Pneumatic and hydraulic systems - A lesson activity for teenagers
One question that teens like to ask about, is how power is transmitted from one place to another using a liquid or a gas. Especially boys! At some point, they start to wonder how a car or some things like construction equipment work.
As a teacher, you may want to start with the basics.
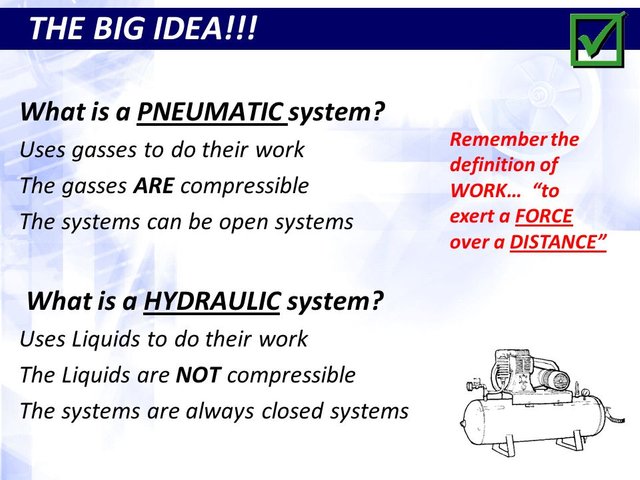
- Pneumatic systems use compressed air or gas to produce an output.
- Hydraulic systems work on the same principle, bit use liquid, such as water or oil, instead of air to produce an output.
- The movement of the output in pneumatic and hydraulic systems can be linear or rotary.
The important parts of pneumatic and hydraulic systems are:
- Cylinders: tubes to suck in the air or liquid
- Pistons: these are inside the tube and compress the air or push the liquid through
- Valves: the valves stop the air or liquid from flowing out.
Pneumatic systems in action
A pneumatic system works with compressed air. Compressed air is able to transmit more force than air that is not under pressure. It is important to note that pneumatic systems can only work in a closed system in which the air or gas cannot escape, otherwise it will not function properly.
The air in a pneumatic system is compressed by means of a pump. For example, when you push on the handle of a bicycle pump you are compressing the air and forcing it into a smaller space
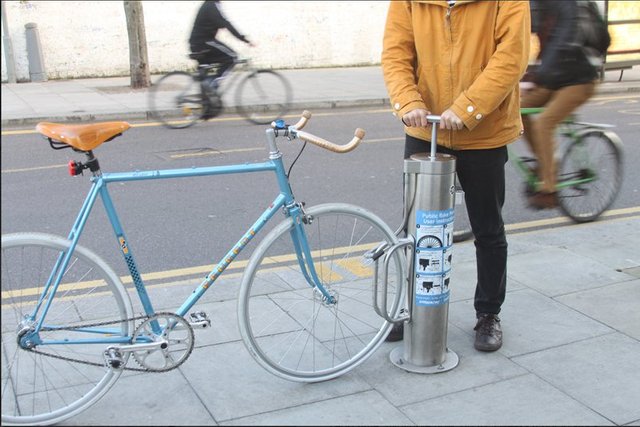

Image source
Uses of a pneumatic system
Pneumatic systems are used widely in industry. Many factories use compressed air or other compressed gases in the motors of their machinery. Pneumatic systems are also used in vacuum pumps, jackhammers, trains, dental drills and anti-aircraft weapons.
How does compressed air make mechanisms move?

The lifting device on a forklift makes use of a pneumatic system
Compressed air uses a pneumatic cylinder to create movement. When compressed air enters the base of a pneumatic cylinder, it pushes on the piston and makes the piston rod extend (move out). Air on the other side of the piston escape into the atmosphere. When compressed air enters the rod end of a pneumatic cylinder it makes the piston rod retract (move in).
How can we control the movement of a cylinder by using pneumatic?
We use a valve to control movement. It works like a switch to direct air through tubing to the base, or the rod end, of the cylinder.
Why is compressed air important?
Creating movement and transferring forces are two important actions some machines use. In industry, these tasks are often done by pneumatic (compressed air) or hydraulic (pressurised oil) devices. The concept of fluid power includes both pneumatic and hydraulic mechanisms.
Parts of pneumatic systems
A pneumatic system has three basic parts:
How are pneumatic devices useful in everyday life?
Pneumatic devices push, pull and lift objects, they open and close doors. They can hold and remove materials, and position pieces of material for manufacturing.
This pump is an example of a pneumatic system
Advantages of using compressed air:
- Air is cheap and plentiful.
- Air is easy to compress and can be stored in tanks.
- Pneumatic systems can be interconnected easily by means of hoses, pipes and tubing.
- Pneumatic systems can produce large linear movement.
- Exhaust air can be returned to the atmosphere, so a return line back to the pump is not needed.
- Compressed air is relatively environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages of using compressed air (in industrial compressed air systems):
- The air must be kept dry and clean. This needs special filtering.
- As the air is used at high pressure, safety measures need to be followed.
- Industrial compressed air systems sometimes spray a fine mist of lubricating oil into the atmosphere. This affects air quality.
- Compressed air mat not provide a large enough force. In such cases, higher-pressure hydraulic system might be needed.
Activity:
To investigate how a pneumatic or hydraulic system works, have three syringes ready (two should be the same size, the third one a different size). When connected to either side of a plastic tube, the two syringes and plastic tube form a pneumatic or hydraulic system: the tube of the syringe will be the cylinder and the plunger will be the piston.
Image source
This is how you do it:
- Start with two syringes of equal volume.
- Push the plastic tube over the tip of one syringe with the plunger down.
- Pull the plunger of the other syringe out as far as possible.
- Now connect the other end of the plastic tube to the tip of this syringe.
- Push the plunger of the syringe into the syringe and see what happens.
- Now pull out the plunger of the second syringe completely and fill the syringe with water. Make sure that there are no air bubbles in the water. Push the plunger back in and see what happens now.
- Follow the same steps as above, but use two syringes of unequal volume. The larger syringe should be pulled out.
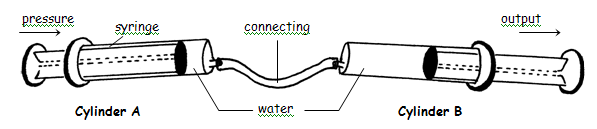
Image source
Bibliography & Extra Reading:
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic systems
- Power systems
- Pneumatics - Wikipedia
- Pneumatic motor - Wikipedia
- Compression/Expansion
- Difference between the two systems
- Compressed air
- Pneumatic cylinder
- Air cylinders
- Compressed air safety
- Dangers of compressed air
- How hydraulic systems work- syringes