Methane and Methanogenesis
What is Methanogenesis?
This is the production/formation of methane by microbes known as methanogen. Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anaerobic conditions.
Methane is really of great importance in many localized situations. It is of considerable microbiological interest because it is a product of anaerobic microbial metabolism. The production is carried out by a high specialized group of organisms called methanogenic bacteria otherwise called methanogens. These organisms uses carbon dioxide aa their terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration converting it to methane. Hydrogen is generally used aa the electron donor in this process.
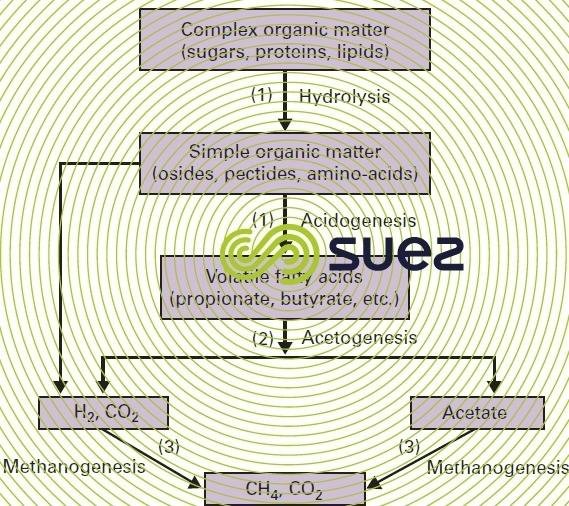
Large molecular weight substances such as polysaccharides, protein and fat and oil can also be converted to methane through the cooperation of some group of bacteria. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide which are immediate precausors of methane are generated through the activities of fermentative anaerobes. Cellulose which is an example of a polysaccharides are converted to cellobiose through the collaborative actions of cellulolytic bacteria. Cellobiose is later converted to glucose which is then fermented by fermentative anaerobes to a variety of fermentation products which includes Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate, Hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The hydrogen produced in primary fermentative processes is immediately consumed by methanogenic bacteria while acetate can be converted to methane by certain methanogens. Key organisms in the conversion of complex material are hydrogen producing fatty acid-oxidixing agents like syntrophomonas and syntrophobacter.
These organisms uses fatty acids or alcohols as energy sources. Hydrogen consuming acetogenic bacteria such as Acetobacterium assist in anaerobic digestion by consuming hydrogen and supplying additional acetate for methanogenesis. However the terminal reaction in anaerobic ecosystem is the production of methane. Nearly all known methanogens are capable of reducing carbon dioxide to methane and the reaction is associated with a reasonable free energy release.
Acetate is also a substrate for methanogenesis but it's role as an immediate precausor of methane depends somewhat on conditions in the ecosystem. In the rumen for example, hydrogen mediated methanogenesis is not predominate while in anaerobic sewage bioreactors, acetate is an important precausor of methane.
Although high level of methanogenesis only occurs in anaerobic environment such swamps and marshes or in the rumen. Other methanogenic habitat are mammalian intestinal tracts, termite intestine, lake muds. Biogenic production of methane by the methanogenic bacteria exceeds considerably the production from gas wells and other inbiogenic sources.
References
• Prescott's Microbiology
Book by Christopher J. Woolverton, Joanne Willey, and Linda Sherwood
• Methanogenesis
If you are interested in reading my previous post about rumen microbial ecosystem.
THE RUMEN MICROBIAL ECOSYSTEM: Actions Of Microorganisms In Achieving Digestion
This post has been resteemed by The Steemit Newbie Resteem Initiative and Newbie Resteem Day. Keep on Steeming.
Thanks a lot.💓💓
This article is undervalued. I can't only be the second voter. I liked your article and I think you will have a great experience here if you continue to write good articles like these.
Thanks for your nice review and wonderful encouragements.