Hypoxia: How diatoms might be holding a major key to human survival
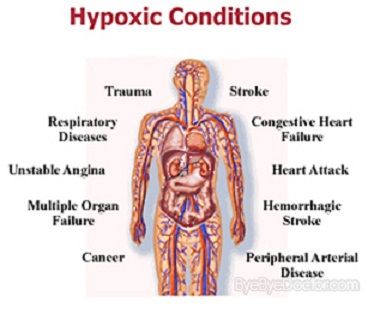
Brief recall: Hypoxia
The term 'hypoxia' is a medical term used to describe a condition in which the body lacks adequate supply of oxygen.
Diatoms
Diatoms on the other hand belongs to a unique group of algae known as the Bacillarophyta. If the definition of plant encompasses all organisms with chlorophyll, diatom as well as other algal divisions will belong to the plant kingdom. They are eukaryotic, microscopic, single celled organisms though sometimes exists as colonies in the shape of filaments/ribbons, fans, zigzag or stars.
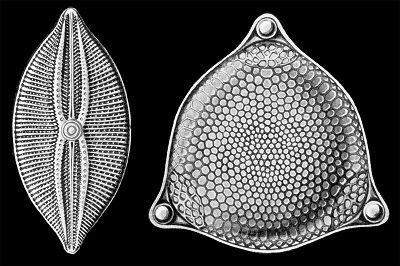
Morphologically, diatoms are divided into two group - the pennate and the centic diatoms. While the latter appear round, discoid, or cylindrical depending on the relative length of their axes, the former is bilaterally symmetrical.
Diatoms, as small as they are, have wide usage. They are quite sensitive to climate induced changes in their environment with their siliceous cell wall well preserved in soils. Studying of diatoms' fossil can therefore be used to create paleoclimatic conditions. They also produce diatomaceous earth or diatomites which is invaluable in filtering aids, functional additives, absorbents, soil amendments and natural insecticides
Why do diatoms hold a major key to human survival?
With their large population in various water bodies around the world, diatoms, being organisms with ability to photosynthesize are responsible for about 25% of all organic carbon fixation on the planet. They contain chlorophylls a and c, xanthophylls and carotenoids. Their photosynthetic food reserve is a polymer of glucose called chrysolaminarin together with lipids. If this is the case, it means diatoms are responsible for almost 25% of the available oxygen for human survival.
Image Credit
Hypoxia
Diatoms
oxygen level
Resource Credit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
