The Electrical Coordinating System of The Body | Neurons and Nerves | Brain and Spinal Cord
The human body has an estimate of 37.2 trillion cells performing metabolic functions to keep it alive and also ensure the certainty of the continuous existence of the human race. These cells exist in different shapes and sizes with varying functions. Similar cells come together to achieve a specific function at a structural level regarded as tissues. Different tissues achieve the construction of an organ, and a group of organs form a functional system of the human body. These cells contain different organelles enabling it to maintain homeostasis as well as carry out everyday life activities. However, these cellular activities are controlled by the nucleus of the cell. But on a large scale, all cells of the body are coordinated on an advanced level by a group of other cells that are specialized at this function; you can as well regard these cells as the politicians, the legislators and the judiciary system of the body. These cells form a system that controls every individual cells function, growth, development and metabolic activities.
The brain, spinal cord and nerves make up the nervous system
The Nervous System
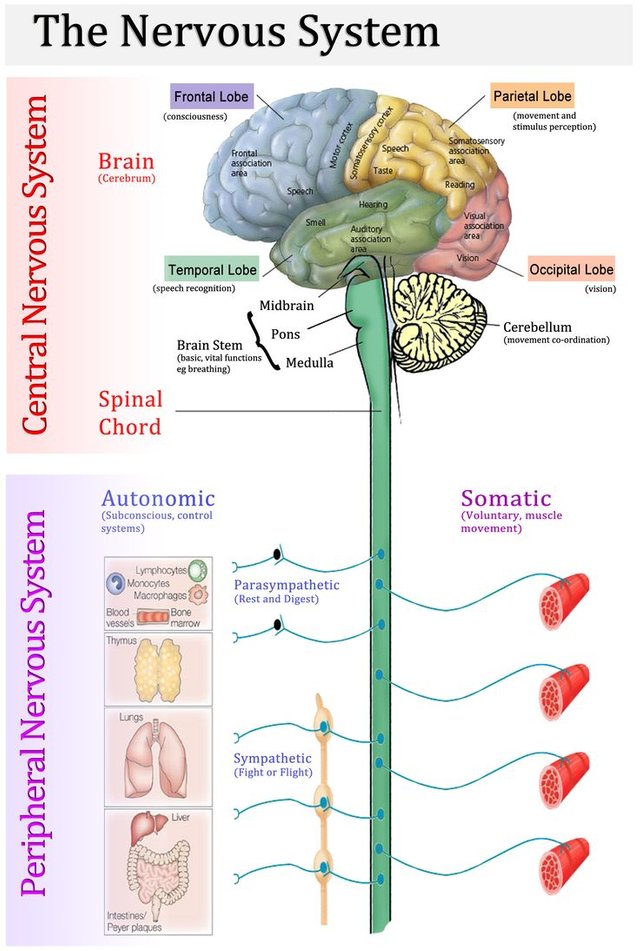
The nervous system is a group of organs speciallised at controlling activities of the diverse organs found in the body with use of electrical signals. It senses, make complex decision and effect quick actions; It is a fast system.
This is a coordinating system of the body that enables the body to continuously react to internal and external environment. Our nervous system is in charge of various activities carried out by the body, example of which is respiration and muscle movements. The nervous system is made up structurally of the Central Nervous System and the Peripheral Nervous System. The central nervous system is composed of the brain and the spinal cord while the peripheral nervous system is further classified into the Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System.
Nervous System
- Cental Nervous System
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Somatic Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System
All organ and system of the body are made up of cells, the principal cell type of the nervous system are the neurons. Other cells are the neuroglial or glial cell which support the neurons structurally.
Neurons
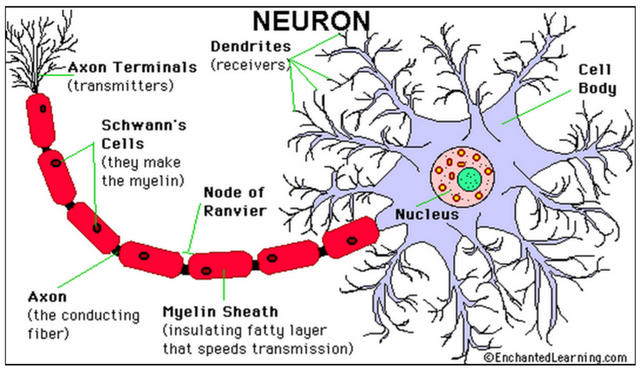
Neurons are the major cells that make up the entire nervous system, they are endowed with the ability to transmit impulses or messages in form of electrical signals
They are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system specialized for rapid communication. They are like electrical wiring of a house. They are made up of three major parts: Cell body, Dendrites and Axon.
Nerve Cell Body
They are also known as the soma or perikaryon. They are irregular in shape,have cytoplasm and cytosol. The cytoplasm of a neuron is often reffered to as neuroplasm. All neurons have large nucleus centrally placed in their cell body, Nissl bodies (or Nissl granules), neurofibrils for cell stability, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, ribosomes and mitochondria for energy generation. Nissl bodies and neurofibrils are found only in neurons and no other type of cell. However, they lack centrosomes essential for cell division and proliferation.
Dendrites
They are branched processes and branches repeatedly. They also have nissl bodies and granules like the soma of the neuron. Dendrites are essential in transmitting impulses (electrical messages) towards the body of the cell. Dendrites are usually shorter than axon
Axon
They are longer processes of the nerve cell compared to dendrites. And they don’t branch repeatedly. They are void of nissl bodies. They transmit impulses away from the soma of the neuron. The longest axon is about 1 meter long.
Types of Neurons
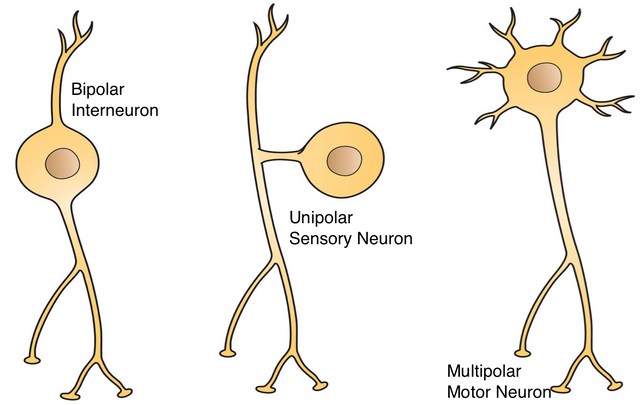
Different types of neurons are scattered in the nervous system where their structural make up will be of advantage in proper coordination and impulse transmission
There are three types of neurons:
- Unipolar/ Pseudounipolar neurons
- Bipolar neurons
- Multipolar neurons
Every nerve cell soma/ cell body have projections which can also be refereed to as poles. In Unipolar or pseudounipolar neurons, there is only one pole projecting from the neuron. This pole then give rise to dendrites and an axon. In bipolar, two poles result from the soma, the first give rise to dendrites while the other gives rise to an axon. In the multipolar neuron, the soma has more than two poles emitting from the soma, one gives rise to axon while the other projections are dendrites.
Functional Neuron
Neurons are so coordinated and specialized that some receive impulses or messages from cells, organs and systems while others give instructions to cells, organs and systems. Based on this explanation, neurons are functionally classified into:
- Motor/ efferent neurons
- Sensory / afferent neurons
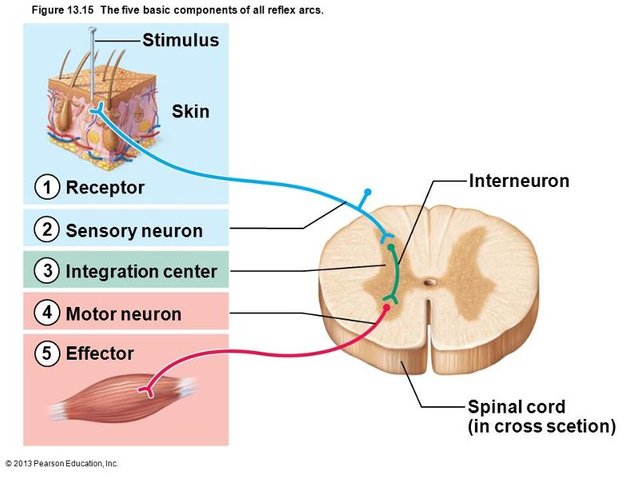
Motor neurons help control locomotion, heart rate, closing and opening of eye, emptying of stomach while sensory help feel temperature change, pain, pressure, see, hear, taste etc
Motor neurons carry motor impulses from the central nervous system which include the brain and spinal cord to peripheral effector organs like muscles, blood vessels etc. These neurons give instructions such as closing of eyelids, raising of shoulder or movement of feet. They only give instructions coming from the brain and spinal cord and can in no way transmit impulses of you stepping on a nail to the brain, it is not functionally their duty.
In the case of feeling pains, you can sensory neurons are specialized for this function. Sensory neurons convey sensory impulses from the periphery like eyes and ears and skin to the central nervous system for processing and decision on what what to do about the impulses received.
Synapse
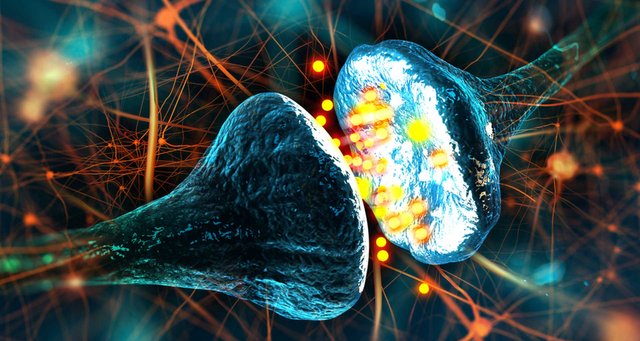
Synapse is a meeting point between two or more neurons, it could be between two axons, an axon and a dendrite or an axon and the soma of another neuron. In the picture above, it is between the knob(axon terminal) of two neurons. The bright yellow stuffs are the neurotransmitter that enable impulse transmittion from the presynaptic neuron to the post synaptic neuron
Neurons communicate at synapses; this is a point of contact between neurons. The neurons communicate either by means of electrical ions or chemical compounds known as neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitter is secreted by a neuron referred to as the presynaptic neuron, this chemical substance then diffuse through the synaptic cleft to excite or inhibit the other neuron involved in forming the synapse. This stimulated neuron is known as post-synaptic neuron.
Neuroglial Cells
They are the supporting cells of the nervous system and are non-excitable; hence they do not transmit nerve impulses. Neuroglial cells in total in the human nervous system is 10 to 15 times more than the neurons. Their function is important in forming blood-brain barrier preventing unnecessary entrance of substances into the brain. Their function is also evident during infections. Neuroglial cells are classified into the centeral neuroglial cells and peripheral neuroglial cells. There are three types of neuroglial cells found in the brain and spinal cord(Centeral Nervous System); Astrocyte, Microglial and Oligodendrocytes. The cells found in the peripheral neuroglial cells include schwann cells and satellite cells. The following are functions of neuroglial cells:
- They provide insulation.
- They provide supporting network.
- They function as macrophages.
- They provide immune and inflammatory response
- They maintain the extracellular fluid around neurons
- They take part in formation of the blood-brain barrier.
Organization of Nerve
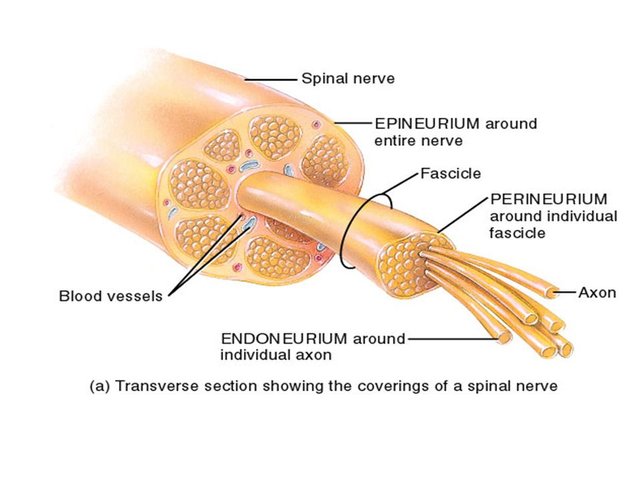
A nerve is made up of many fascicles accompanied with blood vessels for nourishment. Each fascicle is made up of numerous neurons
Neurons are bundled together to form nerves. Each nerve bundle is called a fascicle. The whole nerve is covered by an areolar membrane called epineurium. Each fasciculus/neuron bundle is then covered by perineurium and each nerve fiber axon by endoneurium.
Myelination
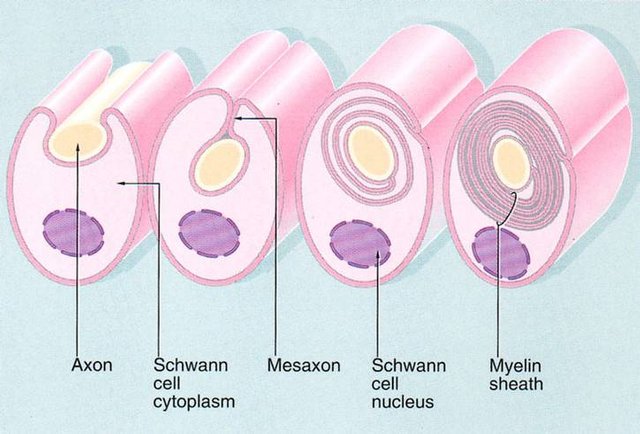
Just like an electrical wire which transmit electricity is insulated by rubber and plastic, neurons are also insulated by myelin sheath which is a continuous enveloping of a portion of axons by cell body of another cell:schwann cell usually
Myelination is the covering of nerve fibers (neuron axon) by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is a thick lipoprotein that insulates myelinated nerve fiber. Though it is not a continous sheath, there are between one myelin sheath and the next one. The space between one myelin sheath and the next is called node of Ranvier. The function of myelin sheath is to enable neuron conduct impulses faster and as well maintain its quality.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System
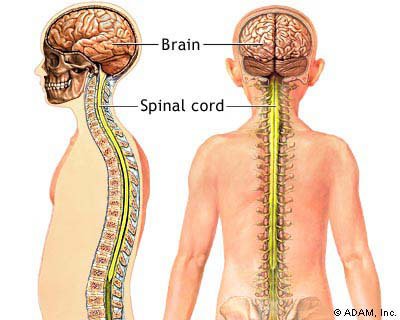
The brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system and are protected by bone. The skull protects the brain and the vertebral column, the spinal cord
The central Nervous System is made up of the brain and spinal cord. They integrate and co-ordinate both incoming and outgoing neural signals. They enable as higher mental functions such thinking and learning.
Nerves are classified into two depending on their location; spinal nerves and cranial nerves. The cranial nerves are found within the cranial cavity and they supply the face and head. There are 12 cranial nerves which are identified by describable names or roman numeral. Spinal nerves exit the vertebral column through the intervetebral foramen of the vertebral bones. There are 31 spinal cord segments and 31 spinal nerves. They initially arise from the spinal cords as rootlests. Some rootless converge to form the anterior or ventral root while the rest form the posterior or dorsal nerve root. The anterior nerve root consist of motor/ efferent fibers while the posterior consist of sensory/ afferent fibers. These two roots (anterior and posterior root) to form a single but mixed spinal nerve which immediately divide into two rami:
- The Posterior/ dorsal ramus
- Anterior / ventral ramus
These rami and their subsequent branches consist of both motor and sensory nerve fibers.
Damage to nerves
Damage to the spinal cord can lead to temporal or permanent dysfunction. Damage can be due to bullet firing, motor accident, office accident, communal violence, industrial accident, rupture in spinal arteries, lack of blood supply etc. The most common spinal cord dysfunctions are transaction and hemisection.
Transection is a cut through the spinal cord which can be complete or incomplete. Complete transaction cause immediate loss of sensation and voluntary movement below the level of transaction. In quick transaction of spinal cord, patient were recorded to having the feeling of their body being cut into two. The person even when calm feels as though the part below the level of transaction does not exist. In case of incomplete transection, the person doesn’t suffers complete loss of co-ordination. Only the part of the body sensation and motor control is lost. Other diseases of the nervous system include myelitis, parkinson's disease, ataxia, degenerative dissease, demyelinating disease, multiple scelorosis.
Further Reading:
- Wikipedia: The Nervous System
- Slideshare: Co-ordination System
- Wikipedia: Neuron
- Wikipedia: Synpse
- Wikipedia: Spinal Cord Injury
Thanks for taking your time to view this course on electrical coordination of the human body. Please follow and do leave a comment


Enchanted with your publications, very informative. Thanks for sharing. regards @damzxyno
Thanks a lot @maurelvys,
I only wish the steemit community think the same.
Hey @damzxyno, great post! I enjoyed your content. Keep up the good work! It's always nice to see good content here on Steemit! :)
Thanks a lot for the complement @exxodus.. I really took my time into it.