved.
mythology and a new era of discovery

Discovery Space Shuttle Launch Mission Astronauts.pixabay
Dreaming flying like a bird is one of the human fantasies since thousands of years ago. Humans want to fly across the sky. Listen to Greek mythology about Daedalus and his son Icarus who fly winged wings that finally melted in the heat of the Sun.
In Indonesia, there are stories of Nini Anteh (Sunda), Lawaendröna (Nias), Gatotkaca (Java), etc. Mythology or legend that was born and survived thousands of years is the intention of the desire. Passing through the span of human civilization - that in fact to realize this dream ultimately becomes a cultural history of human thought will be something far beyond what it wants to achieve. Remember the poems of children's songs "Take the Moon, Mother" or other on the poem "Little Star .. to where you are".
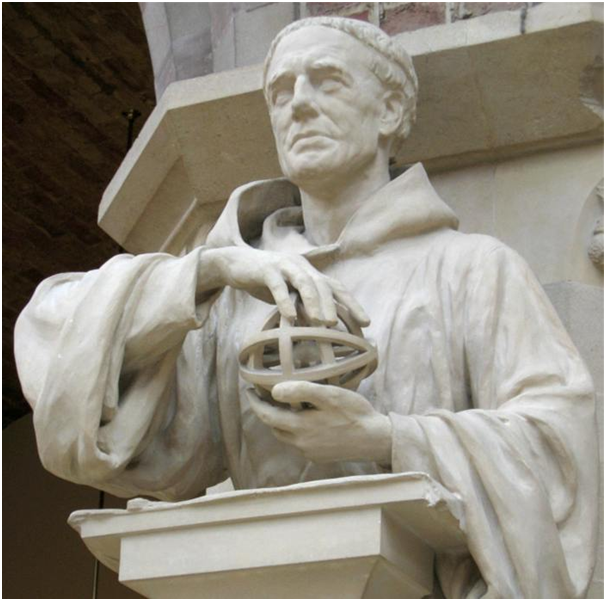

Roger bacon statue.wikipedia
With "advanced" knowledge, the means to achieve that dream come to a great extent. In 1232, for the first time, China used a rocket to invade Mongolia. Basically, the rocket is meant to be fueled by gunpowder-like firecrackers which happen as an adaptation of fireworks or fireworks glides there. The following decade, the British priest - Roger Bacon succeeded in "enhancing" it. Continuing the 15th century, during the Hsia dynasty era in China there was a minister named Wan Pu who tried to fly with a large rocket-powered kite and not long ago even appeared sketches "flying machine" propeller.
There is a unique and noteworthy chapter of history that Galileo Galilei has been known as the inventor of the telescope (1608). In fact, telescope technology has been encountered in the Arab world more than 6 centuries before.
It is Abu Ali Ibn Haytam / Abul Hasan, a student of Ibn Yunus, the inventor of a mathematical theory of how the pendulum works (oscillation theory). In Europe called Alhazen. The optical specialization that one of his creations is the lens, including a remote cylindrical viewing device now called a telescope. His refractive theory leads him to the conclusion that the celestial bodies will appear before the object actually rises, or will still appear on the horizon even though the object has been set. Analysis of atmospheric thickness associated with observations is the result of his brilliant work. The work of al-Haytam adapted Vitello (1270) and then spread throughout Europe, including by Descartes, Kepler, Lippershey, and Galileo who successfully redesigned the telescope in a more modern form.
One thing that is very impressive in this era and should be observed is the emergence of a positive impact on the development of human knowledge and reasoning when found something previously invisible, and something that is heavenly objects far away there. How to view himself as the width of the universe in whose time is said to be infinite. The impact of the presence of the telescope also enriches and reinforce the dream of navigating oceans.
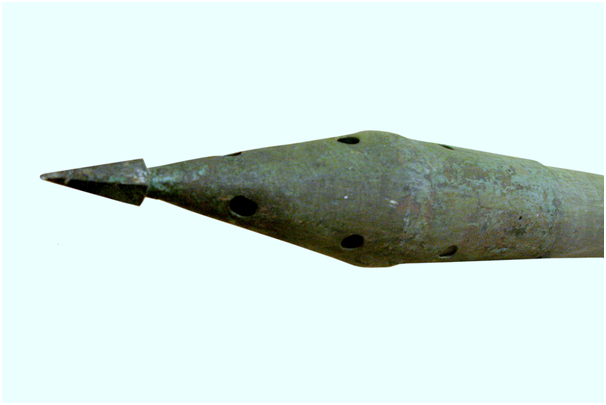

Tip of an early Congreve rocket of the Napoleonic Wars, on display at Paris Naval Museum.wikipedia
Arriving in the 18th century, England Captain Thomas Desaguliers examines the rockets he found from India, especially in terms of his cruising range and power. Then followed by the early 19th century, it was the turn of British Colonel William Congreve to develop Desaguliers results for the military with rocket base material is solid fuel. During the Napoleonic war of 1806, Congrieve's rocket technology was used en masse.
The desire to fly also appears in the classic novel Julius Verne French science fiction writer (From the Earth to the Moon - 1865) who fantasize about a gigantic rocket. In his novel, the rocket is composed of various components and carrying various equipment (only 100 years later materialized). Take the launch site in the Gulf of Florida area and the rocket is named Columbia (immortalized for the name of the rides in the Apollo 11 mission that landed on the Moon in 1969). Was filmed with the title Journey to the Moon by Georges Melier early 1900s.
Meanwhile, the first proposals about the space station appeared in 1869, by the American novelist Edward Everett Hale in Brick Moon and continued in 1870 on his novel Life in the Brick Moon first published in Atlantic Monthly magazine. The concept of "Brick Moon" is as a space station (space station, like the International Space Station which is now orbiting the Earth), as well as military means and navigation tools in the vast ocean of star stars.
20th Century, Century of Space Exploration
Entering the 20th century, the concept of a rocket that is now known to start developing. Spearheaded Constantine Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (1857 - 19 September 1935, Soviet Union), mathematics teacher. His notion of "multi-stages rockets," winged spaceships, space stations, and interplanetary explorers became technological foot breaks that after the last 80 years could only be realized.
Tsiolkovsky is considered the Father of Soviet Space Exploration. However, there is a milestone in parallel to be reckoned with in this arena, in which the Wright brothers made their first flight with an airplane with the aircraft technology now known on December 17, 1903. Followed by Hermann Oberth (Romania / Germany) which for the first time introduced the term "space station". The idea originated as a stepping stone when humans want to the Moon and Mars. Followed by Paul Schmidt (USA) and Robert Goddard (the USA, dubbed the Father of Modern Rocket). Goddard was successful for the first time flying a liquid-fueled rocket (March 16, 1926) from a sliding run in Auburn, Massachusetts, USA.
Meanwhile, in 1952 Werner von Braun published his concept in Collier magazine with a prototype rocket measuring about 80 meters and was in Earth orbit with an altitude of about 1,000 miles. Braun finally made a rocket called type A-2 and V-2 that gave birth to the concept of IRBM / ICBM (Intermediate Range / Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile). Concepts related to cruise missiles.
With ICBM techniques, the effort at this stage culminated on 4 October 1957 when the Soviets successfully launched Sputnik 1 orbiting the Earth at an altitude of 800 km for 162 days. This date is commemorated by the United Nations as the opening of the annual World Space Week event from 2001 and proclaimed until 2020.

Modell av Sputnik 2.wikipedia
Various advances keep rolling are sometimes unique. Call Laika, a dog who managed to become a "crew" Sputnik 2, followed by Explorer I - Earth-orbiting satellite of 1958 by the United States. The Soviets managed to orbit Yuri Gagarin's first cosmonaut with Vostok-1 (12/4/1961, 108 minutes). The US follows with astronaut Alan Sheppard - 5/5/1961. This achievement race is getting tighter by landing for the first time man on the Moon, Neil Armstrong with Apollo 11 (19/7/1969).
Until the year 2000 no less than 4,000-vehicle was launched with a variety of missions. The science of space is becoming more universal. For example, the Salyut (1971, Soviet) and Skylab (1973, US) space stations, as well as the merger of Soyuz (Soviet) with Apollo (USA) of July 1975, are considered symbols of peace.
Space Shuttle
Flight type is increasingly varied. One of them is Space Transportation System (STS) better known as Space Shuttle or NASA space shuttle. It has a height of 56.1 m, a diameter of 8.7 m, and a weight of ± 2000 tons. Based on cruising range including low orbit rides. The launch site is at Cape Canaveral (Kennedy Space Center).

Enterprise is the first prototype. Successfully launched September 17, 1976. STS program itself begins with the launch of Columbia (STS-1) on April 12, 1981. Succeeded with 4 astronauts November 11, 1982 (STS-5), followed Challenger (STS-6, 4 April 1983), Discovery (STS-41-D, August 30, 1984), and Atlantis (STS-51-J, 3 October 1985). Space Shuttle mission ended in its 135th mission on 8-21 July 2011 with the launch of Atlantis (STS-135). There were two calamities, the first explosion of Challenger (January 28, 1986) shortly after the launch (STS-51-L) and the second (STS-107) on February 1, 2003, that exploded Columbia shortly before landing.
The noteworthy mission of Columbia is to put the Chandra X-ray Observatory telescope (STS-93). In addition, the first in terms of putting a commercial satellite along with a crew of 4 (STS-5), took a space laboratory (Spacelab) with 6 crew (STS-9), commanded by female astronaut Eileen Collins (STS-93). Juxtaposed also with another shuttle: Atlantis, Challenger, Endeavor, and Discovery. Many rides are transported by Space Shuttle, such as Hubble space telescope, Spitzer, Compton, Galileo, Magellan, Ulysses, etc. Space travel (spacewalk) was also first performed by the Columbia crew on the mission STS-87, the astronaut Winston E. Scott when assembling the International Space Station. Includes shuttle astronaut Joe Allen who in November 1984 managed to capture the wrong Palapa B-2 satellite placed in orbit.

The merger of two spacecraft was repeated in 1995 between the shuttle Atlantis (US) with Mir (Soviet) space station. Now there is a space station International Space Station (ISS). US and Soviet in 1984, designed 1994 and built 1997. Involving 17 countries: ESA (European Space Agency: Austria, Netherlands, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Italy, Ireland, England, Germany, Switzerland, Norway, France, Spain, Sweden), Japan, Canada, and Brazil.
Finally, the main module after 2006. The shuttle can park there. The development of this technology is also what ultimately bring humans to explore the Solar System.
to be continued.......
BEST REGARDS @irza
Reference :
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daedalus
- https://tatangmanguny.wordpress.com/dongeng-sunda/nini-anteh-sang-penunggu-bulan/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_rockets
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roger_Bacon
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galileo_Galilei
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ibn_al-Haytham
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Congreve_rocket
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sir_William_Congreve,_2nd_Baronet
- https://www.space.com/19994-konstantin-tsiolkovsky.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Konstantin_Tsiolkovsky
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Launch_System
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progress_Rocket_Space_Centre
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Shuttle_Solid_Rocket_Booster
Hi, I found some acronyms/abbreviations in this post. This is how they expand: