Artificial Satellites [The space Age] [Benefits for the earth]
The first exciting step into space was taken on Octuber 4, 1957. On that historic day, a Soviet rocket boosted Sputnik 1, the world's first artificial satellite, into Earth orbit. The Space Age had begun.
Since that day, thousands of artificial satellites have been placed in orbit around the Earth. Astronauts have gone to the moon and returned. People have lived and worked in Earth orbit for extended periods of time. Slowly, humans are taking their first tentative steps beyond the home planet and into the solar system. At the same time, we learning more about our planet and finding ways to improve our lives.

Artificial Satellites
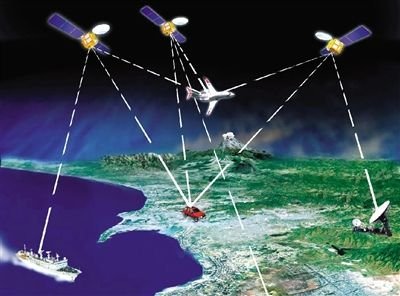
Artificial Satellites are satellites built by people. Like the moon, which is Earth's natural satellites, artificial satellites travel just fast enough so that they neither escape the Earth's gravity nor fall back to the Earth's surface. There are several different types of satellites orbiting the Earth. Communications satellites, weather satellites, navigation satellites, and scientific satellites are among the artificial satellites that orbit the Earth today. Each of these types of satellites has specific function.
Communications Satellites:
Many of the satellites orbiting the Earth are communications satellites. Communications satellites beam television programs, radio messages, telephone conversations, and other kinds of information all over the world. You can think of a communications satellite as a relay station in space. The satellite receives a signal from a transmitting station on Earth. The satellite then beams the signal to a receiving station somewhere else on Earth. In this way, information is quickly transmitted from one place to another, even on the other side of the world.
Communications satellites are often placed in geosynchronous (jee-oh-SIHNG-kruh- nuhs) orbit. A geosynchronous orbit is one in which the satellite revolves around the Earth at a rate equal to the Earth's rotation rate. As a result, the satellite stays in one place above a certain point on the Earth's surface. Three such satellites placed equal distances apart at an altitude of about 35,000 kilometers above the Earth can relay signals to any place on Earth.
Weather Satellites:
Artificial weather satellites have greatly improved our ability to track weather patterns and forecast weather conditions all over the world. By studying and charting weather patterns, scientists can predict the weather with greater accuracy than ever before. These predictions are particularly important in tracking dangerous storms such as hurricanes. Through the use of weather satellites, scientists today can better predict when and where a hurricane will strike. This information gives people in the path of a hurricane time to protect. Themselves and their property and often saves lives.
Navigation Satellites:
Navigation satellites are another type of artificial satellite. They send precise, continuous signals to ships and airplanes. Using information from navigation satellites, sailors and pilots can determine their exact locations within seconds. This information is especially useful during storms when other kinds of navigation equipment may not provide accurate information. Someday it may even be possible for cars and trucks to use navigation satellites to pinpoint their locations.
Scientific Satellites:
Many different types of scientific satellites now Earth. Long before Sputnik, scientists looked forward to the day when they could observe the Earth and the universe from orbiting satellites. They thought scientific satellites would help them to solve old mysteries and to make new discoveries about the universe. And they were correct.
In 1958, the first satellites launched by the United States, Explorer 1, discovered the Van Allen radiation belts around the Earth. Since that time, other scientific satellites have added greatly to our knowledge of the universe. One satellites in particular - the Infrared Astronomy Satellite, or IRAS- has solved many mysteries of the universe. IRAS has found evidence of planetary systems forming around distant stars, as well as evidence of massive black holes at the center of the Milky Way and other galaxies. (A black hole is a collapsed star that is so dense that nothing -not even light- can escape its grip.)
Other scientific satellites focus their attention on Earth. In 1991, the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite was sent into orbit to study the Earth's protective ozone layer. This satellite was the first in a series of environmental science satellites launched as part of Mission to planet Earth. Mission to planet Earth is a long-term research program that will use scientific satellites to study the Earth's environment.
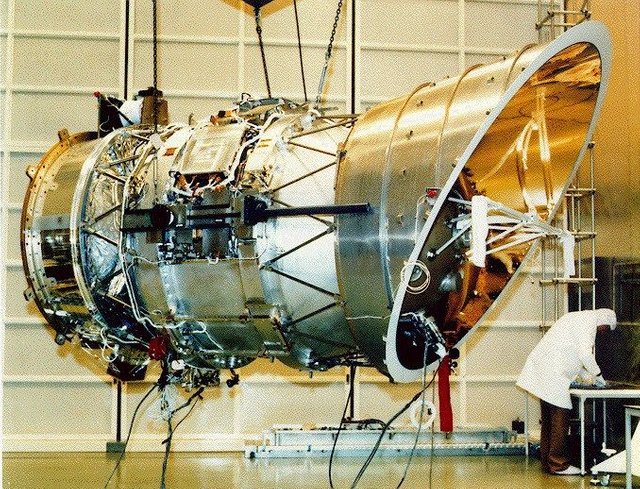
Laboratories in Space
In 1973, the United States launched Skylab into orbit. Skylab was a space station designed to allow astronauts to perform experiments in space. Astronaut could dock their spacecraft to with Skylab and enter its laboratory. Later the astronauts could reenter their spacecraft and return to Earth with their data. Visiting crews aboard Skylab made detailed studies of the sun, conducted several health-related experiments, and learned to work in space. Skylab was the United States' first laboratory in space. Today Spacelab has taken the place of Skylab. Spacelab is a laboratory that is designed to be carried into orbit by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory can be fitted with different types of scientific equipment, depending on the types of experiments being performed.
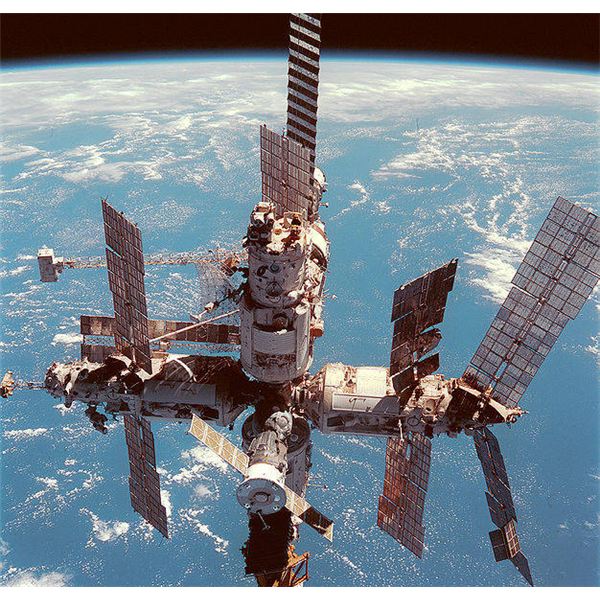
In 1986, the Soviet Union launched a space station called Mir. (The Russian word Mir means peace.) Space station Mir was designed as a series of modules that could be added to the original basic module. Today, Mir consists of four permanent modules. Eventually, two more modules may be added on. Cosmonauts, who often remain on the space station for months, perform a variety of scientific experiments aboard Mir.
Mir is now the largest and most complex space station ever to orbit the Earth. The United States, however, is planning to build its own space station, possibly as a joint venture with Russia, Japan, and several other national. The space station will be built in orbit from parts carried into space by the Space Shuttle. Someday the space station may serve as a base for return trips to the moon and for the exploration of Mars.

Space Technology Spinoffs
Although most of the major discoveries of the space program have been made far from the Earth, many aspects of space technology have practical applications. Because these applications have been spun off the space program, they are called space technology spinoffs. They owe their existence to the exploration of space. Thousands of spinoffs from heart pacemakers to lightweight tennis rackets, have resulted from applications of space technology.
Space technology even it is intended for use far beyond the frontiers of Earth may have practical applications for billions of people who will never get farther the Earth's surface.

Images:
Source 2
Source 3
Source 4
Source 5
Source of information:
https://www.youbioit.com/es/article/shared-information/15589/que-son-los-satelites-artificiales-y-como-funcionan
https://www.ecured.cu/Sat%C3%A9lite_artificial
http://www.geoenciclopedia.com/satelites-artificiales/
http://www.monografias.com/trabajos39/satelites-artificiales/satelites-artificiales.shtml
https://sites.google.com/site/3bsatelitesartificiales/satelites-artificiales2
http://www.brighthub.com/science/space/articles/95865.aspx


Excellent publication It is interesting everything that science allows us to have, for observe our universe. Regards @gmaktub
Thanks for your comment. If the science is incredible.
Excellent content, a lot of success @gmaktub
Thank you :)