Studies of the Minerals and his Technological Application

Image edited for @dark69

The minerals constitute the solid ground of the planet, forming aggregations known with the rock name, the majority of these rocks they are of scarce interest economic, but in some cases, a concentration anómalmente high of some, minerals can be profitable, for the man and to constitute the so-called mineral deposits. The minerals are neither perpetual nor immutable, but his trasformaciones happen along million years, being in appearance imperceptible for the short life of the human species, the processes that generate the minerals and the rocks are aspects of the same geologic cycle to scale of the balloon, of which they inform on all the litofera and the astenosfera, as well as the hidrosfera, the ambience and the biosphere.
The litosfera consists of mobile badges on the astenosfera, his formation being realized continues in the back oceanic ones and his destruction in the zones of subducción, this way in true points of the badges litoséricas, especially in the limits between them, conditions take place fisicoquímicas (pressure, temperature, chemical composition, water presence), so that the minerals stop existing and others form at the expense of the previous ones.

The process of cooling allows often the progressive crystallization of the minerals, being the first ones in the most refractory forming, as the olivino, the piroxenos and the plagioclasa cálcicas, which form the basic and ultrabasic rocks relatively poor in silicon. These rocks can contain anomalous profitable quantities of cromita, sulfides of nickel and copper, minerals of plantinoides, leading to named deposits ortomagmáticos, in the places where the continental crust is slimmed, the magmas of the top cloaks rich in sodiums and potassium, they can climb across deep invoices, causing ultrabasic crystalline, very interesting rocks for his contents in rare grounds and diamonds.

Deposit of sulfur. (Image edited for @dark69)
The water that contains these residues magmáticos can be so many people that the pressure of the rocky environment cannot support it in solution, coming to separate of the same one in a real process of boiling, these warm waters it separates dragging silica, chlorides and a lot of metals in solution, which they will precipitate in breaks and will cause lodes hiodrotermales, not necessarily all the water, that generate these deposits hidrotermales produces of residues of the crystallization magmáticas, but, since they have proved the analyses isotópicos, big parts there is meteoric water of infiltration warmed in depth for the thermal aureole of the magmas.

When the minerals are in contact with the ambience, litosfera and hidrosfera, great meteorizan, that is to say, trasforman in stabler others and the rocks they disintegrate, the most resistant minerals form particles of diverse sizes, which the waters and the wind trasportan and they deposit, causing sediments clásticos, as gravel, sand, slimes and clay, emphasize for his big economic interest the gravels and sand rich in gold, diamond, platinum, ilmenita, circón and monacita. There waters down trasportan dissolved the rest of the components, which they precipitate forming new sediments, this precipitation, due to chemical factors and to the activity of you are alive, it takes place in the coast and marine platforms, beds of lakes, rivers and oceanic funds, where it is mixed by the sedimentation of particles, this way there form the calcareous muds, the fosforitas, the evaporitas of aragonito, plaster, halita or silvinita, the layers of oxides of iron or the nodules of oxides of iron or the nodules of oxides of manganese.

The salt works are zones of the coast, where the marine waters are dammed to favor the evaporation and the consequent precipitation of you go out that they contain. (Image edited for @dark69)
Little to few ones the sediments summit with new others, going so far as to reach several km from thickness; this way they go compactándose and expelling the water that they caught between the minerals.

In the zones of seduction of the litosfera it still produces to itself major distortions of the piled up sediments, going so far as to reach, along with the water and existing fluids, temperature and the highest pressures, in these conditions, the minerals metamorfean or they crystallize trasfromandose in new others, as the clorita, muscovita, biotita, tremolita, distena, asilliamanita, graphite. In more extreme conditions, these rocks can go so far as to melt whole or partially, leading to magmas acids, which initiate a new cycle petrogenético.

Symmetry.
To identify a mineral, it is necessary to recognize his symmetry based on the punctual observation of the elements present, these are axes d symmetry, planes and center of symmetry. Good now well an axis symmetry is that imaginary line of the such crystal that by means of a money order of this one of x grades about if same he turns to find, a similar morphology to the previous one. I could exist binary axes of symmetry (when x = 180 grades), tenarios (when x = 120 grades), quaternary (when x = 90 grades, and senarios (when x = 60 grades). A plane of symmetry is that imaginary surface of the crystal, which divides the same one in two equal opposite parts. As other one side we have the center of symmetry it is that imaginary point of the crystal, which produces an inverted image of a face of the same one in the opposite pole.

Based on the present elements of symmetry, one differentiates following crystalline systems:
Cubic.
Characterized for possessing 4 ternary axes, being able to exist also planes, quaternary and binary axes and his center.
Tetragonal.
Characterized for presenting a quaternary axis, being able to appear also binary, flat axes and his center.
Trigonal.
It is characterized for presenting the only ternary axis, although there can appear binary, flat axes and his center.
Hexagonal.
It presents an axis senario, although there can appear also binary, flat axes and his center.
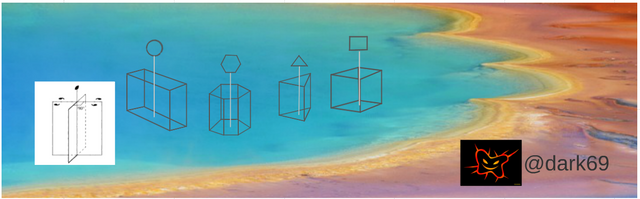
The number of basic axes of symmetry, which can be in a crystalline material comes down to the cuatros (senario, binary, ternary, quaternary), represented in this figure. (Image edited for @dark69)
Application of the glazing in the technology.
• The most common technological application of liquid crystal is that of screens of liquid crystal (LCD). This application takes a big importance, reason as which I have dedicated a page to her.
• A screen LCD is the union of a few segments of small size known as pixels, which by means of modifications can present information. One composes of two glass badges between that there is material in the shape of liquid crystal. We find this technology in many devices; from a clock or a calculator up to screens of television or of computer advanced.
• the glazing also is used to transmit and to amplify energies, but across more advanced methods. Ruby glazing uses in the beams laser in the microscopic surgery.
• The crystal of quartz is used in clocks, computers, radioes, TV sets and teams of telecommunication.
• In the inorganic substances all the elements are strongly connected. Nevertheless, in the organic materials there differ clearly outlying units (molecules), formed by atoms joined between
• yes, whose union, it is much weaker (molecular glazing). They are generally material softer and unstable than the inorganic ones.
• photovoltaic Panels: A photovoltaic panel consists of a crystal of silica that, on having been stimulated by a photon, is capable of detaching electrons (photoelectric effect), which are gathered by a conductive material. The manufacture of photovoltaic panels has the need of securing of flat glazing.
• the jewelery shop, big variety of artificial precious stones being obtained with scarce colors in the natives.
• Waffle of monocrystalline silicon with chips electronic grabadosOblea of monocrystalline silicon with chips electronic engravings.
• Other properties of the glazing, in addition to the electronic ones and the mechanical ones, are in the base of our current technologies, as the laser or the components of not linear optics that they allow us to generate or to manipulate bundles of light.

Application of the glazing in the technology. (Image edited for@dark69)
That looks like to them the important thing of the minerología, has made use, for his development and the contribution for the development of others science, and his diversity of application in technology.
In gratitude to the entire scientific community of stemmit and #stem-Spanish, #steemstem, from the sciences this does not have any border, but if his universe, with the knowledge they are very infinite. @dark69
Bibliography consulted.
Manual of mineralogy, Volume 1 for Cornelis Klein, Cornelius S. Hurlbut
CREDNER, H. (1891): Elemente der Geologie. - 796 pages, 579 figures; Verlag von Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig (Germany)
HARTMAN, H.L. (ed.) (1992): SME Mining Engineering Handbook.-2º edition Vol.1 SME Portcity Press (USA)
Huang, W. 1991. Petrology. Limusa. 546 p.
HURLBUT, C.S. * KLEIN, C. (1982). Manual of Mineralogy of Dana. Reverté, Barcelona.
HURLBUT, C.S. * KLEIN, C. (1993). Manual of Mineralogy. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Scotese, C. R., (2001): Atlas of Earth History, Volume 1, Paleogeography, PALEOMAP Project, Arlington, Texas, 52 pp.
SANDS D.E. Introduction to the crystallography. Reverté, 1993, 163 p.
Tarbuck, E.J. and Lutgens, F.K. (2005): Sciences of the Earth: An introduction to the physical Geology. 8th ed. 710 pp.
Monroe, J.S.; Wicander, R.; and Well Rodriguez, M. (2008): Geology: Dynamics and evolution of the Earth. Assembly hall, 726 pp.

Congratulations @dark69! You have completed the following achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP